07MicrobialGenetExamIAnswers
advertisement
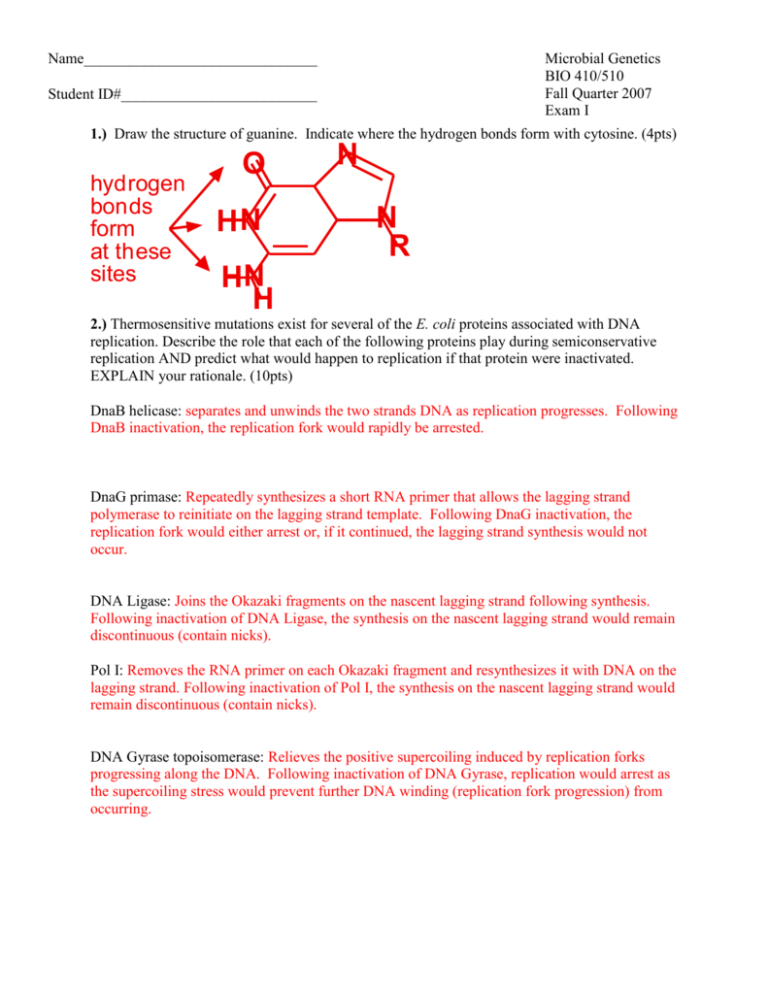
Name_______________________________ Microbial Genetics BIO 410/510 Fall Quarter 2007 Exam I StudentpID#__________________________ 1.) Draw the structure of guanine. Indicate where the hydrogen bonds form with cytosine. (4pts) hydrogen bonds form at these sites O HN N N R HN H 2.) Thermosensitive mutations exist for several of the E. coli proteins associated with DNA replication. Describe the role that each of the following proteins play during semiconservative replication AND predict what would happen to replication if that protein were inactivated. EXPLAIN your rationale. (10pts) DnaB helicase: separates and unwinds the two strands DNA as replication progresses. Following DnaB inactivation, the replication fork would rapidly be arrested. DnaG primase: Repeatedly synthesizes a short RNA primer that allows the lagging strand polymerase to reinitiate on the lagging strand template. Following DnaG inactivation, the replication fork would either arrest or, if it continued, the lagging strand synthesis would not occur. DNA Ligase: Joins the Okazaki fragments on the nascent lagging strand following synthesis. Following inactivation of DNA Ligase, the synthesis on the nascent lagging strand would remain discontinuous (contain nicks). Pol I: Removes the RNA primer on each Okazaki fragment and resynthesizes it with DNA on the lagging strand. Following inactivation of Pol I, the synthesis on the nascent lagging strand would remain discontinuous (contain nicks). DNA Gyrase topoisomerase: Relieves the positive supercoiling induced by replication forks progressing along the DNA. Following inactivation of DNA Gyrase, replication would arrest as the supercoiling stress would prevent further DNA winding (replication fork progression) from occurring. Name_____________________________ page 2 3.) Escherichia coli replication machinery makes a mistake about once every 1010 times it incorporates a nucleotide. E. coli O157 is a pathogenic strain that was isolated from hamburgers at Jack in the Box restaurants in the late 1990’s. It caused severe fevers and death in several customers. Its genome contains approximately 5 * 106 basepairs. How many changes (mutations) would be expected to occur in its genome each time it replicates? Show your work. (3pts) (5 * 106 bases / genome) * (1 error/ 1 * 1010 bases) = (5 * 106 bases / genome) * (1 error/ 1 * 1010 bases) = 5 * 10-4 errors / genome 4.) The actual error (mutation) rate per cell division in E. coli strain O157 was measured and it was found to make a mistake about once every 106 times it incorporates a nucleotide. How many changes (mutations) occur in its genome each time it replicates? Show your work. (2pts) (5 * 106 bases / genome) * (1 error/ 1 * 106 bases) = (5 * 106 bases / genome) * (1 error/ 1 * 106 bases) = 5 * errors / genome 5.) The mutS gene of E. coli O157 is inactivated by a mutation. MutS is part of the methyl directed mismatch repair system. Describe how DNA methylation allows replication to correct errors that were made during replication. (4pts) Methylation occurs at GATC sites on the DNA. Since the methylation process takes some time to occur, the methyl-directed mismatch repair system is able to identify which strand is the newly replicated (unmethylated) strand of the DNA. Mismatched base pairs are then excised from the unmethylated, daughter strand and the region is then re-replicated to correct the error. 