Chapter 1 Lesson 1~ Cells cells split or divide to form new cells 1 ½
advertisement

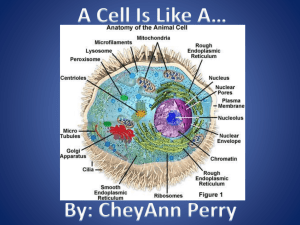
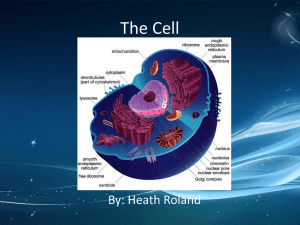
Chapter 1 Lesson 1~ Cells cells split or divide to form new cells 1 ½ million organisms have been identified (over 1 billion have not been named) more multicellular than unicellular have been identified organelles perform life functions Animal Cell (cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, vacuole) ~ cell membrane: gives shape, controls what moves in & out (ticket taker) ~ cytoplasm: gel-like liquid ~nucleus: control center (brain) ~mitochondria: supplies energy (rechargeable battery) ~ vacuole: storage (water, food, waste) Plant Cell (cell membrane, cytoplasm, nucleus, mitochondria, vacuole, cell wall, chloroplast) ~ cell wall: strength (only in plants) ~ vacuole (one large) stores water ~ chloroplast: green, energy from sun turns to food Cell Organization cell: building block tissue: group of cells with same job organ: group of tissues with same job organ system: organs that work together to do a certain job Chapter 1 Lesson 2~ Classifying Life Classification: grouped by shared characteristics Kingdom: grouped by internal form/structure The 6 kingdoms Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Plant & animal kingdoms only contain multicellular organisms Animal kingdom Vertebrates: have backbone Invertebrates: no backbone Plant kingdom Vascular: contains tubes or vessels Nonvascular: no vascular tissue Fungus kingdom Differ from plants (must get food from other organisms) Only other kingdom to have a cell wall Bacteria Kingdom No nucleus or mitochondria Rod-shaped, sphere-shaped, spiral-shaped Protist Kingdom Unicellular or multicellular Make own food or eat other Bigger than bacteria (most microscopic) Viruses Bridge the gap between living/nonliving Not alive, but reproduce Chapter 1 Lesson 3~ Plants Nonvascular: small, no transport system (moss) Vascular: all sizes, tube system (flowers, trees) Seed plants: produce seeds (oak tree-acorn) Seedless plants : produce spores (ferns) Types of Seed Plants Gymnosperm: no flowers (evergreens) Angiosperm: produce flowers (apple tree, tulip, corn) Roots: absorbs water, stores food, anchors plant Parts of a Root Root hair: absorbs like a sponge (part of epidermis) Root cap: protects root Epidermis : absorbs water & nutrients Cortex: stores food & nutrients Transport vessels: Xylem & Phloem Types of Roots Aerial : never touch the ground Fibrous: thin branching, not deep Taproots: single main root, deep in ground Prop roots: grow at bottom of plant’s stem, support Support (soft & woody) Transport ~ xylem: move water & minerals UP the stem (one-way system) ~ phloem: moves sugars from leaves to other parts (two-way system) Stems ~ cambium: separates & produces xylem & phloem Leaves Function: photosynthesis (process of making food) 6CO2 +6H2O + energy = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Cuticle: top layer (prevents evaporation) Stomata: tiny pores allow air to enter Guard cells: allows water & air to leave the plant Transpiration: loss of water through plants leaves Cellular respiration: breaking down of sugars Chapter 1 Lesson 4~ Classifying Animals SIMPLE INVERTEBRATES Sponges: only animal without real tissue or organs (asymmetrical) Cnidarians: soft-bodied, aquatic (radial symmetry) Worms: all have bilateral symmetry Flatworms: flat body, head with eye, mouth Roundworms: simple nervous & digestive system Segmented worms (annelids): divided into sections, two-way digestive system; have a stomach, heart, brain COMPLEX INVERTEBRATES Mollusks: muscular foot or tentacles, mantle, internal organs, bilateral symmetry Echinoderms: skeleton inside the body (endo), radial symmetry, use water pressure for functions Arthropods: small & light with hard skeleton on outside (exo), bilateral symmetry VERTEBRATES Fish: cold-blooded animals Jawless: forced to suck their food Cartilaginous: cartilage instead of bone, fins & jaws Bony: bone covered nerve cord, jaws, fins, & swim bladder Amphibians: cold-blooded, bridge the gap between land and water (spend life in both) Reptiles: land animal with 1 or 2 lungs, thick scaly water-proof skin, cold-blooded Birds: 2 legs, 2 wings, hollow bones, feathers, warm-blooded Mammals: milk, hair, & large brains, warm-blooded Monotreme: lays eggs, fed milk from mothers Marsupial: pouched mammal Placental : develop within mother Chapter 1 Lesson 5~ Animal Systems Skeletal System: bones, tendons, ligaments (protection & support) Muscular System: cause movements by contracting & relaxing Digestive System: food is broken into nutrients to be used Esophagus: tube from mouth to stomach Stomach: contains acid to break down foods Small intestine: absorbs nutrients Excretory System: removes waste Liver: breaks down toxins Kidney: filters waste from blood Respiratory System: lungs & passages that lead to them (oxygen IN~ carbon dioxide OUT) Circulatory System: heart & blood vessels (gets nutrients from intestine & carries to the rest of the body) Capillaries: waste passes through these into the blood Closed circulatory: blood is carried through blood vessels Open circulatory: arthropods, animals blood moves around the body cavity Nervous System: brain, nerve cord, nerves, sense organs Endocrine System: glands that produce hormones Adrenaline: helps body adjust to stress