Day 1- Rational Numbers
Pre-Algebra
Number Systems
Notes
Name_____________________
Teacher___________________
Period____________________
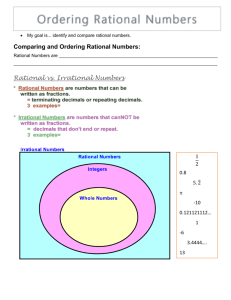
Day 1- Rational Numbers
A rational number is any real number that can be expressed as the ratio of two integers a
, where b is not equal to zero. b
Examples:
A rational number can be expanded so that the decimals either repeat or terminate. In order to convert a fraction to a repeating decimal, use long division and divide the numerator by the denominator.
Class Examples:
1.) Determine if 5
12 is a rational number and convert it to a decimal.
2.) Determine if 3
8 is a rational number and convert it to a decimal.
3.) Determine if
3
2
5
is a rational number and convert it to a decimal.
Some square roots are also rational. Any number that has a whole-number square root is a perfect square.
Examples:
All rational numbers can be represented on a number line. To plot rational numbers on a number line, first convert them to the same form.
Class Examples:
4.) Plot and label a point for each rational number below on the number line.
2
2
,
1
3
4
,
0 .
25
,
4
,
1
9
,
72 .
5 %
-1 0 1 2
5.) Plot and label a point for each rational number below on the number line.
4
15
, 6
3
,
2
1
4
,
9
,
65 %
,
1 .
75
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
Day 2- Irrational Numbers
An irrational number is any real number that cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers a
, where b is not equal to zero. An irrational number can be b expressed as infinite, non-repeating decimal.
Class Examples:
1.) The value of the number pi ( irrational number.
) is 3.1459265358… Explain why is an
The square roots of positive numbers that are not perfect squares are also irrational. You can estimate the value of a square root by deciding which two perfect squares it lies between and then using guess and check to estimate its value more precisely.
2.) Explain why
2 is irrational. Then estimate its value.
3.) Graph the approximate location of
34
on a number line.
4.) Estimate the value of
2 10
5.) Estimate the value of 2 .
.
6.) Estimate the value of
18
.
2
7.) The area of a square is 67 square meters. Find the exact length, in meters, of one side of the square then graph the value on the number line.
Day 3- Compare and Order Rational and Irrational Numbers
Sometimes, you may need to compare or order rational and irrational numbers. The symbols below will help you do this:
> means “is greater than”
< means “is less than”
= means “is equal to”
To compare rational and irrational numbers convert the numbers to decimal form.
Then compare the digits to determine which is greater.
Class Examples:
1.) Which symbol (< , > , =) makes this sentences true?
7.745966…
59
2.) Order the numbers below from least to greatest. Graph on the number line below.
28 %
,
2
1
2
,
2
7
,
9
-3 -2 -1 0 1 2 3
3.) Order the following numbers from least to greatest.
,
3
1
3
,
14
4.) Order the following numbers from least to greatest.
1
9
,
5
,
0 .
8
,
3 .
5