SpeedLearningProcess.. - al b`s website
Speed Learning by
Al Bernstein
Signal Science, LLC
www.signalscience.net
This is an outline of Accelerated Learning Techniques by Brian Tracy and Colin
Rose 1
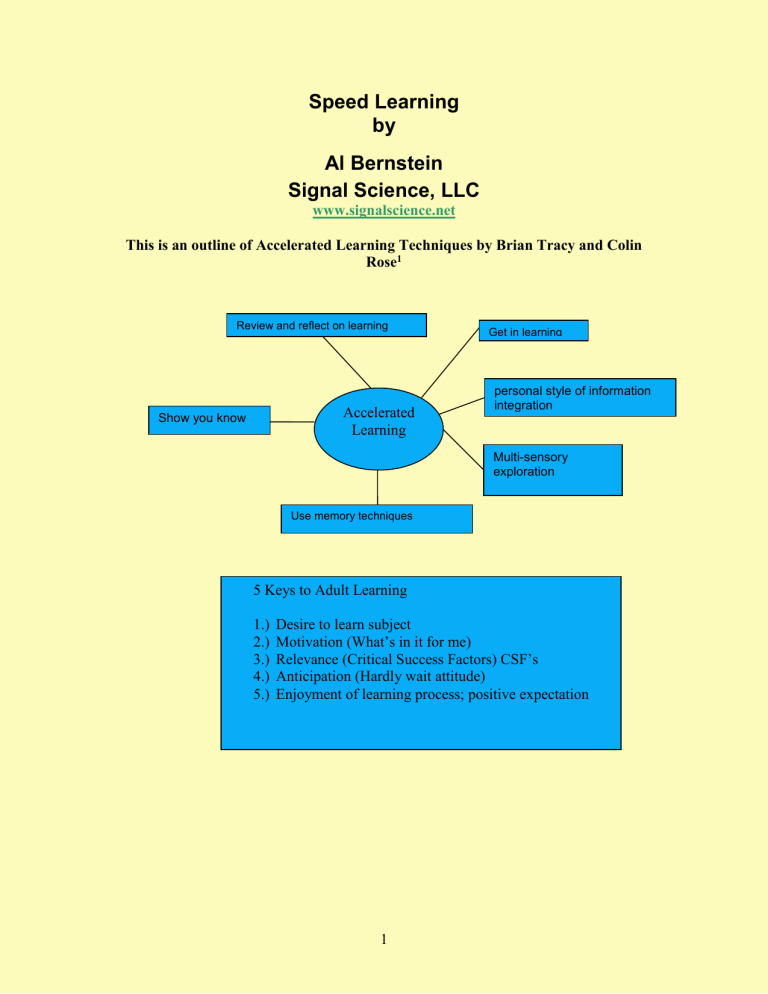
Review and reflect on learning process
Show you know
Accelerated
Learning
Use memory techniques
Get in learning state personal style of information integration
Multi-sensory exploration
5 Keys to Adult Learning
1.) Desire to learn subject
2.) Motivation (What’s in it for me)
3.)
Relevance (Critical Success Factors) CSF’s
4.) Anticipation (Hardly wait attitude)
5.) Enjoyment of learning process; positive expectation
1
I.) Intensely desired goals makes you smarter
Create a vivid mental image of yourself achieving the goals
Write clear written goals on paper
Create affirmations to manage inner dialogue and enable progress
towards goals
Plan time on long term, sub-goals, small action steps, use small time slots to learn
Carry index cards and reading materials with you to facilitate good use of time
Set deadlines for achieving goals and share goals with other people
II.) Use relaxation techniques to create a receptive mind before learning session (mental warm up analogous to physical warm up)
Classical music enables learning
Breathing techniques to get into a deep relaxation state
Relax neck and shoulders
III.) Modalities of learning
Learning Modality Percent of learners
Eyes
Ears
Touch
35
25
40
Use multi-sensory approach and build on strongest learning modalities material to learn
Organize material based on how you learn best
Learn organized material
IV.) Get the big picture first by perusing the material, chapter heading and subheadings.
