Supplementary Notes 2 - Word file
advertisement

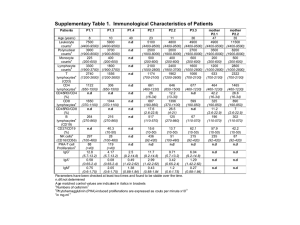
Supplementary Methods XLP families, genetic mapping and sequencing. For this study, informed consent were obtained from patients and families. Patients and relatives were typed for 35 microsatellites markers mapped on chromosome X and spaced at an average distance of 5 cM by the Centre National de Génotypage, Evry, France. In addition, 6 microsatellites markers (STSs ; DXS8098, DXS8093, DXS8009, DXS8044, DXS8033 and DXS8050) were genotyped using UniSTS sequence and mapping information available from the NCBI (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The six exons of XIAP were amplified from genomic DNA extracted from peripheral blood cells and sequenced using standard procedures. The deletion in family 3 was detected by PCR using the following pair of oligonucleotides corresponding to sequences in the flanked introns of the exon 2 of XIAP : forward primer (5’ intron of the exon 2), 5’AAAATAAAGTATGCCAGGTA3’; reverse primer (3’ intron of exon 2), 5’AATTCCCTATCCCACTG3’. The amplified product of 431 bp was sequenced revealing a deletion of 2606 nucleotides. Sequences of introns and intron-exons organization of XIAP were obtained from NCBI. SAP has been sequenced in XIAP-mutated patients and sequences were found to be normal. Mutations in SAP in SAP-deficient patients have been previously described10. Cells. K562 and 293T cells were from ATCC. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by Ficoll-Paque density centrifugation from blood samples. PHA-induced T cell blasts were obtained by stimulating PBMCs with 6.25 µg.ml-1 of PHA (Sigma) for 3 days and then subsequently cultured with 100 UI.ml-1 IL-2 for 5 to 18 days. To obtain NK cells, PBMCs were stimulated with 2000 UI.ml-1 IL-2 for 7 days. Expanded NK cells were then purified by negative selection. T cells stained with Phycoerythrin (PE)-conjugated anti-CD3, anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 antibodies were removed from the culture by passing through magnetic columns coated with anti-PE antibodies (Mylteni Biotch.). Purified B cells, CD4+ cells, CD8+ cells and monocytes were obtained by positive selection from PBLs with (PE)conjugated anti-CD19, anti-CD4, anti-CD8 or anti-CD14 antibodies, respectively. Dendritic cells were obtained by stimulating CD14+ cells for six days with GM-CSF and IL-4 following standard procedures. The purity of the different cell populations obtained was > 95%. The MAB11 cell line is a PBL-derived NKT cell line22 (a gift of M. Bonneville, Nantes). The control and XIAP-deficient EBV-transformed B cell lines were obtained following standard protocols. Immunoblots. Cells lysates and immunoblots were performed as described. Anti-XIAP (clone 28), anti-cIAP-1 (B75-1) and anti-cIAP-2 (F30-2285) mAbs were from BD Biosciences and anti-Ku80 (KuAb-2) mAb from NeoMarkers. Rabbit polyclonal antibodies to the N-terminus portion of XIAP (H202) were from Santa Cruz Biotechnology Inc. Rabbit polyclonal antibodies to Fyn and SAP have been previously described23. Cytotoxicity assay. The cytolytic activity of NK cells was evaluated with a standard 4-h 51 Chromium release assay. The percentage of specific lysis was calculated according to the standard formula13. For redirected antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (RADCC), NK cells were incubated with 5µg.ml-1 of anti-2B4 (C1.7) or anti-CD16 (3G8) antibodies for 30 min at 4°C, washed and then incubated with L1210 FcR+ target cells at a ratio NK cells/target cells of 4/1. Apoptosis assay. PHA blasts were stimulated with 5 to 20 ng.ml-1 of anti-CD95 antibodies (APO-1.3) or 5 µg.ml-1 of killer TRAIL, a trimeric recombinant TRAIL (Alexis Biochemicals) for 24 h. Apoptotic cells were detected by propidium iodide staining as described. The percentage of induced apoptosis was calculated according to the formula20 : 100 x (% of experimental apoptotic cells-% of spontaneously apoptotic cells/100-% of spontaneously apoptotic cells). For activation-induced cell death (AICD), PHA blasts were stimulated with 10 µg.ml-1 of plate bound anti-CD3 (UCHT-1 or OKT-3) antibodies for 24 or 48 hours in the presence of 40 UI.ml-1 IL-2. AICD was blocked by adding 3 µg.ml-1 of blocking anti-CD95 (SM-1) and anti-FasL (AbC199) antibodies (AbCyst S.A.) during the assay. All assays were done in duplicate. Expression of CD95 on PHA blasts and EBVtransformed cell lines was controlled by flow cytomery and found to be similar on XIAPdeficient cells and