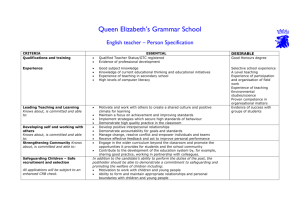
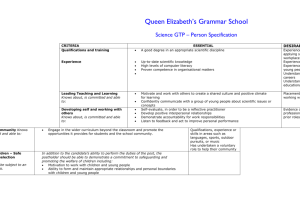
Oral Surgery
advertisement

Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia Wzór sylabusa przedmiotu 1. Basic information Faculty: Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry Field of study: English Dentistry Division, full-time Academic year: 2015/2016 Course: Oral Surgery Course code: 25441 Head of department: Department of Oral Surgery Medical University of Warsaw Faculty of Medicine and Dentistry Ul. Nowogrodzka 59 02-006 Warszawa, building 11B, 1st floor Tel. (22) 502-12-42 Prof. dr hab. Andrzej Wojtowicz Year of study: Year 3 Semeter: Semester V i VI Course type: major, oral surgery, 25441 Department: Prof. Andrzej Wojtowicz, DDS, PhD Wojciech Popowski, DDS, PhD Piotr Wychowański, DDS, PhD Persons responsible for teaching: Piotr Wesołowski, DDS, PhD Tomasz Kamiński, DDS Erasmus YES/NO (availability for students within Erasmus programme): YES, course in English Prof. Andrzej Wojtowicz, DDS, PhD Person responsible for curriculum: Dr Wojciech Popowski, DDS, PhD ECTS credits: 4 2. Objectives Strona 1 z 10 Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia The teaching objective in oral surgery is to thoroughly prepare future dentist to independently perform surgical procedures within the oral cavity. Participation in classes provides the students with an opportunity to acquire knowledge and skills required to diagnose and differentiate pathologies within the oral cavity, perform basic oral surgery procedures and to decide upon patient referral to Cranio-Maxillo-Facial unit or related specialty units. 3. Prerequisite 1. Successful completion of Year 2 4. Learning outcomes List of learning outcomes Symbol Description Reference to learning outcome (kod przedmiotu)_ (numer efektu oraz jego kategoria W-wiedza, U-umiejętności, K-kompetencje) K- knowledge F.W2. Student knows and understands the mechanisms that lead to organ and systemic pathologies (including infectious, invasive, autoimmune, immunodeficiency, metabolic and genetic diseases) F.W2 Student knows the mechanisms of inflammatory conditions and other pathologies within the oral cavity, with particular focus on odontogenic pathologies and their influence on patient's general health; F.W4. Student knows the viral, bacterial and fungal oral flora and its significance; F.W4. Student knows the composition of physiological oral flora and factors that negatively affect biological balance in the oral cavity; knows the pathomechanism of inflammatory conditions with particular focus on odontogenic infections; knows the effect of oral pathological bacterial flora on patient's general health; human papilloma virus (HPV) - Gram-positive Streptococcus species, Gram-positive bacilli: Eubacterium, Actinomyces, Corynebacterium, Rothia, Lactobacillus, Propionibacterium; Gram-negative bacilli: Actinobacillus, Porphyromonas, Prevotella; and Neisseria, Veillonella cocci, - Candida albicans, Candida tropicalis, Candida glabrata, Candida parapsilosis, Candida quilliermondii; Student knows and understands the concept of focal infection, knows the potentially adverse effect of pathological bacterial flora of the oral cavity in high risk patients (patients after radiation therapy, taking Strona 2 z 10 Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia immunosuppressive medications etc.); student knows the pathomechanism, symptoms and signs, course of tuberculosis, actinomycosis and syphilis within the head and neck; F.W6. Student knows the principles of local anaesthesia in the masticatory system; F.W8. Student knows of periapical diseases; the management F.W6. Student knows the types and mode of action of local anaesthetics, indications and contraindications for using anaesthetics, indications and contraindications for anaesthetic allergy testing, know the types of nerve blocks in the oral cavity, knows the principles of infiltration anaesthesia in the oral cavity, knows the basics of general anaesthesia including the mode of action of pharmaceutical agents used in premedication; F.W8. Student knows the principles of surgical treatment of periapical lesions, endodontic preparation prior to surgery, differentiation between inflammatory periapical lesions and odontogenic tumours, knows indications and contraindication for enucleation of periapical lesions, patient preparation, possible complications in root apicoectomy, hemisection, amputation, premolarization; knows