6.) The E. coli origin or replication contains multiple DnaA boxes and AT-rich 13-mers. Describe what role each of these plays in the initiation of replication? (5pts) Multiple DnaA proteins bind in a sequence specific manner to the DnaA boxes and associated with each other. The DnaA binding induces stress on the surrounding helical DNA regions and promote strand separation at the AT-rich regions. These single stranded regions then serve as the binding sites for the delivery and loading of the DnaB helicase by DnaC to initiate the subsequent steps of establishing the replication forks. Name_____________________________ page 3 A soil bacteria that was isolated replicates in every 10 hours when grown in lab cultures. To examine whether replication occurs conservatively or semiconservatively in this bacteria, you decide to utilize a variation of the approach that Meselson-Stahl originally used to examine this question in E. coli. For your controls, you grow the bacteria in two separate culture media for several generations. C1.) One culture is grown in normal media C2.) The other culture is grown in media that contains 5-bromouracil, an analog of thymine that has a much higher buoyant density. For your experimental analysis, you inoculate a third culture of the bacteria in normal media and allow it to grow for 2 days. At this time, you then transfer the cells into media containing 5bromouracil. To examine the mode of replication, you collect a portion of the cells E1) immediately after changing the media, E2) 10 hours after you changed the media, and E3) 20 hours after you changed the media. You then lyse the cells and load the cell lysates (and DNA) from each sample in neutral CsCl gradients before centrifuging them to equilibrium. The results of your controls, C1 and C2, are shown below. 7.) On the tubes below, clearly indicate where the DNA would be expected to appear if the bacteria replicate conservatively? (5pts) 5-bromoNormal media uracil media C1 C2 0 hrs E1 10 hrs E2 8.) On the tubes below, clearly indicate where the DNA would be expected to appear if the bacteria replicate semi-conservatively? (5pts) 20 hrs E3 0 hrs E1 10 hrs E2 20 hrs E3 Name_____________________________ page 4 9.) What DNA sequences are important for factor independent transcriptional termination? How are these thought to promote transcription termination? (3pts) Termination by this mechanism relies upon an inverted repeat sequence that is followed by a stretch of UUUUs in the RNA transcript. Transcription of the inverted repeats produces a hairpin in the RNA that destabilizes the RNA polymerase enough to dissociate it when followed by a string of UA base pairs in the transcription bubble. The UA base pairs are less stable than GC base pairs due to the lower number of hydrogen bonds formed between these base pairs. 10.) What DNA sequences are important for factor dependent transcriptional termination? How are these thought to promote transcription termination? (3pts) Factor dependant termination occurs when a protein factor, such a Rho, binds to a specific sequence on the RNA transcript. In the case of Rho, the rut sequence is bound. The Rho factor is an RNA helicase that, in effect, chases or follows the RNA polymerase and dislodges it at specific pause sites downstream on the transcript. Since Rho can only bind to rut when translation is not "hiding" the rut sequence, this also provides a mechanism to regulate the transcription of polycistronic messages. 