ELEMENTS Using Textbk (pg 172-173) or Planner make flashcards
advertisement

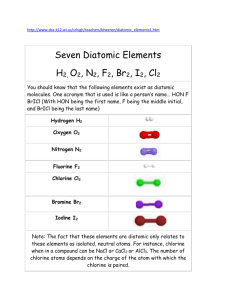
ELEMENTS Using Textbk (pg 172-173) or Planner make flashcards for the following elements (spell accurately) and their chemical symbols (use correct format): hydrogen / helium / lithium / beryllium / boron / carbon / nitrogen / oxygen / fluorine / neon / sodium / magnesium / iron / nickel / cobalt / argon / copper / tin / zinc / silver / lead / bismuth / cadmium / gold / mercury / bromine / potassium / chlorine / phosphorus / iodine / tungsten / sulfur / uranium / vanadium / yttrium / calcium / silicon / gallium / aluminum / manganese / chromium / platinum / francium / arsenic / germanium / antimony / tellurium / astatine / polonium / xenon / radium / curium / thorium / barium / strontium BINARY and TERTIARY COMPOUNDS vs DIATOMIC MOLECULES: (1) BINARY COMPOUND is a compound composed of “2” DIFFERENT elements CHEMICALLY COMBINED (2) TERTIARY COMPOUND is a compound composed of “3” DIFFERENT elements CHEMICALLY COMBINED (3) DIATOMIC MOLECULE is composed of “2” of the SAME KIND of ATOM (a) ONLY the following ELEMENTS make DIATOMIC MOLECULES: *hydrogen [H]; oxygen [O]; nitrogen [N] and GROUP 17 (the halogen family) (4) Examples of COMPOUNDS: (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) (i) (j) table salt = NaCl = BINARY sand = SiO2 = BINARY oxygen gas = O2 = DIATOMIC MOLECULE table sugar = C12H22O11 = TERTIARY bromine gas = Br2 = DIATOMIC MOLECULE water = H2O = BINARY glucose = C6H12O6 = TERTIARY chalk = CaCO3 = TERTIARY iron oxide (rust) = Fe2O3 = BINARY fluorine gas = F2 = DIATOMIC MOLECULE