the mechanisms of bone healing, including healing of defects after cyst enucleation; knows indications and contraindications to guided bone regeneration in relation to defects after cyst enucleation; F.W15. Student knows and understands the basics of antimicrobial therapy and antimicrobial resistance; F.W15. Student knows and understands the basics of antimicrobial therapy and antimicrobial resistance: - classification of antibiotics (main groups of antibiotics used to treat odontogenic infections) - mode of action (bactericidal, bacteriostatic agents), dosing - indications and contraindications for antibiotics (allergies to antibiotics, preparation in increased risk patients, indications for antibiotic prophylaxis, antibiotic prophylaxis protocol in increased risk patients, complications related to long-term antimicrobial therapy); F.W17. Student knows the therapeutic methods for pain reduction and relief as well as anxiety and stress reduction; F.W17. Student knows the main groups of analgesics (dosing), indications and contraindications for using analgesics, complications related to analgesics overuse, methods of pain therapy other Strona 3 z 10 Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia than pharmacological, types of pain and their causes, pain symptoms in various head and neck diseases; F.W19. Student knows the principles of anaesthesia in dental procedures and main pharmacological agents; S- skills F.W19 Student knows the groups of local anaesthetics, dosing of local anaesthetics, indications and contraindications for using anaesthetics containing vasoconstrictors, techniques for infiltration anaesthesia and nerve blocks, types of syringes and devices used for local anaesthesia; knows the protocol after needlestick injury; F.W22. Student knows and understands the pathomechanism of oral diseases affecting general health. F.W22. Student knows the principles of odontogenic infection spread within anatomic spaces of the head and neck; knows local and general complications of head and neck inflammatory conditions; knows and understand the concept of focal infection; knows the potentially adverse effect of pathological bacterial flora of the oral cavity in increased risk patients (patients after radiation therapy, taking immunosuppressive medications etc.); F.U1. Student takes medical history from the patient and their family; F.U1. Students has practical skills in history taking - chief complaint, symptoms reported by the patient, previous treatment, past medical history, family history; F.U2. Student performs physical examination of patient; F.U3. Student explains the nature of the ailment to the patient, determines therapeutic management, collects informed patient consent, and establishes a prognosis; Strona 4 z 10 F.U2. Student has practical skills in general examination, dental examination, extra- and intraoral; extraoral examination - within the head and neck, general skin assessment, ability to examine nerve openings, lymph nodes (submandibular, jugular). eyeball position, nasal patency, temporomandibular joint examination; intraoral examination - assessment of the vermillion, vestibule, oral cavity proper, alveolar processes and dentition; ability to measure pulse, blood pressure; ability to read and interpret results from additional tests; F.U3. Student is able to establish contact with patients and present diagnosis, prognosis and propose treatment in an affordable manner and to fill in informed consent forms Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia F.U4. Student conveys unfavourable health information to the patient or their relatives; F.U4. Student is able to establish contact with the patient and present unfavourable prognosis for further treatment with empathy; F.U7. Student determines indications to perform a specific dental procedure; F.U7 Student knows how to interpret information gathered during history taking and examination, which allows to make a diagnosis and treatment plan (to specify indications for tooth extraction, abscess incision, biopsy; to decide whether treatment can be performed in outpatient settings or requires hospitalisation); can qualify patients for elective procedures, such as surgical removal of impacted teeth, apicoectomy, cyst enucleation, alveoloplasty etc.; F.U8. Student knows the prevention of oral diseases; F.U8 Student knows how to prevent inflammatory conditions, oral cancer, health-promoting activities in relation to oral