11.) Briefly describe (or draw) the events involved during translation elongation (do not include events that are associated specifically with initiation or termination). Include the following terms, if appropriate (not all terms are appropriate). TATA Box, 30S Subunit, 50S Subunit, 70S Subunit, RNA Polymerase, Shine Delgarno, rho, ATP, GTP, formylmethionine, P site, A site, RF1, IF3 and IF1, IF2, EF-Tu, EF-G, t-RNA, sigma factor. (6pts) A. EF-Tu loads a charged tRNA into the empty A site of the 30S ribosome subunit using GTP as an energy source. (EF-Ts then exchanges the GDP for GTP on Ef-Tu to "recharge" the enzyme for the next round. B. The polypeptide attached to the tRNA in the P site is transferred (bonded) to the amino acid-tRNA in the A site using a peptidyltransferase activity found on the 50S subunit. C. GTP charged EF-G powers the ribosome forward moving the tRNA containing the polypeptide into the P site. (The cycle then repeats.) You’ve identified a small gene from a strain of Streptomyces whose expression prevents other bacteria from growing when Streptomyces is present. You are interested in this peptide because of its potential as a new antimicrobial agent. The entire open reading frame (ie. the TRANSLATED portion of the mRNA transcript has following the sequence: 5'… GUG AUC AUU AUA ACU ACC ACA ACG UAA… 3' 12.) Using the table for the genetic code and your knowledge of how translation occurs, translate the given DNA sequence into its appropriate amino acids. (4pts) fMet-Ile-Ile-Ile-Thr-Thr-Thr-Thr 13.) What’s the absolute minimum number of different tRNA molecules that would be needed to translate this peptide? Why? (2pts) At least three, an initiation tRNA, an Ile-tRNA and a Thr-tRNA. The wobble position of an anticodon on a given tRNA may recognize multiple bases, meaning that the same tRNA may deliver a given amino acid to codon sequences that differ at the wobble position. Name_____________________________ page 5 The gene below encodes Homo sapiens coagulation factor III, a cell surface glycoprotein that enables cells to initiate the blood coagulation cascade. This protein is the only one in the coagulation pathway for which a congenital deficiency has not been described. Your working for a biotech company that is interested in producing drugs to treat specific forms of hemophelia. Your task is to clone this gene into an expression vector as a potential mode of treatment. 1 61 121 181 241 301 361 421 481 541 601 661 721 781 841 901 961 1021 1081 1141 1201 1261 1321 1381 1441 1501 1561 1621 1681 1741 1801 1861 1921 1981 2041 2101 gggggggggg cccaacctcc gacatggaga ctcctgctcg gcagcatata aaacccgtca aaatgctttt aagcagacgt tctgctgggg ctcggacagc gaagatgaac ggcaaggact gccaaaacaa agtgttcaag gagtgtatgg gtatttgtgg gcaggagtgg tgttggagct tacatggaaa gatatgacct atgtaacgaa tgcacataac caaaaacaaa tttttttttt tctcggctca gagtagctgg gagatggggt ccaccttggc agcttttgag atttctagga ggaatacatt gagacattgg taagtggcat agagtttatg aaaaaggttt atattgagat cccccgcgca ccagccccac cccctgcctg gctgggtctt atttaacttg atcaagtcta acacaacaga acttggcacg agcctctgta caacaattca ggactttagt taatttatac acactaatga cagtgattcc gccaggagaa tcatcatcct ggcagagctg actgcaaatg cgcaaatgag gttattacca tggtactaca atgctttaga tgggaaaatg tttgagacgg cttgcaccct gattacaggt ttcaccatct ctcccaaaga gggctgactt cttttctaac tggaaattca tattctgggc taaacatttg atttaaggta