Professional use - Quadratech Diagnostics
advertisement
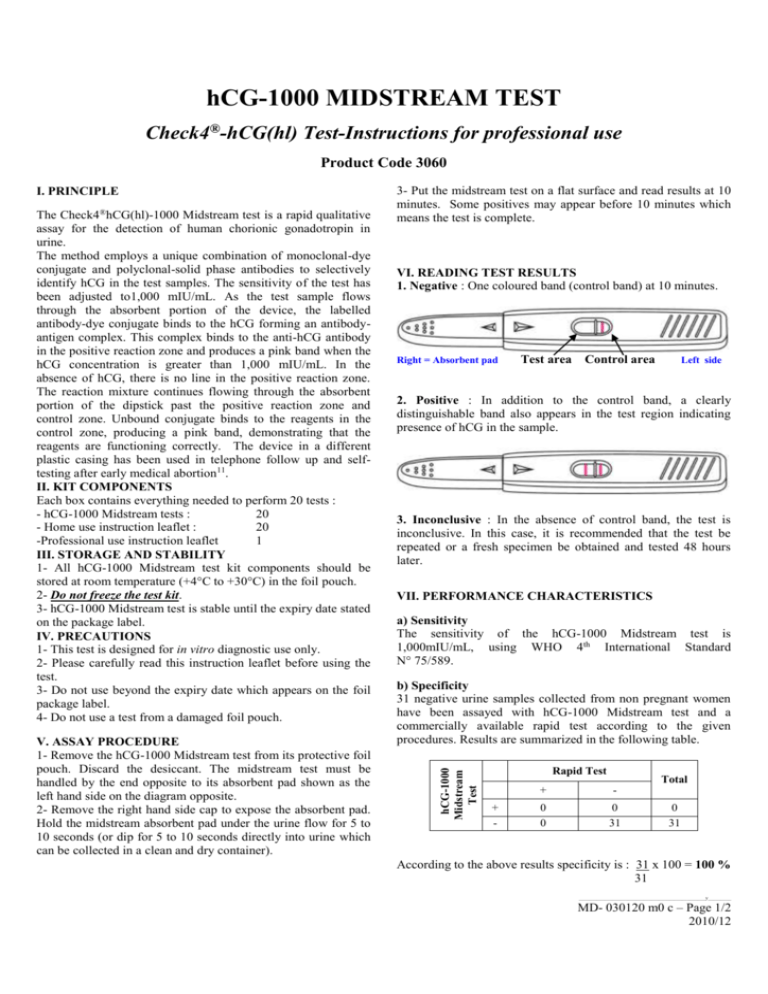
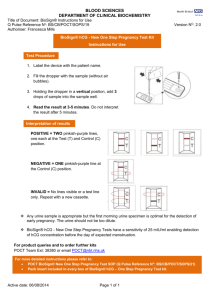
hCG-1000 MIDSTREAM TEST Check4®-hCG(hl) Test-Instructions for professional use Product Code 3060 The Check4®hCG(hl)-1000 Midstream test is a rapid qualitative assay for the detection of human chorionic gonadotropin in urine. The method employs a unique combination of monoclonal-dye conjugate and polyclonal-solid phase antibodies to selectively identify hCG in the test samples. The sensitivity of the test has been adjusted to1,000 mIU/mL. As the test sample flows through the absorbent portion of the device, the labelled antibody-dye conjugate binds to the hCG forming an antibodyantigen complex. This complex binds to the anti-hCG antibody in the positive reaction zone and produces a pink band when the hCG concentration is greater than 1,000 mIU/mL. In the absence of hCG, there is no line in the positive reaction zone. The reaction mixture continues flowing through the absorbent portion of the dipstick past the positive reaction zone and control zone. Unbound conjugate binds to the reagents in the control zone, producing a pink band, demonstrating that the reagents are functioning correctly. The device in a different plastic casing has been used in telephone follow up and selftesting after early medical abortion11. II. KIT COMPONENTS Each box contains everything needed to perform 20 tests : - hCG-1000 Midstream tests : 20 - Home use instruction leaflet : 20 -Professional use instruction leaflet 1 III. STORAGE AND STABILITY 1- All hCG-1000 Midstream test kit components should be stored at room temperature (+4°C to +30°C) in the foil pouch. 2- Do not freeze the test kit. 3- hCG-1000 Midstream test is stable until the expiry date stated on the package label. IV. PRECAUTIONS 1- This test is designed for in vitro diagnostic use only. 2- Please carefully read this instruction leaflet before using the test. 3- Do not use beyond the expiry date which appears on the foil package label. 4- Do not use a test from a damaged foil pouch. V. ASSAY PROCEDURE 1- Remove the hCG-1000 Midstream test from its protective foil pouch. Discard the desiccant. The midstream test must be handled by the end opposite to its absorbent pad shown as the left hand side on the diagram opposite. 2- Remove the right hand side cap to expose the absorbent pad. Hold the midstream absorbent pad under the urine flow for 5 to 10 seconds (or dip for 5 to 10 seconds directly into urine which can be collected in a clean and dry container). 3- Put the midstream test on a flat surface and read results at 10 minutes. Some positives may appear before 10 minutes which means the test is complete. VI. READING TEST RESULTS 1. Negative : One coloured band (control band) at 10 minutes. Right = Absorbent pad Test area Control area Left side 2. Positive : In addition to the control band, a clearly distinguishable band also appears in the test region indicating presence of hCG in the sample. 3. Inconclusive : In the absence of control band, the test is inconclusive. In this case, it is recommended that the test be repeated or a fresh specimen be obtained and tested 48 hours later. VII. PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS a) Sensitivity The sensitivity of the hCG-1000 Midstream test is 1,000mIU/mL, using WHO 4th International Standard N° 75/589. b) Specificity 31 negative urine samples collected from non pregnant women have been assayed with hCG-1000 Midstream test and a commercially available rapid test according to the given procedures. Results are summarized in the following table. hCG-1000 Midstream Test I. PRINCIPLE Rapid Test + - Total + - 0 0 0 31 0 31 According to the above results specificity is : 31 x 100 = 100 % 31 _________________________________________________y_________ MD- 030120 m0 c – Page 1/2 2010/12 c) Hook effect Specimens containing high levels of hCG (1,000,000 mIU/mL) consistently showed positive results when tested with the hCG1000 Midstream test. d) Cross reactivity The following concentration of homologous hormones are found to have no interference with hCG-1000 Midstream test : hTSH hLH hFSH 1,000 µIU/mL 500 mIU/mL 1,000 mIU/mL WHO 68/38 WHO 2nd IS 80/552 WHO 1st IS 83/575 Menopausal urines : A study was performed using 50 urine specimens from non pregnant or post-menopausal women. Specimens from postmenopausal women were chosen because urine from these individuals frequently interferes with pregnancy tests, due to cross reactivity with other gonadotropin hormones. All 50 urine specimens tested over 5 days were negative when tested with hCG-1000 Midstream test. e) Interferences Potentially interfering substances were added to urine which had hCG levels of 0 and 25 mIU/mL. The level of interfering substances was determined to be in excess of levels that would be excreted after 8 hours by the human kidney. In each case, no interference with the expected results of hCG-1000 Midstream test was observed. Acetaminophen Albumin Ampicillin Ascorbic acid Atropin Bilirubin Caffeine Gentisic acid Glucose Haemoglobin Tetracycline 20 mg/dL 1.4 g/dL 20 mg/mL 20 mg/dL 20 mg/dL 30 mg/mL 20 mg/mL 20 mg/mL 2 g/dL 30 mg/mL 40 mg/mL VIII. LIMITATIONS 1- In addition to pregnancy, hCG has been found in patients with both gestational and non-gestational trophoblastic disease. Since the hCG of trophoblastic neoplasms is similar to that found in pregnancy, these conditions, which include choriocarcinoma and hydatidiform mole, should be ruled out before a diagnosis of pregnancy is reached. 2- A normal pregnancy cannot be distinguished from an ectopic pregnancy based on hCG levels alone. Also, spontaneous miscarriage may cause confusion in interpreting test results. 3- hCG levels may remain detectable for several weeks after normal delivery, delivery by caesarean section, spontaneous abortion or therapeutic abortion. 4- As it is true with any diagnostic procedure, the physician should evaluate data obtained by the use of this kit in light of other clinical information. 5- The presence of hydroxyethyl-cellulose in the composition of catheter lubricant may give false positive results with hCG-1000 Midstream test at a concentration equal or higher than 0.1%. IX. BIBLIOGRAPHY 1- Braunstein, G.D., Rasor, J., Adler, D., Danzer, H., and Wade, M.E., Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol., 126, 678-681 (1976). 2- Braunstein, G.D., Vaitukaitis, J.L., Carbone, P.P., and Ross, G.T., Ann. Inter. Med., 78, 39-45 (1973). 3- Morgan, F.J., Canfield, R.E., Vaitukaitis, J.L., and Ross, G.T., Endocrinology, 94, 1601-1606 (1974). 4- Kohler, G. and Milstein, C., Nature, 256, 495-497 (1975). 5- Thompson, R.J., Jackson, A.P., and Langlois, N., Clin. Chem., 32, 476-481 (1986). 6- Engvall, E., Methods in Enzymology, 70, 419-439 (1980). 7- Rasor, J.L., and Braunstein, G.D., Obstet. Gynecol., 50, 553-558 (1977). 8- Lenton, E.A., Neal, L.M., and Sulaiman, R., Fertility and Sterility, 37, 773-778 (1982). 9- Elliott, M.M., Kardana, A. Lustbader, J.W. and Cole L.A. Endocrine, 7, 15-32 (1997). 10- Cola, L.A. Clin. Chem., 43, 2233-2243 (1997). 11-Cameron, S.T., Glasier A., Dewart H., Johnstone A. and Burnside A. Contraception 2011.11.010 Temperature limitations Consult operating instructions Do not re-use In vitro diagnostic use Manufactured by: VEDALAB – France Distributed by: Quadratech Diagnostics Ltd, PO Box 167, Epsom, Surrey KT18 7PE, UK info@quadratech.co.uk _________________________________________________y_________ MD- 030120 m0 c – Page 2/2 2010/12