Geology_101_Homework_2
advertisement

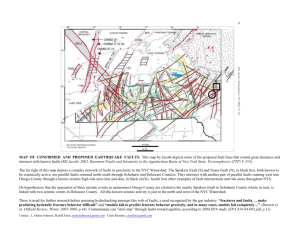
Geology 101 Homework 2 Quiz on this material will be Thursday, March 13 Show me completed work for credit on or before Thursday, March 20 Write your answers on a separate piece of paper. Interlude C, pages 318-329 1) Explain the evidence for the theory that the outer core of Earth is liquid. 2) Explain the factors that affect the speed of a seismic wave as it travels through the Earth. Chap. 11 1) What is the difference between stress and strain? 2) What is the difference between ductile and brittle behavior for rocks? 3) There are two important brittle-ductile transitions in the upper 600 km of the Earth. In what layers or between which layers are they located? 4) Draw pictures of normal, reverse, and strike-slip faults using arrows to show motion along the faults and naming the type of stress that causes these faults. 5) How do continents grow? 6) What causes mountain ranges to rise? What causes mountain ranges to lose elevation over time? 7) How is the achievement of isostatic equilibrium related to the properties of the asthenosphere? Chap. 10 1) Discuss how seismologists identify recurrence intervals for earthquakes and how that knowledge can be applied to assess risk. 2) How are earthquake epicenters located? 3) What is the difference between the Mercalli intensity scale, the Richter scale, and the seismic moment scales for measuring earthquakes? 4) What is the difference between a Richter magnitude 8 and a Richter magnitude 7 earthquake? 5) What is the evidence for subduction? How does it relate to our concepts of asthenosphere and lithosphere? Interlude C Travel time Reflection Refraction Moho P-wave shadow zone S-wave shadow zone Seismic tomography Chap. 11 Orogeny Anticline, syncline Brittle, ductile Detachment fault Craton and shield Isostatic equilibrium Fault vs. joint Stress vs. strain Normal fault, reverse fault, strike-slip fault Tensional, compressional, and shear stress Chap. 10 Aftershock, foreshock Body waves (p-waves, swaves) Surface waves Fault scarp Intraplate earthquakes Liquefaction, resonance Tsunami Seismic gaps Recurrence interval Wadati-Benioff zone