ttctatatgg aatttattta ccccctcgca gggcgccacg gccccgggtc cgcccaggtg gaaatcaact cactgttcaa cacagagtgt ggtcttctcc tgagaactcc gagttttgaa cagaaggaac actttattat gtttttgatt ctcccgaaca aggggaattc tgtcatcatc gaaggagaac ctatattgca tatttcggag ttagcattct accaattcca ttatatattc tcttaaaaaa agtcttgctc ccgtctctcg gcgcactacc tggccaggct tgctagtatt caatccatgt atatgtctat aaacaattgg agcttcctaa agagctaact cttaaagctt ggattttcta atatacttta ctccctctgg gaacccgctc ccgcgccccg gccggcgctt aatttcaaga ataagcacta gacctcaccg tacccggcag ccagagttca caggtgggaa aacactttcc tggaaatctt gatgtggata gttaaccgga agagaaatat ctggctatat tccccactga ctgtgaccga catgaagacc ggttttgaca agttttaatt cgcacttaag tcctgggtgg tgttgcccag ggttcaagca acgccaagct ggtcttgaat atgggcgtga aggaaagtaa aatatagtgt gcaaactttg tatgctttac atatttttat ctatggttga tttatgtagg aataaaggtg ccggcccagg gatctcgccg agaccgccgt caggcactac caattttgga agtcaggaga acgagattgt ggaatgtgga caccttacct caaaagtgaa taagcctccg caagttcagg aaggagaaaa agagtacaga tctacatcat ctctacacaa atgtttcata gaacttttaa ctggagttca tcagcattag tttaacacca gattaaccag acttttgaaa gctggagtgc attgtctgcc aatttttgta tcctgacctc accaccatgc aatggaagga ttaggttctt tattaatgtg aatctgcact aagactacta cattgtatat taatattgtt actggaaaaa gcgccttcag ccaactggta cgctcggacg aaatactgtg gtgggaaccc ttggaaaagc gaaggatgtg gagcaccggt ggagacaaac tgtgaccgta ggatgttttt aaagaaaaca ctactgtttc cagcccggta tggagctgtg gtgtagaaag aaggaagcac gaggatagaa aaaaactctt tcactttgaa tggcaccttt gtcgtccaag agcttttttt agtagcacga tcagcctccc ttttttagta agtgatccac ccagccgaaa aattgggtgc ttttttttca ttaagtgcag ttaactgact tacaaactac ataatttttt ctatttgtat tttttttttt 14.) Design two 15 base primers that you could use in a PCR reaction to amplify this gene from human cells? (4pts) 5’ GGG GGG GGG GCC CCC 3’ 5’ AAA AAA AAA ATT TTT 3’ 15.) You know that you will need to clone your PCR product into a BamHI restriction site, GGATCC, found on the expression vector. Modify your primers below such that you will be able to easily clone the PCR product into a BamHI site on an expression vector. (3pts) 5’ NNN NNN GGA TCC- GGG GGG GGG GCC CCC 3’ 5’ NNN NNN GGA TCC- AAA AAA AAA ATT TTT 3’ 16.) The human genome contains 3.3*109 basepairs. Is the 15 base sequence of your primer likely to be unique in the human genome? On average, how many times would your primer sequence be found on the human genome? Show your work (4pts) 4 possible bases at every position… so a sequence 15 bases long would be found every… 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 * 4 bases 415 bases = a specific15 base sequence would be found once in every 1,073,741,824 bases. With 3.3 * 109 bases in the human genome a specific 15 base sequence would appear, on average, 3.3 * 109 bases/ 1.07 * 109 bases = 3.08 times… so its not long enough to be unique. Name_____________________________ page 6 Your biotech company is using 4 different experimental cloning vectors called pEXPRESS1, pEXPRESS2, pEXPRESS3, and pEXPRESS4. All the vectors have similar constructions (shown to the right). However, the cloning region on each vector is slightly different. Each of the vector cloning regions is shown below. 