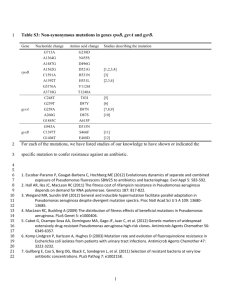
Lett Appl Microbiol
advertisement

Lett Appl Microbiol. 2010 Jul;51(1):48-53. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2010.02857.x. Epub 2010 Apr 23. Multiple drug resistance and strength of attachment to surfaces in Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates. Haddadin RN, Saleh SA, Mahmoud RA, Shehabi AA. Source Department of Pharmaceutics and Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Jordan, Amman, Jordan. Abstract AIMS: To investigate the presence of a relationship between the strength of attachment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to stainless steel surfaces and their observed multiple drug resistance. METHODS AND RESULTS: Multiple drug resistance of clinical and environmental isolates of Ps. aeruginosa was evaluated using disc diffusion method. The blot succession technique was used to quantify the strength of attachment of Ps. aeruginosa isolates. Different multiple drugresistant Ps. aeruginosa isolates exhibited variable attachment strength. Although the highest multiple drug-resistant clinical isolate was shown to have the least attachment strength among clinical isolates, a weak correlation was found between attachment strength and multiple resistance among our investigated Ps. aeruginosa isolates. CONCLUSIONS: There is a weak correlation between multiple drug resistance and strength of attachment to stainless steel surfaces. SIGNIFICANCE AND IMPACT OF THE STUDY: Even low-resistant Ps. aeruginosa could have the potential of attaching firmly to surfaces and forming biofilm.