normal control cells. Flow cytometry. NK and NKT cells were detected from isolated PBMCs using the following mAbs conjugated to FITC, PE and APC : anti-V11 TCR (C21) and anti-V24 TCR (C15) from Beckman Coulter and anti-CD3 (SK7), anti-CD56 (MY31) and anti-CD16 (3G8) from BD Biosciences. APC-conjugated GalCer-loaded CD1d tetramers were kindly provided Maria Leite-de-Moraes, Hôpital Necker-Enfants Malades, Paris. PBMCs were stained using standard procedures, and analyzed on a FACSCalibur cytometer with Cell Quest software (BD). With the exception of patient P1.3, all patients tested for NKT cells were moderately sick and had either no treatment (P2.1, P2.2 and P3.3) or maintenance corticosteroid therapy (P1.1 and P1.7) at the time of the analysis. Statistical analysis. The statistical analysis of results were performed with two-tailed Student’s t tests using the PRISM software (GraphPad Software Inc.) . Reconstitution assay. Lentiviral infections were done with a modified pTRIP plasmid (a gift of P. Charneau, Institut Pasteur, Paris) containing the 5’ HIV long terminal repeat (LTR), the human ubiquitin promoter, the human XIAP coding sequence, an internal ribosome entry site (IRES) and the GFP coding sequence (pTRIP-GFP-XIAP). Viral infectious supernatants were obtained from 293T cells transfected with the pTRIP-GFP-XIAP together with an encapsidation plasmid (p8.1) and a VSV envelope expression plasmid (pHCMV-G) as described21. PHA blasts or EBV-transformed B cells were infected with the viral supernatant by spinoculation three times. Infected cells were examined for GFP-positive cells four days after the last cycle of spinoculation by flow cytometry. RT-PCR. Total RNA of lymphocytes from two XIAP-deficient patients and two healthy control individuals was extracted using TRIzolTM reagent (Invitrogen Life Technologies) according to the manufacturer instructions. Reverse transcription was performed using a SuperScript First-Strand Synthesis Kit (Invitrogen Life Technologies) and cDNAs were used as templates to amplify by PCR, THOC2, XIAP, STAG2 and SAP genes with the following primers using standard protocols : THOC2-F: 5’ CAGCTGTGTATATTTCCTCG 3’ ; THOC2-R: 5’ TTACCAAGTACCCTGGCCTC 3’; XIAP-F: 5’ TGCAAATATCTGTTAGAAC 3’; XIAP-R 5’ GAGTTAGATTAAGACATAAA 3’; STAG2-F: 5’ ATGTGGCACTAAATCTTAGC TGCTAATAACTGAGGAAGGG 3’ ; CCGGAATTCCGCCACCATGGACGCAGTGGCTGTG CCGGTGAATTCCTCTTCATGGGGTTTCAGGCA TGAAGGTCGGAGTCAACGGATTTGGT 3’STAG2-R: 3’ SAP-F: 3’ 3’ ; ; ; 5’ 5’ SAP-R: 5’ G3PDH-F: 5’ G3PDH-R: 5’ CATGTGGGCCATGAGGTCCACCAC 3’. Products were resolved by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis and were detected by ethidium bromide staining. X chromosome inactivation. The inactivation of the X chromosome was determined by analyzing the methylation pattern of the human androgen-receptor gene as described24. Briefly, genomic DNA from cells were first digested with RsaI for three hours at 37°C and with or without HpaII for six hours at 37°C. Digested DNAs were then used as templates to amplify by PCR with specific radiolabelled oligonucleotides, the polymorphic CAG repeat contained in the human androgen-receptor gene. The PCR products were electrophoresed in 5% polyacrylamide urea-containing gel. Supplementary Notes References for the supplementary methods 22. Couedel, C. et al. Diverse CD1d-restricted reactivity patterns of human T cells bearing "invariant" AV24BV11 TCR. Eur J Immunol 28, 4391-7 (1998). 23. Latour, S. et al. Regulation of SLAM-mediated signal transduction by SAP, the X-linked lymphoproliferative gene product. Nat Immunol 2, 681-90 (2001). 24. Allen R.C., Zoghbi H.Y., Moseley A.B., Rosenblatt H.M., Belmont J.W. Methylation of HpaII and HhaI sites near the polymorphic CAG repeat in the human androgen-receptor gene correlates with X chromosome inactivation. Am J Hum Genet 51, 1229–1239 (1992). Values of means s.d. of Figures 2 and 3 Figure 2b. NKT cells per million of CD3+ cells; values of means s.d.: Ctr, 987576.5 ; SAP, 4119.5 ; XIAP, 11353 ; SIM, 846235.6. Figure 3a. % of induced apoptosis by anti-CD95 antibodies stimulation; values of means s.d.: 5 (ng/ml): XIAP, 23.856.6 and Ctr., 17.16.7 ; 10 (ng/ml): XIAP, 6010.45 and Ctr., 44.611.2 ; 15 (ng/ml): XIAP, 7111.6 and Ctr., 54.712.3 ; 20(ng/ml): XIAP, 82.810.2 and Ctr., 65.211 ; 100 (ng/ml): XIAP, 92.56.4 and Ctr., 79.38.6 Figure 3b. % of induced apoptosis by AICD; values of means s.d. : XIAP, 51.817.05 and Ctr., 10.77.3 Figure 3c. % of induced apoptosis by TRAIL; values of means s.d.: XIAP, 15.72.8 and Ctr., 2.72.6.