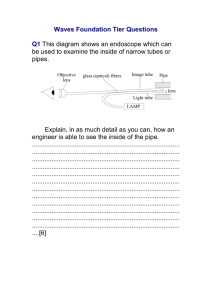
CHAPTER 6 : LIGHT
advertisement

CHAPTER 5 : LIGHT SPM 2005, Section C, No. 11 [20 Marks] 1 (a)Figure 11.1 Figure 11.1 (i) Define the power of a lens [1 marks] (ii) Give two reasons why R is used as the objective lens of the telescope. [2 marks] (iii) Using lenses R and S, draw a ray diagram on Figure 11.1 to show the formation of the final image by the telescope at normal adjustment. Use a scale of 10 cm to 1cm. [5 marks] (iv) Calculate the magnification of the final image formed by the telescope at normal adjustment. [2 marks] (b) Presbyopia is an inability of the eye to adjust the focussing of far and near objects. This is usually happens when we get old, where the ciliary muscle is less able to change the shape of the eye lens to focus the image on the retina, as shown in Figure 11.2 and 11.3 Figure 11.2 Figure 11.3 As an optician, you have three designs of lenses, X, Y and Z, in your shop. The cross-section of X, Y and Z are shown in Figure 11.4 62 Figure 11.4 (i) Choose the most suitable design of lens in Figure 11.4 to correct the sight of a person with presbyopia and explain the suitability of the design. (ii) Explain why the other two designs are not suitable. Either low or high refractive index glass can be used to make the lenses. (iii) Which type of glass is most suitable to make the lens chosen in (b)(i) ? Give reason for your choice. [10 marks] SPM 2008, Section C, No. 11 [20 Marks] 2 Diagram 11 shows a light signal traveling through an optical fibre made of glass. Diagram 11 (a) Name the phenomenon involved at Y. [1 mark] (b) (i) State two changes that happen to the light ray when it passes from air into the optical fibre at X. [2 marks] (ii) Explain why the light ray follows the path shown in Diagram 11.1 when it hits the wall of the optical fibre at Y. [2 marks] 63 (c) The optical fibre in Diagram 11.1 can be used in telecommunications and medicine. You are asked to investigate the characteristics of optical fibres for use in these fields as shown in Table 11. Optical fibre P Q R Features of optical fibre Single fine optical fibres Bundles of fine parallel optical fibres Bundles of fine parallel optical fibres Comparison between refractive index of the inner core, ni, and the outer cladding, n0 Flexibility Purity of the inner core. ni > n0 High Very high n0 > ni Low Low ni > n0 High Very high S Single fine optical fibres ni > n0 Low High T Bundles of fine parallel optical fibres n0 > ni High High Table 11 Explain the suitability of each feature of optical fibre in Table 11 for use in telecommunications and medicine. Determine the most suitable optical fibre that is capable of carrying the largest number of signals simultaneously. [10 marks] (d) Diagram 11.2 and Diagram 11.3 show a ray of light passing into glass and diamond respectively. [ Refractive index : Glass = 1.50 ; Diamond = 2.42 ] Diagram 11.2 (i) Calculate the critical angle of diamond and of glass. Diagram 11.3 [2 marks] (ii) Copy Diagram 11.2 and Diagram 11.3 and complete the path of the light ray in glass and in diamond until it finally emerges from each object. [3 marks] 64