18.) For each vector, determine if the Coagulation factor III product is likely to be expressed when your PCR product is cloned into the Bam HI site. Explain Why or Why not in each case. (8 pts) Cloning Region pEXPRESS Vectors ampicillin resistance origin of replication Promoter Shine Stop Transcription BamHI site -35-10 Delgarno ATG codons termination GGA TCC consensus sequence UAA UAG sequences Cloning Region of pEXPRESS 1 pEXPRESS1: Coagulation factor III product will not be expressed when the PCR product is cloned into the Bam HI site because the gene will be upstream of the promoter and ribosome binding site that are needed for transcription and translation to occur. Shine Promoter Stop Transcription ATG BamHI site codons Delgarno -35-10 termination GGA TCC UAA UAG sequence consensus sequences Cloning Region of pEXPRESS 2 pEXPRESS2: Coagulation factor III product will not be expressed when the PCR product is cloned into the Bam HI site because the ribosome binding site that is needed for transcription is upstream of the transcriptional promoter. Thus the mRNA containing the gene will not be translated because it does not contain the Shine Delgarno sequence. Promoter Shine Stop Transcription -35-10 Delgarno ATG BamHI site codons termination GGA TCC UAA UAG consensus sequence sequences Cloning Region of pEXPRESS 3 pEXPRESS3: Coagulation factor III product will be expressed when the PCR product is cloned into the Bam HI site. The open reading frame, when cloned into the BamHI site, has a transcriptional promoter, the mRNA have a ribosome binding site before the first start codon as well as additional stop codons prior to the end of the transcript. Promoter Shine -35-10 Delgarno ATG BamHI site GGA TCC consensus sequence Transcription Stop termination codons sequences UAA UAG Cloning Region of pEXPRESS 4 pEXPRESS4: Coagulation factor III product will probably be expressed when the PCR product is cloned into the Bam HI site. If the open reading frame includes its own stop codon, the gene should be expressed normally. Name_____________________________ page 7 The Luria-Delbruck experiment demonstrated that bacteria can become resistant to bacteriophage T1 infection through random mutations, rather than through a directed change. You decide to try and see if the random mutation hypothesis also applies to how bacteria become resistant to the antibiotic, rifampicin. You do the following experiment. You inoculate 200 mls of media with a dilute bacterial culture. Then, you split the culture A) growing 100 mls in a single flask, and B) growing the other half in 100 separate, 1 ml test tubes. After allowing the cultures to grow for several hours, you spread A) 1ml aliquots from the single flask on 100 plates that contain rifampicin, and B) the 100 1ml cultures onto 100 plates that contain rifampicin. You allow each set to incubate overnight and count the number of rifampicin resistant colonies on each plate in the morning. Five representative plates from A) the single 100 ml flask are shown below: 19.) If mutations arose primarily through a process of directed change, CLEARLY diagram how you would expect to five representative plates to look from B) the 100 individually grown 1ml cultures. Explain why. (4pts) The experiment would predict that each cell has an equal probability of generating resistance to the antibiotic WHEN exposed to it. Since all cells were exposed to the antibiotic at the same time, each plate should have roughly equal numbers of mutations. 