pathology; principles for F.U11. Students know the principles of management in general and local complications during and after dental procedures; F.U12. Student prescribes medications taking into account interactions and side effects; F.U13. Student keeps patient documentation, prepares referrals for tests or specialist dental or medical treatment; Strona 5 z 10 F.U11 Student possesses skills in managing general complications during local anaesthesia and oral surgical procedures (anaphylactic shock, syncope, hypoglycaemia, epileptic seizure, myocardial infarction etc.); is able to treat local complications related to local anaesthesia and oral surgical procedures (management of haematoma, subcutaneous emphysema, dry socket, nerve trunk and ramus injuries, prolonged bleeding, maxillary tuberosity fracture, alveolar fracture etc.); F.U12. Student knows how to prescribe pharmaceuticals, such as antibiotics, antiinflammatory and analgesic medicines; knows the principles of antibiotic prophylaxis and their application in practice; is able to assess whether various medicines allow to perform surgery; is able to communicate with physician in case of patients with co-morbidities in order to ensure safe patient preparation for surgery; knows which medicines preclude performing surgical procedures in outpatient setting; F.U13. Student knows how and is able to keep medical records (outpatient medical record), prepare referrals for Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia basic blood tests, dental radiographic examinations, histopathological examination, microbiological tests, communicate with the patient's physician on their current health and planned treatment; is able to fill in sick leave form, knows how and is able to fill in patient informed consent to perform procedures; F. U.16 Student describes pathological cellular, tissue and organ lesions according to basic mechanisms; C- competencies F.W16. Student is able to provide macroscopic assessment and description of pathological lesions of the oral cavity taking into account lesion size, shape, consistency, colour, relation to its bed etc.; initial differentiation of benign and malignant lesions based on clinical presentation, effect of lesions on oral physiology, treatment modalities (ability to collect samples for histopathological examination) Competencies gained by students after completing Year 3 should allow them to independently see patients under the supervision of lecturers. This involves sufficient knowledge and skills that allow to independently take medical history and perform physical examination, local anaesthesia and simple tooth extractions under the supervision of lecturers. 5. Types of classes Type Hours Groups Minimum number of persons per group Lecture 10 1 entire course Seminar 15 4 20 Classes 30 21 4 6. Course topics and curriculum content np.: W1-Wykład 1- Temat wykładu…- Treści kształcenia;….- Wykładowca- prof. Dr hab. Jan Nowak W2-Wykład 2- Temat wykładu…- Treści kształcenia;….- Wykładowca- prof. Dr hab. Jan Nowak S1-Seminarium 1- Temat …- Treści kształcenia;….- Wykładowca- prof. Dr hab. Jan Nowak ) Course topics contain logical sequence and range of knowledge, and its clinical application. Subject matters include e.g. clinical anatomy of the head and neck, odontogenic infections, tooth extraction procedures, procedures aimed at tooth preservation (apicoectomy, hemisection), cysts, odontogenic tumours (benign and malignant), injuries (diagnosis, management) Year 3: theory, introduction. Lecture topics: Strona 6 z 10 Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia W1. Head and neck embryology and anatomy, clinical aspects. W2. Basic examination, medical interview, physical and additional examination in oral surgery. W3. Perioperative pharmacology in oral surgery. W4. Preparation of patients with co-morbidities to oral surgery procedures. W5. Basic procedures in oral surgery: extractions, management of impacted teeth. Seminar topics: S1. Principles of work and cooperation with the patient. Hygiene, asepsis and antisepsis during surgical procedures. S2. Head and neck anatomy. Elements of embryology pt. 1. S3. Head and neck anatomy. Elements of embryology pt. 2. S4. Patient examination pt. 1. - medical history - physical examination S5. Patient examination pt. 2 – additional examinations, indications (laboratory tests, blood tests, radiographic examinations) S6. Characteristics of local anaesthetics, types of anaesthesia. General