Biology Notes
advertisement

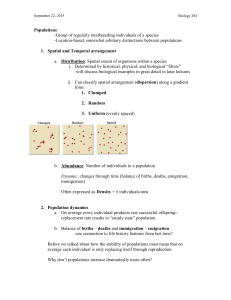
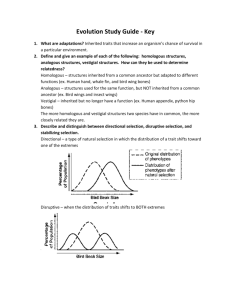
Biology Notes- Evolution Species – is a group of individuals that can interbreed and produce healthy, fertile offspring. Population – a group of individuals of the same species living in a specific area. Variation – the difference found within individual members of a population. Variation can be extreme or subtle (barely noticeable). Not all variations can be seen. Some differences are biochemical and occur on a cellular level. These biochemical variations may be permanent or temporary based on local conditions (a rabbit changing fur color with the seasons). Most variations are the result of random mutation and/or recombination. Variations of are three types, Beneficial, Neutral, or Harmful. A Beneficial variation allows the particular individual of the population to become more successful and therefore increase the number of individuals in the population with this variation. The individual survives better has more offspring and passes on the gene. This is also called an adaptation. An inherited trait that increases populations chances of survival and reproduce in a particular environment is called an adaptation. A Neutral variation does not affect the particular individual of the population in relation to its’ successfulness and therefore the number of individuals in the population with this variation will remain approximately the same. The individual survives no better or worse and has the same number of offspring as those individuals in the population without the variation. A Harmful variation causes the particular individual of the population to become less successful and therefore decrease the number of individuals in the population with this variation. The individual survives worse (usually not at all) and so is not alive to produce offspring and so cannot pass on the gene. Some species become uniquely adapted to a specific area (habitat) or its role in the habitat. This is called a niche. A niche includes where the organism lives, what they eat, how they raise their offspring and what their predators are. It also can all the environmental factors to which a population is adapted too, ALL POPULATIONS CHANGE OVER TIME!!! This change in a population is due to natural selection based on the normal variations that are found in any species population. In the most basic terms this is what EVOLUTION is, change over time. There are two different thoughts of how this evolution occurs, Gradualism and Punctuated Equilibrium. Gradualism – proposes that new species evolve as the genomes (populations genotypes) change over enormous spans of time. Punctuated Equilibrium - suggests that populations remain genetically stable for long periods of time and are interrupted by brief periods of rapid genetic change. This rapid change could be caused by rapid changes in the environment (ice age, meteor crashing to Earth- believed to cause the extinction of dinosaurs). This rapid genetic change will cause new genetic variations causing the creation of new species. Homologous structures - are structures that are the result of species that had a common ancestor. This structure will adapt with the specific species but the similarities are present. Think of a human arm, whale fin, and bat wing all three of these had a common ancestor that gave rise to these structures. Analogous structures – distantly related organisms sometimes have characteristics that are similar in function but different in structure. In example, bird wings and insects wings. Both serve the same function- flying but they were not inherited from a common ancestor. Convergent Evolutions As the environment acts on distantly related populations, resulting in different species looking similar. This different species looking alike has sometimes caused scientists to think species that are not closely related to be classified as being closely related. Divergent Evolutions When isolated populations of a species evolve independently. Divergent evolution often occurs as a result of geographic barriers restricting the species into two (or more) groups that undergo their own specific evolution. Geographic Isolation Similar species restricted from interbreeding by some type of geographical barrier, such as water, deserts or mountains. Adaptive Radiation Is the evolution of many diversely adapted species from one common ancestor. Adaptive radiation occurs as a specific population adapts to exploit a different niche that allows it to be more successful. This will allow one species to adapt and undergo Speciation to become a new species.