Thermal Physics OBJECTIVES
advertisement

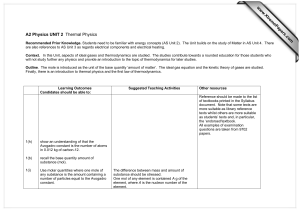
Thermal Physics: Objectives Rosie Heating matter Must be able to Define and understand the meaning of specific heat capacity. Activity Measurement of specific heat capacities of solids and liquids: a direct method using an electric heater will be expected. Yvonne Energy transfer Calculation of energy transferred. Sources of serious experimental error should be identified and understood. Energy transfer = mcΔT Activity Joulemeter to measure electrical energy transfer using a temperature sensor and data logger. Chris Change of state Must be able to Define and understand the meaning of Specific latent heat. Understand that energy is needed to pull molecules apart. Energy transfer = lΔm Activity Temperature sensor and data logger to display cooling curves — with and without changes of state. Alkis Pressure Solids transmit force, fluids transmit pressure. Be able to Apply the equation p = F/A Activity You will not be given this equation Pressure sensor to measure excess lung pressure. Helen The behaviour of gases Experiment demonstrating that for a fixed mass of gas at constant V: p/T = constant Activity Use temperature and pressure sensors to investigate the relationship between the pressure and temperature of a gas at a constant volume. Josie The absolute scale of temperature Understand the concept of absolute zero of temperature. Temp K = Temp oC + 273 Louisa Ideal gas equation Use a pressure sensor to demonstrate that, for a fixed mass of gas, at constant temp T: pV = constant For ideal gases pV = nRT In calculations the amount of gas will be given in moles You will not be given this equation Dave Be able to use and understand the ideal gas law. Kinetic model of an ideal gas & Brownian motion Be able to use of the model to explain the change of pressure with temperature. Know the assumptions on which the model is founded. p = 1/3 ρ <c2> The average kinetic energy of molecules is proportional to the temperature (Kelvin). Conservation of energy & Internal energy Real gases have a random distribution of potential and kinetic energy amongst molecules. Appreciation that hot and cold objects have different concentrations of internal energy. Heating Random interchange of energy between bodies in thermal contact, results in energy flowing from hot to cold. Electrical and mechanical working Understand that forces can move either charges or masses. The process is ordered and independent of temperature difference. Andrew The first law of thermodynamics The increase in internal energy is equal to the sum of the energy given by heating and working. Activity Research the development of the laws of thermodynamics. The heat engine Understand the work done by an engine when energy flows from a hot source to a cold sink. Activity Demonstrate thermocouple engine. Efficiency Efficiency of energy transfer is useful output divided by input. Maximum thermal efficiency = (T1– T2) T1 Environmental considerations Understand the use of energy and sustainable growth. The heat pump Calculate the work needed to pump energy from cold to hot. Thermal Physics: Equations The following equations will be provided to you. You will find them at the back of your Unit 2 exam paper.