Unit 6 Chemical Bonds
advertisement
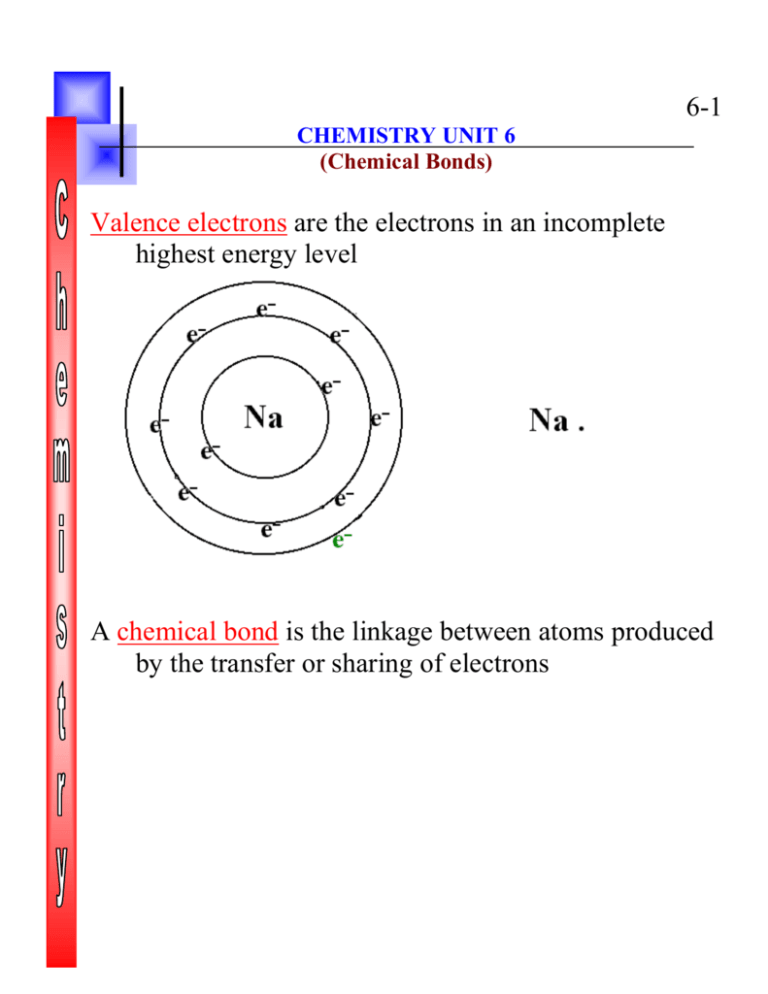
6-1 CHEMISTRY UNIT 6 (Chemical Bonds) Valence electrons are the electrons in an incomplete highest energy level A chemical bond is the linkage between atoms produced by the transfer or sharing of electrons 6-2 Electron transfer results in ionic bonding Ex: Na and Cl 6-3 Electron sharing produces covalent bonding Ex: water H2O 6-4 Finding Energy changes from Ionic bonding Ex: The formation of Na and Cl ions from Na and Cl atoms. What is the total energy change? Is the reaction Endothermic or exothermic. Na + Cl Na+ + Cl- (what happened) 1st: Na loses an electron [endothermic] Na + ionization energy + eNa+ 2nd: Cl gains an electron [exothermic] Cl + e- Cl- + electron affinity 3rd: and Cl- bond to form Cl- which we are told gives off 189 kcal Na+ Na+ So: 1 mole Na + 119 kcal 1 mole Na++ e1 mole Cl + e 1 mole Cl + 83 kcal ____1 mole + 1 mole Cl- 1 mole Na+Cl +189 kcal 1 mole Na + 1 mole Cl 1 mole Na+Cl +153 kcal Na+ By canceling above, the total reaction is exothermic. 6-5 A Molecular formula indicates the kinds of atoms in a compound formed and the ratio of these atoms Ex: H6O3 Na22Cl22 An Empirical formula indicates (1) the kinds of atoms in the compound formed (2) the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms in a compound Ex: Na17Cl17 is a Molecular formula NaCl is an Empirical formula The Oxidation state of an element is represented by a signed number called the oxidation number Oxidation number rules: 1. The oxidation number of a free element is zero. 2. The oxidation number of a mono-atomic ion is equal to its charge. 3. The algebraic sum of the oxidation numbers of all the atoms in a compound is zero. A chemical reaction in which an element attains a more positive oxidation state (loss of electrons) is called oxidation 6-6 A chemical reaction in which an element attains a more negative oxidation state (gain of electrons) is called reduction The substance that is reduced is called the oxidizing agent The substance that is oxidized is called the reducing agent Ex: In the reaction between sodium and sulfur (Na0 + S0 Na2+1S-2) Describes the following: Sulfur reduced by sodium Sodium oxidized by sulfur Sulfur is the oxidizing agent Sodium is the reducing agent Positive ions are called cations Ex: Na+ Negative ions are called anions Ex: Cl- 6-7 A covalent electron pair is two shared electrons that forms the bond between two atoms Ex: water A molecule is the smallest chemical unit of a substance that is capable of stable independent existence Ex: one water molecule Diatomic molecules consist of two atoms Ex. H2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 O 2 N2 6-8 Bond energy is the energy required to break chemical bonds Ex: Breaking up a H - H bond A single covalent bond consist of 1 pair of electrons being shared Ex: Diatomic Flourine F2 A double covalent bond consists of 2 pairs of electrons being shared Ex: Calcium Oxide A triple covalent bond consists of 3 pairs (6) electrons being shared Ex: Ethyne C2H2 In a molecule containing three atoms either the atoms are in a straight line or they form a bent molecule Ex. Straight: Be Cl2 Bent: H2O 6-9 Ex: If Na is in with F and Cl. Which one will get to bond with Na? Ex: In a water molecule, where do the electrons stay most of the time? Percentage of Ionic character of a bond A-B, X is electronegativity XA - XB % I.C. = ---------------------- * 100% XA Ex: Na-Cl What is % ionic character? When is a bond covalent or ionic; polar or non-polar Bonds with more than 50% ionic character are ionic Bonds with between 5% and 50% ionic character are polar covalent Bonds with less than 5% ionic character are considered to be non-polar covalent 6-10 Hybridization is the combining of two or more orbitals of nearly the same energy into new orbitals of equal energy Ex: CH4 Electronegativity is the degree of attraction an atom has for the shared electron in a covalent bond In a non-polar covalent bond there is an equal attraction for the shared electron, which results in a balanced distribution of charge Ex: H-H In a polar covalent bond there is an unequal attraction for the shared electrons, which result in an unbalanced distribution of charge Ex: H-F 6-11 A non-polar molecule is composed of non-polar bonds or uniformly spaced, like polar bonds Ex: H-H Polar molecules have an unbalanced distribution of electrons, thus have two regions of different electric charges Ex: Water Resonance is a bonding situation that cannon be represented by a single formula Ex: sulfur dioxide (SO2) A polyatomic ion is a charged group of covalently bonded atoms Ex: NH4+ ; NO3- ; PO4---