Write out what key points you already know
What I already know about his subject is ________. Fill in the blank with as many things as possible
State what things I need more help on and develop a learning map to
the best of your ability
Break subject up into small steps
O.k. to roam around subject and find something of interest
Ask lots of questions and write them down
2
V.) Mind Mapping
Sub
Branches
Theme
Sub
Branches
Sub
Branches
Can try different themes for a mind map and experiment. Mind map helps organize information and makes you more intelligent, creative, and organized in the process.
Core ideas and keywords only on the mind map
Requires practice
VI.) Additional Techniques
Tick marks after interesting passages and pages
Underline new key information with a highlighter pen
Make things more dramatic to make information more memorable
Summarize material out loud
Sit quietly and visualize material (make it into a mental movie) especially
before falling asleep
Walk around while relaxing or listening
Put key ideas on post it notes
Note making rather than note taking; create notes in own words
Take breaks, let information soak into the mind (absorption period)
Buddy system of learning; get a partner and dialogue a subject
→
faster and deeper learning
3
Note: The more brain you use, the more you can use. Explore the subject leads to a deeper understanding. Explore around the subject in areas that peak interest.
7 Intelligences (Howard Gardner)
Intelligence Type
Verbal
Math/Logic
Visual/Spatial
Musical
Interests
Plays, poetry, books, radio talk shows, languages, learn from books, write things down
Solve puzzles impatient with illogic, patterns and relationships, logical step by step manner
Notice things other people don’t. Good sense of direction, highly visual
(minds eye), films, slides, and video tapes, graph, slider maps
Natural sounds, musician, hearing music, learn and retain lyrics from songs
Interpersonal
Intrapersonal
Know how people feel, interested in how people think and feel
Daydream fantasize, individualistic, privacy – quiet, structural environment, explain decisions, thinks a lot, and goal oriented
Physical Intelligence Natural mechanical ability, don’t like to sit still, tactile learning, sports games, physical exercise, remember from doing with hands
The key is to use as many of the intelligence categories as possible.
Intelligence Type
Verbal
Math/Logic
Activities
Describe new subjects and ask questions aloud
Make a flow chart or diagram in a step by step manner
4
Visual/Spatial
Musical
Create a strong mental image
Choose and play background music
Interpersonal Teach someone else; ask them what they think
Quietly reflect on subject Intrapersonal
Physical Intelligence Index cards containing main ideas, sort in logical order, take with you
Key: Exploration is a large part of learning
VII.) Memory Techniques
Two types of memory short and long terms memory
Short term memory transferred to long term memory using associations to link data in long term memory to data to be learned. Associations can be described by learning maps.
4 R’s Memory
1.) Review
2.) Registration
→
long term memory
3.) Retention
→ keep in long term
Memory
4.) Recall
→ recall on demand
Action required recall
Key: Exploration
→ a better memory a.) Multi-sensory review; read it aloud, picture in head, jot down reminders b.) Imagine boss asked you to report c.) Imagine how to teach a course on this material d.) Imagine writing a book from a new viewpoint that is clearer
Key: Memory
→ a library full of books
Mental Fitness Program (17 memory techniques)
1.
Make decision to remember
2.
Take regular breaks (we tend to remember the first and last things we did better)
3.
Review what you have learned/highlighted i.) Learn material ii.) Review after 1 hour
5
iii.) Review after one day iv.) Review after 1 month v.) Review after 6 monts vi.) Total time for all review sessions added together is 30min.
4.
Create multi-sensory memories
5.
Make visual interactions interact via exaggerated images, odd series of events, color, brightness
6.
Multi-sensory memory spelling
Chunk word into syllables psy chi a trist, see, feel, hear the word
7.) Review new material with music
→ create a review concert, play recording as you review, music provides association for memory.
8.) Organize the material meaningfully; groups, categories that relate to each other. Memory maps are good for this.
