RTi – Overview
advertisement

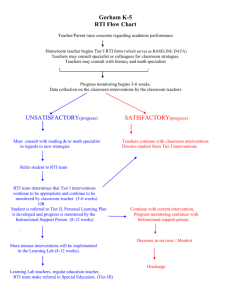
Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 IDEA 2004 revisions incorporated the focus of NCLB encouraging schools to focus on student performance outcomes and accountability § 614(b)(6)(A). RtI is presented as an option not as a requirement. (Origin of Rti: (1) With over 20 years of chronic misdiagnosis of students having LD RTi is being as a method/practice to differentiate between individual pathology and common place problems (developmental delay or lack of environmental support). (2) Studies indicate that “…providing all students an equal opportunity to succeed requires more than [setting] higher standards and greater accountability for instruction, better teaching, increased discipline…it also requires addressing barriers to learning.”(Adelman & Taylor, 2006) The ACT adds language for use in defining the criteria used to determine specific learning disability. LEA’s may use student response to research-based intervention (RtI) as part of the evaluation process. Discrepancy model (significant difference between assessed ability and student performancePerformance v. verbal scores) may continue to be used. Schools are encouraged to implement the RtI model within initiatives of broader school reform that address student learning and preemptively prevent academic failure. Two salient features of RtI are: identifying students not achieving at the same rate as their peers, and providing appropriate interventions. In doing so, schools also satisfy the requirements of NCLB, IDEA, and Least Restrictive Environment (LRE). PDE has developed tools to assist school entities to develop/implement RtI – School Intervention Model… School-Wide Positive Behavior Support (SWPBS), data analysis, and intervention strategies. Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 1 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Research indicates: When schools raise student achievement levels-problem behavior decreases, when schools work to decrease student maladaptive behavior academic performance increases. PDE/PaTTAN developed training tools to assist schools: o Universal Screening o Explicit Instructional Strategies o Team strategies for use in data driven analysis and decision-making o Progress Monitoring o Using RtI in making determination of Special Education Eligibility o Training for school administrators What are the ‘Big-Ideas’ in RtI?? o RtI has been ‘on the scene’ for at least 20 years…simply stated, it is a… Logical structure to efficiently allocate resources Commitment to use best findings to plan, design, implement guide instruction Commitment to use logical, decision-making to guide instruction Paradigm shift intent on prevention and intervention before students fail. o Core Characteristics— ALL students receive high quality, researched-based, differentiated instruction in general education core curriculum ALL staff assume an active role in student assessment and in instruction in the core program. Specialists deliver intense support services. ALL students receive progressively (public health model) intense levels of targeted researched-based interventions dependant upon student need. Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 2 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Data drives instructional decisions and the student’s movement through the tiers. Student movement through the tiers is bi-directional and determined by student response to instruction. Supports are provided through categorical and non-categorical delivery models. PA Multi-tiered RtI Model (primary, secondary, tertiary- aligned with SWPBS/Resiliency Model- Academic and Behavioral Systems of Support) o Tier 1: Benchmark and School-wide interventions for Students at Benchmark and ALL students: ALL students receive differentiated instruction in researched-based core program (reading, math, behavior) ALL staff support instruction in the core curriculum ALL students are screened for academic and behavioral concerns minimum of 3 ax’s per year Grade-level data analysis teams set annual grade level goals and grade-wide interventions for students to achieve benchmarks. Students identified through screening or progress monitoring as academically or behaviorally ‘at-risk’ are referred to Tier 2 for more intense support. Tier 2: Strategic and Targeted Interventions for Students at Risk of Academic Failure and/or Behavioral issues. Tier 1 supports are IN ADDITION TO all Tier 1 instruction/supports Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 3 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Students provided more intense targeted instruction in area of deficit. Interventions are researched-based, provided on basis of assessment and delivered with fidelity. Specialists in homogeneous, small groups, based upon student need, may deliver instruction. Student progress is monitored frequently, minimum 2x’s/year. When data indicates student has/or will satisfy required benchmark return to Tier 1 support occurs. When data indicates student is not making adequate progress toward benchmark, movement to Tier 3 support occurs. Tier 3: Intensive Intervention for Low Performing Students. Tier 3 interventions are IN ADDITION to Tier 1 supports. Tier 3 interventions are more intense (+time, +frequency, +duration, individual/small group, direct and explicit). Interventions are: researched-based, assessment driven, done with fidelity. Student progress is monitored weekly. Students responding to interventions may return to Tier 2 or 1 but may require progress monitoring. Students not responding to interventions at Tier 3 may be referred for evaluation for special education eligibility. Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 4 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Pros for RtI: Focus is on student outcomes Increases accountability for ALL students Promotes collaboration and shared responsibility among general educators, related service providers, administrators, and parents. Earlier identification- eliminates “wait to fail” method of intervention. Reduction in volume of students referred for Special Education services. (Reduction in stigma attachment!) Reduction in over identification of minority students. Instructionally relevant data drives decision-making. Cons for RtI: RtI that places emphasis on student deficits while ignoring environmental influences or the transactional interplay between both (reciprocal determinism) will result in misguided efforts. RTi emphasis is on direct instruction (National Reading Panel sponsored) with emphasis on teaching specific skills using very specifically directed lesson plans and reading programs with Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 5 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 ongoing assessment. Critics argue that research on directinstruction is limited and does not promote confidence in reading outcomes. They argue the NRP was overloaded with proponents of direct instruction who used correlational data to infer causation. RtI may be prone to error with identification of LD among high ability students. RtI may be prone to error with identification of ED among students with emotional stressors demonstrating low motivation. Research is not available on large scale to determine efficacy of RtI. Implementation Issues: Accepting Change Moving from 2 systems in education (regular education v. special education) to 1 system for all students. Recognizing RtI is a regular education process to be support by special education. Translating RtI theory into classroom-based practices Selection of Structure and Components Resources can dictate the model selected Common models (Public Health model) v. atypical models Personnel, decision-making process will be impacted by resources and model selected. Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 6 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Balancing Rigid tiers v. flexible models Stable frameworks promote consistent application – promote research and model replication. Flexible models reduce research and replication options. Flexible models can be more responsive to student needs and maximize problem-solving opportunities. Movement within and between Tiers Little agreement on criteria for Tier shift Research-based data may limit use of beginning reading, math, & written expression choices…few scientific studies exist at the elementary and secondary level. Resources needed Time/Space/Materials Documentation- increased paperwork (progress monitoring) Financial Support – little comparison data available RtI v. Traditional practices. Technical Assistance – short term and long term vision and planning Inter school collaboration opportunities (Communities of Practice) Opportunities to ask questions-get answers Community participation - Students, Families, Business, Government Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 7 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Professional development School leaders, teachers, support staff Illumination of Research-based practices Connecting researched-based practices to preidentification instructional strategies Articulating researched-based practices instructional strategies in a manner unique to individual students. RtI - Information links: www.promisingpractices.net www.devstu.org/cdp/ www.pattan.net (professional development) http:/ /smhp.psych.ucla.edu www.nasponline.org/resources/principal/nasp.pdf www.nrcld.org/presentations/CEC April 2005.ppt Reference: The School Leaders Guide to Student Learning Supports. Adelman, H.S., & Taylor, L.(2006). California, Corwin Press Response to Intervention: An Overview, What is it? Why Do It? Is It Worth It? Tilly II, D.(2006) The Special Edge, 19, 1-16. Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 8 Response to Intervention – RtI: Overview -Notes on Salient PointsApril 10, 2007 Chuck Haley- PDE/BSE – 4/2007 9