Transition from High School to College
advertisement

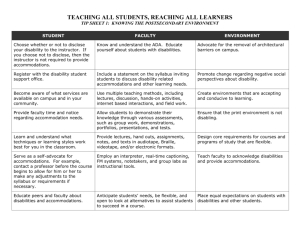
Differences between Secondary and Postsecondary Education High Schools Applicable Laws Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) Colleges/Universities Grinnell College Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), as amended Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973. Dept. of Housing and Urban Development Regulations FERPA (Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act) All of the information in the College section is applicable. Enable student success Provide equal access Disability Services provides equal access; other services for all students available to enhance success Connecting with the Disability Resources If a staff member or teacher believes a student has a disability the h.s. must work with the student and their family to create an IEP and transition plan. Students must self-report and All of the information in the actively seek resources from the College section is applicable. disability services office. Disability services offices will often reach out to students who have disclosed to other staff but the student must respond to that outreach and complete the accommodations process in order to receive services. Documentation Individual Education Plan (IEP) Student self-report Director’s observations and interactions Section 504 plan Current evaluations from applicable professional including diagnosis, testing results, and other points may be required. -Student must get evaluation at own expense. Section 504, Rehabilitation Act of 1973 Goal School conducts evaluations as needed. Documentation guidelines based on Association on Higher Education and Disability (AHEAD) guidance (http://www.ahead.org). IEPs and504s from high school and student interviews may be used as additional information. Parental Role Student Role Teachers/ Professors/ Curriculum/ Grades School is required to include parents in process. College officials are precluded from including parents once student is enrolled (regardless of age). The student can dictate how they do (or do not) want their parents involved in their accommodations process. Parents have access to student records. Parents do not have access to students’ records in most cases. Once enrolled, parents do not have access to any disability services records unless student signs written consent. Parents advocate for student. Students advocate for themselves. Student is identified and supported by parents/teachers. Students self-identify to disabilities services or other designated staff (even if parents contact the office first). Once a student comes forward, the Disability Services office will explain policies, procedures, and philosophy to student. Implementing accommodations is school’s responsibility. Seeking and implementing accommodations is the student’s responsibility. Student chooses whether or not to self-identify and/or use services. Modifications to curriculum and/or changes to the pace may be made. (Not for college credit classes, however.) Modifying essential components of courses and/or curriculum is not an option. The College is writing intensive. Students are required to write in most classes. Multi-sensory approaches may or may not be used. The frequency of tests and assignments varies. The types of evaluations vary significantly. Group work and class participation is a frequent expectation. Multi-sensory approaches used. Frequent testing, and graded assignments used. Attendance taken and reported. Grades may be modified based on curriculum. Attendance may or may not be taken; student is responsible for attending class. Grades based upon the objectives and standards listed in the course syllabus. Classroom attendance is considered an essential component of the curriculum. Students that miss class frequently, regardless of the reason, may encounter situations where faculty will not take the late work and may fail the student for lack of participation. Course Selections Courses selected and by counselor; Requirements requirements may be modified to accommodate disability. Process High school I.E.P. team drives the process. Housing Usually not Accommodations relevant as most traditional-aged h.s. students live at home. Student is responsible for knowing requirements and with the guidance of an advisor, selecting courses. Course substitutions for requirements may occur in specific situations. Students must articulate any concerns or issues with particular requirements to their advisor. Most often the student and their adviser can choose courses in the open curriculum which minimize the impact of the disability. When a student (or parent of a student) discloses a disability to an employee (excluding Health and Counseling Services), the information is to be communicated to Disability Services (or the faculty-staff member refers the student disability services). If the Disability Services office receives information regarding a disability from any source, staff members then reach out to student to let the student know of available resources, policies, procedures, and philosophy. Some colleges have the housing staff make accommodation decisions; others have the disability services provider make such decisions. Students are to make requests for housing accommodations to Residence Life staff who process accommodation requests. Residence Life staff may consult with other disability services professionals to determine the best accommodations. Adapted from Beloit College, Learning Enrichment and Disability Services Office Retrieved from http://www.beloit.edu/dss/assets/How_College_is_Different_than_H.S._Fall_2010.pdf Differences Between Secondary and Postsecondary Disability Laws Differences Secondary Education What is the law? IDEA and Section 504 What is the IDEA: To provide a free, appropriate public intent of the education in the least restrictive law? environment to students with disabilities. 504: To ensure that no otherwise qualified person with a disability is denied access to, benefits of, or is subjected to discrimination in any program or activity provided by any public institution or entity. Who is covered All infants, children and youth requiring under the law? special education services until age 21 or graduation from high school. Postsecondary Education ADA and Section 504 (Subpart E) To ensure that no otherwise qualified person with a disability will be denied access to, or the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination by any program or activity provided by any public institution or entity. All qualified individuals with disabilities who meet the entry age level criteria or particular program entry criteria of the college and who can document the existence of a disability as defined by the ADA. Students are responsible for selfidentification and for obtaining disability documentation from a professional who is qualified to assess their particular disability. They student, not the institution, assumes the cost of the evaluation. Who is responsible for identifying and documenting the need? School districts are responsible for identifying, evaluating and planning educational services at no expense to the parent or individual. Who is responsible for initiating service delivery? School districts are responsible for identifying students with disabilities and providing special instruction, individualized education plans, and/or accommodations. Students are responsible for notifying the Disability Support Services staff of their disability and of their need for accommodations. Accommodations (not special education) are provided on a semester by semester basis in order for students with disabilities to have equal access to the institution's programs, services and activities. Who is responsible for enforcing the law? IDEA is basically a funding statute, enforced by the Office of Special Education and Rehabilitation Services in the U.S. Department of Education. ADA/504 are civil rights statues, enforced by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), U.S. Department of Justice, and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). Section 504 (Subpart E) is a civil rights statute enforced by the Office for Civil Rights (OCR), U.S. Department of Education. The ADA is also a civil rights statute enforced by the U.S. Department of Justice, and the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC). Differences Secondary Education What about self- The parent or guardian is the primary advocacy? advocate. Students with disabilities should learn about their disability, the importance of self-advocacy, the accommodation(s) they need, and ways to become a selfadvocate. Postsecondary Education Students must be able to communicate what their disability is, their strengths, weaknesses, how the disability impacts and functionally limits major life activities. They must be able to identify and justify any requested accommodations.