Chapter 16
advertisement

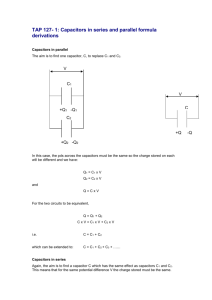
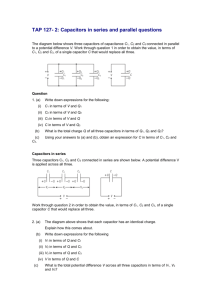
January 29, 2009 PHY 2054 Discussion Spring ‘09 Conceptual Review: Chapter 16 A . Potential Energy & Potential 1. A charge moves along an electric field. Does the potential energy of the charge increase or decrease? 2. A charge q is released from rest and moves along electric field E over a distance of d. What is the change in kinetic energy of the charge? B. Potential due to Point Charges 1. How do you calculate the potential due to multiple point charges? 2. Relate the work required to move a charge to infinity with the initial potential energy of the charge. C. Capacitors 1. Does the potential difference across a capacitor increase or decrease if you increase the plate spacing w/o altering the charge on the plates? 2. Does the charge on a capacitor increase or decrease if you increase the plate spacing w/o altering the potential difference between the plates? D. Combination of Capacitors 1. Two capacitors are connected in parallel/in series. What quantity they have in common? 2. Describe when two capacitors are said to be connected in parallel or series. E. Energy Stored in Capacitor 1. Two capacitors are connected across a battery. The total energy stored in the circuit is larger when they are connected in parallel/series. F. Capacitors with Dielectrics 1. A dielectric is inserted in a parallel-plate capacitor after a battery is disconnected from the capacitor. Does the potential difference across the capacitor increase or decrease? 2. A dielectric is inserted in a parallel-plate capacitor w/o disconnecting it from a battery. Does the charge on the capacitor increase or decrease? January 29, 2009 PHY 2054 Discussion – Spring ‘08 Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 16) 1. A uniform electric field, with a magnitude of 600 N/C is directed parallel to the positive x-axis. If the potential at x = 3.0 m is 1 000 V, what is the change in potential energy of a proton as it moves from x = 3.0 m to x = 1.0 m? (Potential & Potential Energy) a. 8.0×10 -17 J b. 1.9×10-16 J c. 0.80×10-21 J d. 500 J 2. An electron is released from rest at the negative plate of a parallel-plate capacitor. If the distance across the plate is 5.0 mm and the potential difference across the plate is 5.0 V, with shat velocity does the electron bit the positive plate? (Kinematics of Charged Particles) 1.0×106 m/s a. 2.6×10 5 m/s b. 5.3×106 m/s c. d. 1.3×106 m/s 3. A point charge of +3.0 C is located at the origin of a coordinate system and a second point charge of -6.0 C is at x = 1.0 m. At what point on the x axis is the electrical potential is zero. (Potential due to Point Charges) a. -0.25 m b. +0.25 m c. +0.33 m d. +0.75 m 4. A solid conducting sphere of 10 cm radius has a net charge of 20 nC. If the potential at infinity is taken as zero, what is the potential at the center of the sphere? (Potential in a Conductor) a. 36 μV b. 360 μV c. 1 800 V d. 18 000 V 5. Using a 1-mF capacitor, a 2-mF capacitor, and a 3-mF capacitor, which of the following capacitances cannot be made by a combination that use all three? (Combinations of Capacitors) mF c. 11/3 mF a. 6 mF b. 6/11 d. 5/11 mF 6. If C1 = 25 µF, C2 = 20 µF, C3 = 10 µF, and V0 = 21 V, determine the energy stored by C2. (Energy stored in a Capacitor) a. 0.72 mJ b. 0.32 mJ c. 0.40 mJ d. 0.91 mJ 7. A parallel-plate capacitor has dimensions 4.0 cm 5.0 cm. The plates are separated by a 1.0-mm thickness of paper (dielectric constant = 3.7). What is the charge that can be stored on this capacitor, when connected to a 1.5-V battery? (Capacitors with Dielectrics) 4.8×10-11 C d. 9.8×10-11 C Answers: 1-b 2-d 3-c 4-c 5-d 6-d 7-d a. 20×10-12 C b. 4.8×10-12 C c.

![Sample_hold[1]](http://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005360237_1-66a09447be9ffd6ace4f3f67c2fef5c7-300x300.png)