and local complications. S7. Test. S8. Armamentarium in oral surgery: - for tooth extraction – forceps - for surgical procedures: removal of impacted teeth, apicoectomy, cyst enucleation (sets) S9. Indications and contraindications for tooth extraction. S10. Complications during and after tooth extraction - management of early and late (long-term) complications. S11. Types of incisions in oral surgery (indications). Suturing technique. Types of suture materials. S12. Salivary gland disorders. S13. Temporomandibular joint disorders. S14. Disorders of cranial nerves - types of disorders (inflammations, neuralgias, cranial vessel syndromes). Diagnostics and therapy. Strona 7 z 10 Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia S15. Test. 7. Means of verifying learning outcomes Class forms Learning outcome Seminars Knowledge Lectures Skills Practical classes Teaching contents S1- S6, S8-14, W1-W5 S1- S6, S8-14, W1-W5 Means of verifying learning outcomes Pass criteria Learning outcome - according to resolution of the senate - test grades - obligatory presence at lectures - no absence 2 tests - assessment of student's predispositions to verbal and procedural communication with the patient, - assessment of each procedure performed by the student - minimum number of procedures performed - no absence 8. Assessment criteria Form of examination: test Grade 2,0 (fail) Criteria inadequate level of achievement 3,0 (poor) all pass criteria are met 3,5 (fair) satisfactory level of achieving learning outcomes 4,0 (good) good level of achieving learning outcomes 4,5 (very good) very good level of achieving learning outcomes 5,0 (excellent) achievement of all learning outcomes 9. Literature 1. James R. Hupp, Myron R. Tucker, Edward Ellis, III: Contemporary Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery. Mosby 2013; 6th edition 2. Karl R. Koerner: Manual of Minor Oral Surgery for the General Dentist. Wiley-Blackwell 2006; 1st edition 3. James L. Hiatt, Leslie P. Gartner: Textbook of Head and Neck Anatomy. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins 2009; 4th edition 4. Paul Coulthard, Keith Horner, Philip Sloan, Elizabeth Theaker: Master Dentistry Volume 1. Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery, Radiology, Pathology and Oral Medicine. Churchill Livingstone 2013, 3rd edition 10. ECTS credits calculation Types of activity Hours Strona 8 z 10 ECTS credits Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia Contact hours with academic teacher: Lectures 10 0.33 Seminars 15 0,5 Practical classes 30 1.0 Types of activity Hours ECTS credits Student's individual work (exemplary types of work): Preparation to seminars 30 1.0 Preparation to practical classes 6.54 0.22 Preparation to tests 28.56 0.95 Other No hours for preparing research papers and presentations at student congresses Total 120.1 11. Additional information (Np. informacje o kole naukowym działającym przy jednostce, informacje o dojeździe na zajęcia itp.) Lectures in the winter semester convey newest reports from consensuses and latest standards in oral surgery. Attendance to lectures is a necessary element to acquire modern knowledge and simultaneously provides solutions to distinguishing exam questions. Presence at lectures is verified by attendance lists. Presence at seminars and clinics is obligatory, and is necessary to pass the course. Test forms include oral and written examination. Students shall present for classes with protective clothing and footwear (changed). The Students Scientific Association at the Department of Oral Surgery brings together students of dentistry from years 3, 4 and 5. Working in the association allows to broaden knowledge in oral surgery and prepare research projects individually or in teams. Lectures on interesting topics are held during scientific meeting of the Association. Students have the opportunity to present results from their research work on annual regional and national scientific conferences. Active members of the Scientific Association organize and participate in oral surgery and implant dentistry congresses. Information of the Scientific Group Information of the activity of the Students Scientific Association are displayed on the notice board at the Department. Strona 9 z 10 Załącznik nr 2 do procedury opracowywania i okresowego przeglądu programów kształcenia Podpis Kierownika Jednostki Podpis Osoby odpowiedzialnej za sylabus Podpisy Osób prowadzących zajęcia Strona 10 z 10