20.) If mutations primarily arose randomly within growing populations, CLEARLY diagram how you would expect to five representative plates to look from B) the 100 individually grown 1ml cultures. Explain why. (4pts) The experiment would predict that mutations occur randomly within the population prior to any exposure to the antibiotic...some of these mutations confer resistance to the antibiotic and depending on when they first occur in each culture, a given culture may have many (if the mutation occurred early) or few to no (if the mutation occurred late to never) resistant mutants. The number on each plate should vary significantly. 21.) Does this experiment involve positive or negative selection? (2 pts) positive selection 22.) If 20 out of your 100 plates of 1ml cultures had no colonies on them, and the cultures had 108 cells/ml, calculate the mutation rate (a) for generating resistence to rifampicin using the Poisson expression, where the probability of having i mutations per culture is represented by P(i) = ( mi e-m )/ i! and a = m/n. (5pts). 20 out of 100 cultures had 0 mutations. So the probability of having zero mutations (Pi ) is 20/100, and i= 0 mutational events per culture in this situation. Name_____________________________ Pi (20/100) 0.2 0.2 -ln(0.2) .916 = = = = = = ( mi e-m )/ i! ( m0 e-m )/ 0! ( 1 e-m )/ 1 e-m m m 1.6 mutational events per culture and each culture has 1 x 108 cells a = m/N a a = = 1.6 mutational events/1 x 108 cells 1.6 x 10-8 rifR mutational events per cell division page 8 Name_____________________________ page 9 Primer design (10pts): Design primers for recombineering that would delete the recF gene of E.coli and replace it with the catRsacB cassette from plasmid pEL4. >E. coli 1 31 61 91 121 151 181 211 241 271 301 331 361 391 421 451 481 511 541 571 601 631 661 691 721 751 781 811 841 871 901 931 961 991 1021 1051 - |EG10828|recF: 1074 bp - Recombination and repair g ccagagcgcggcttatgttgtcatgccaatgagactgta atg tcc ctc acc cgc ttg ttg atc cgc gat ttc cgc aac att gaa acc gcg gat ctc gcc tta tct ccc ggc ttt aac ttt ctg gta ggt gcc aac ggc agt ggc aaa acc agc gtg ctg gaa gcc atc tat acg ctc ggc cat ggt cgg gcg ttt cgc agt ttg cag att ggt cgc gtc att cgc cat gag cag gag gcg ttt gtt ctc cac ggg cga tta cag ggc gaa gag cgc gag aca gcg att ggc tta acc aaa gac aaa cag ggc gac agc aaa gtc cgc atc gac ggt aca gac ggg cat aag gtc gcg gaa ctg gcg cac ctg atg cca atg cag ttg ata acg cca gaa ggg ttt act tta ctc aac ggc ggc ccc aaa tac aga aga gca ttc ctc gac tgg gga tgc ttt cac aac gaa ccc gga ttt ttc acc gcc tgg agc aat ctc aag cga ttg ctc aag cag cgc aat gcg gcg ctg cgc cag gtg aca cgt tac gaa cag cta cgc ccg tgg gat aaa gag ctg atc ccg ctg gcg gag caa atc agc acc tgg cgc gcg gag tat agc gcc ggt atc gcg gcc gat atg gct gat acc tgt aag caa ttt ctc cct gag ttt tct ctg act ttc tct ttc cag cgc ggc tgg gag aaa gag aca gaa tat gct gag gtg ctg gaa cgt aat ttt gaa cgc gat cgc cag cta acc tac acc gcg cac ggc ccg cac aaa gcg gac tta cgc att cgc gcc gac ggt gcg ccg gtg gaa gat acc tta tcg cgt ggg cag ctt aag ctg ttg atg tgc gcc tta cgt ctg gcg caa gga gag ttc ctc acc cgt gaa agc ggg cgg cgg tgt ctc tac ctg ata gat gat ttt gcc tct gag ctt gat gat gag cgt cgc ggg ctg ctt gcc agc cgc tta aaa gcg acg caa tca cag gtc ttt gtc agc gcg atc agt gct gaa cac gtt ata gac atg tcg gac gaa aat tcg aag atg ttt acc gtg gaa aag ggt aaa ata acg gat taa cccaagtataaatgagcgagaaacgttgatgtcgaattc t Primers used to PCR amplify the cat-sacB cassette: Primer-L: CCTGTGACGGAAGATCACTTCG Primer-R: CTGAGGTTCTTATGGCTCTTG Forward primer: 5’gccagagcgcggcttatgttgtcatgccaatgagactgtaCCTGTGACGGAAGATCACTTCG Reverse primer: 5’agaattcgacatcaacgtttctcgctcatttatacttgggCTGAGGTTCTTATGGCTCTTG