9.) Memory flashing i.) Notes on learning map or key points ii.) Study carefully for a few minutes iii.) Put notes and learning map aside and write from memory iv.) Compare rewrite to original notes v.) Repeat iii.) and iv.) until rewrite and original are the same
10.) Make flash cards (scientific formulas, index cards, or portable notebook)
11.) Flash maps
→ ring binder put all learning maps in binder (extension of flash cards)
12.) Mnemonic to remember a word ACE ≡ (Attitude Commitment
Excellence)
13.) Let information sink in overnight. Try learning something right before sleep
14.) Number points you need to remember
15.) Whole learning (try learning an item as a whole) i.) Read completely through ii.) Re-read it again iii.) Repeat re-read with more and more visualizations, actions, and movement
16.) Over learn to remember an item better
17.) Compress lots of information into an easily recalled format maps
→ chunking and labeling i.) Make notes in form of learning map ii.) Title each learning map with a single word iii.) Invent mnemonic to remember all titled words iv.) Review iii.) to remember titled words
VIII.) Power Reading Strategies
Faster reading
→ better concentration otherwise mind wanders
Hear words at 250 words per minute
6
See 2000 words/minute
Lots of filler words that can be skipped
See groups of words
→ reduce words by 70%
Look at keywords only
Eye movement
→ skips field of vision
Choose Reading material (look at date, insure that you want to actually read the material)
1.) Read each line of print and look several words in from the beginning
2.) Finish sentence several words before from end of the line
3.) Move hand/finger across and down the page and increase reading speed much faster to read by sight only and not say words to self. Read each page in 2-3 seconds.
Power Reading 8 Steps
1.) Overview of material (ask questions), look at date, Authors, index, and references.
2.) Preview material – scan read 7 sec/page. Be selective in what you read – 3 min/chapter.
3.) Sketch out everything you know about the subject in the chapter – 3 min/chapter.
4.) Write down questions about the material – 3 min/chapter
5.) Read text of each chapter – 15 sec/page – underline keywords and mark sections with ticks.
6.) After view, re-read chapter slowing down at difficult sections 10/min chapter, read sections aloud.
7.) Make notes in a learning map format – 10 min/chapter
8.) Review notes 10 min next day, 10 minutes one week later, 10 minutes one month later giving a total of three reviews – a total of 30 minutes.
Notes:
Only read material that is interesting or relevant.
Refuse to read less important things.
Skim and scan magazines.
Use table of contents as a guide
Rip out articles of interest and throw the magazine away.
Explore and play with material to learn and keep in memory
Stop and reflect on key points and re-read.
IX.) Review Techniques
7
Practice memory techniques
1.) How to demonstrate what you have learned
2.) How to reflect on the learning process so I can improve it the next time
Show that you know
1.) Test yourself
2.) Practice to be confident and fluent with material
3.) Use material to make it a part of you and to apply it
4.) Test myself regularly which gives me the opportunity to demonstrate what I know ≡ checking to see if I got it or not i.) Go over memory map/notes ii.) Try flashing to see how much I remember (?) iii.) Test with flash cards iv.)
Create a mental movie of what I’ve learned v.) Put what I have learned to use
Think about material to be learned consciously as I’m doing → become an unconscious skill ≡ learning is easy and fun
Two ways to practice something before I use it
1.) Mental Rehearsal see myself actually using what I have learned, picture myself performing well in mind’s eye
2.) Role Playing ≡ act out what you learn by yourself or with someone else
3.) Use the Material independently away from where you first learned it (explain it to yourself or someone else)
Errors you make
→ helpful feedback on progress
Progress
→ taking risks
→ making mistakes
→ failures are only temporary
Evaluation of any Stage of Learning Process
1.) What was the best and most effective part of the learning process?
Which mode did I most enjoy?
2.) How could I improve the learning process?
8
Keep a learning log ≡ record of achievement to track progress, record thought in learning process. This could simply be a notebook ≡ blueprint to where you want to go
3.) Multi-sensory Learning ≡ Expand out of comfort zone and experiment with techniques that will stretch and expand comfort zone
1 http://www.nightingale.com/prod_detail.aspx?productidn=11970
9







