Working with Genomes – Chapters 16 & 17
advertisement
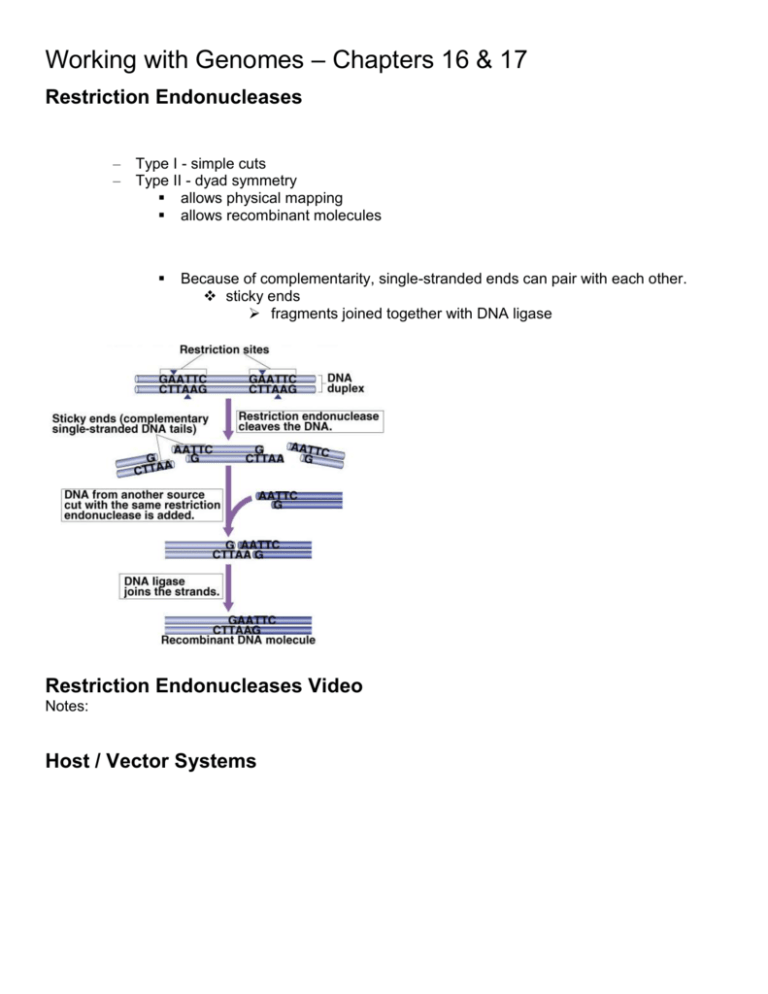
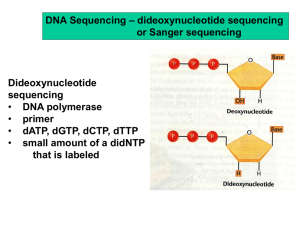
Working with Genomes – Chapters 16 & 17 Restriction Endonucleases – Type I - simple cuts – Type II - dyad symmetry allows physical mapping allows recombinant molecules Because of complementarity, single-stranded ends can pair with each other. sticky ends fragments joined together with DNA ligase Restriction Endonucleases Video Notes: Host / Vector Systems Using Vectors to Transfer Genes • Chimeras – One of first recombinant genomes was a bacterial plasmid into _______________ _____________________________________. Viruses can also be used as ___________________________ into host cells. Early Genetic Engineering Genetic Engineering Video Notes DNA Libraries • A collection of DNA from a ___________________________________________________ – genomic library - ______________________________________________________ – cDNA library is limited to expressed genes __________________________________ isolated from/by ___________________ DNA Libraries Notes on cDNA Genetic Engineering Experiment • • Four stages – DNA cleavage ______________________ cleaves source DNA into fragments – production of ______________________ DNA fragments inserted into _____________________ – Cloning – Screening clones with ___________________________ identified from clone library preliminary screening - eliminate any clones ________________________ _____________________________________ • employ vector with gene for _____________________ and lac Z’ gene • expose to growth medium Secondary screening (gene of interest) – hybridization - cloned genes form base pairs with ____________________________ ___________________________________ grow on agar then ___________________________________ treat filter with ___________________________ and perform autoradiography Genome Maps • • Genetic maps show the ______________________________ on a chromosome as determined by ___________________________________. – measured in centimorgans (cM) one cM = 0.01% recombination Physical maps are diagrams showing the __________________________ within specific DNA sequences. – measured in base-pairs (bp) – 1,000 base pairs equal 1 kilobase (kb) use _________________________ to cut sequences use sequenced-tagged sites (STSs) to construct large genome maps Physical Maps with Restriction Enzymes Physical Maps with Sequence-Tagged Sites Genome Sequencing • Sequencing – sequencing of entire genomes now practical due to technological advances sequencers provide accurate sequences for DNA segments up to ________ long five to ten genome copies sequenced to reduce _______________ • Artificial chromosomes – vector used in cloning _________________ of DNA Larger than what??_________ ______________________________ (YAC) ______________________________ (BAC) Sequencing by whole genomes – clone-by-clone sequencing - cloning larger inserts in BAC requires construction of a physical map, then placing site of BAC clones for later sequencing •