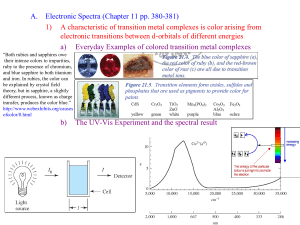
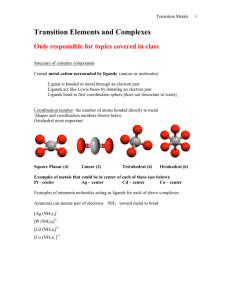
Transition Metal/Coordination Chemistry
advertisement

CH186 Transition Metal/Coordination Chemistry Exam Questions From Spring 2001 Semester 1) a. Write the electronic configuration for each of the following transition metal atoms and ions. Use [Ar] to represent the argon core configuration: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6. Cu Mn3+ Ni2+ Co b. Indicate the coordination number about the metal and the oxidation number of the metal in each of the following coordination compounds and complexes: [MnO4]- K[CuCl2] Na4[Co(C2O4)2Br2] [Cr(edta)]- Coordination No. Oxidation No. c. Give the correct IUPAC name for each of the following coordination compounds: Na2[Ni(CN)4] [Mn(en)2I2]ClO4 2) Give the indicated isomers for each of the following coordination compounds and complexes. a. b. c. d. 3) 4) 1 structural formula for the linkage isomer of [Cr(H2O)5(NO2)]I structural formula for the coordination-sphere isomer of [Co(o-phen)2(NH3)(SCN)]Cl drawing of all possible stereoisomers of the octahedral complex, [Fe(en)(C2O4)Br2]drawing of all possible stereoisomers of the square planar complex, [Pd(PPh3)2BrCl] (PPh3 = triphenylphosphine, a monodentate ligand that bonds through the P atom.) For each of the following sets, indicate the complex you would expect to absorb the shorter wavelength (higher energy) visible light. a. [Fe(NH3)6]3+ [FeF6]3[Fe(CN)6]33+ 3+ b. [Co(en)3] [Co(o-phen)3] [Co(NH3)6]3+ Draw the crystal field d orbital energy level diagram, show the placement of d electrons for each of the following complexes: a. b. 5) 2 [Mn(C2O4)3]3- (octahedral geometry) [Fe(o-phen)3]2+ (octahedral geometry) Solutions of the following M3+ complexes are colored in aqueous solution: [MF6]3-, [M(en)2F2]+, [M(en)3]3+, and [M(en)F4]-. The colors observed are green, red, orange, and violet. Based on the spectrochemical series, match the color to the complex. Answers for Spring 2001 Transition Metal/Coordination Chemistry Exam Questions 1. a. Cu = [Ar]3d104s1 Mn3+ = [Ar]3d4 Ni2+ = [Ar]3d8 Co = [Ar]3d74s2 b. 2. [MnO4]- K[CuCl2] Na4[Co(C2O4)2Br2] Coordination No. 4 2 6 6 Oxidation No. +7 +1 +2 +3 c. sodium tetracyanonickelate(II) bis(ethylenediamine)diiodomanganese(III) perchlorate a. b. c. [Cr(H2O)5(ONO)]I [Co(o-phen)2(NH3)Cl]SCN d. Cl PPh 3 Cl Pd Pd Br PPh 3 Ph 3P Br [Fe(CN)6]3[Co(o-phen)3]3+ 3. a. b. 4. a. 5. [MF6]3- = green [M(en)2F2]+ = red [M(en)3]3+ = orange [M(en)F4]- = violet 3 PPh 3 b. [Cr(edta)]- CH186 Transition Metal/Coordination Chemistry Exam Questions From Fall 1999 Semester 1) a. Write the electronic configuration for each of the following transition metal atoms and ions. Use [Ar] to represent the argon core configuration: 1s2, 2s2, 2p6, 3s2, 3p6. Cu Mn2+ Cr3+ b. Give the coordination and oxidation numbers for the transition metal atom in each of the following coordination compounds. Na[Co(edta)] K[Ag(CN)2] [Ni(NH3)4]Br2 [Co(en)2Br2] Coordination No. Oxidation No. 2) a. Name each of the following coordination compounds using the IUPAC rules. [Mn(H2O)5Cl]Br Na3[FeF6] b. Write the correct structural formula for the isomers indicated for each of the following coordination compounds. Note that a structural formula is a chemical formula that shows how the atoms are bonded to one another in a molecule. Na[FeCl4] is a structural formula. linkage isomer of [Co(NH3)5(ONO)]Cl ionization isomer of [Fe(NH3)5I]Br2 3) Draw all possible stereoisomers for each of the following complexes. Label the diastereoisomers as cis or trans. If no stereoisomers are possible, indicate this fact and draw the only structure possible. [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] (square planar) [Fe(en)2Br2]+ 4 4) Using crystal field theory, draw the crystal field d orbital energy level diagram for each of the following complexes by assigning electrons to 3d orbitals. [Co(en)2]2+ (square planar) [FeF6]3- (octahedral) 5) For the following complex, draw an orbital diagram for the isolated metal ion. Then, using valence bond theory, draw the orbital diagram for the metal ion in the complex and indicate the geometry of the complex. Also, clearly indicate which hybrid orbitals the metal uses for covalent bonding with the ligands. [FeCl4]- (5 unpaired electron) 6) 5 The colors observed for the four complexes of metal ion M3+, [M(en)3]3+, [M(ox)3]3-, [MF6]3-, and [MI6]3-, are blue, green, violet, and yellow. Match the color to the complex. Answers for Fall 1999 Transition Metal/Coordination Chemistry Exam Questions 1. a. Cu = [Ar]3d104s1 Mn2+ = [Ar}3d5 Cr3+ = [Ar]3d3 b. Coordination No. Oxidation No. 2. 3. Na[Co(edta)] 6 K[Ag(CN)2] 2 [Ni(NH3)4]Br2 4 [Co(en)2Br2] 6 +3 +1 +2 +2 a. pentaaquachloromanganese(II) bromide sodium hexafluoroferrate(III) b. [Co(NH3)5(NO2)]Cl [Fe(NH3)5Br]BrI [Ni(NH3)2Cl2] Cl Cl H3N Ni NH3 Cl Cl trans Ni NH3 NH3 cis [Fe(en)2Br2]+ cis #1 4. [Co(en)2]2+ (square planar) [FeF6]3- (octahedral) 6 cis #2 trans 5. Fe3+ [Ar] 3d FeCl4- [Ar] 3d 6. 7 [M(en)3]3+ = yellow [M(ox)3]3- = violet [MF6]3- = blue [MI6]3- = green __ 4s __ __ __ 4p 3 sp __ __ __ __ __ 4d __ __ __ __ __ 4d tetrahedral