generation of a laser-plasma ion flow in a microwave cavity
advertisement

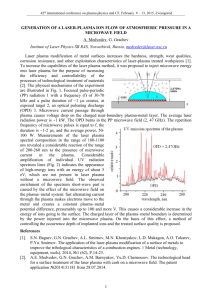
40th international conference on plasma physics and CF, February 11 – 15, 2013, Zvenigorod. GENERATION OF A LASER-PLASMA ION FLOW IN A MICROWAVE CAVITY A. Medvedev, G. Grachev Institute of Laser Physics SB RAS, Novosibirsk, Russia, medvedev@laser.nsc.ru The possibility of obtaining an additional flow of laser plasma ions to the near-boundary surface is being experimentally investigated by passing microwave-range electric current through the plasma. Electric current leads to redistribution of the space charge and formation of near-electrode zones, with voltage drop much greater than the plasma temperature. Therefore, one should expect (as in the gas discharge) that the energy of ions going to the surface will be the same as the near-electrode voltage drop. However, in the case of gas discharge plasma as the external source frequency increases, the energy of ions going to the surface decreases, so that in the microwave frequency range the effect of plasma-surface interaction is not observed. With increasing frequency the oscillation amplitude of electrons also decreases, and in the microwave range it becomes smaller than the Debye length. The situation is different in dense laser plasma (1015-1017cm-3) for an area of several GHz. The electrons passing through the screening layer manage to leave the bulk, charging the plasma and increasing the positive space charge layer that forms an ion flow to the surface. Nevertheless, such investigations have not been performed yet. To inject microwave energy into the plasma we use a toroidal cavity resonator in which laser plasma is initiated in the area of toroidal resonator capacitor. A 2.47 GHz magnetron, which is switched on synchronously with the plasma-initiating laser pulse, is used to create microwave oscillations. Control of the magnetron power supply makes it possible to regulate the delay (with respect to the laser pulse leading edge beginning with 0.1 s) and duration (from 0.5 s and higher) of microwave pulses. The operation frequency of the pulse-periodic laser-plasma setup [1] is in the range from 1 to 100 kHz. The microwave generator has a pulsed power of 5 kW, and a mean power of 1.5 kW. A circulator (0.3/26 dB) is used for stable operation of the magnetron with respect to the reflected wave in the microwave channel. The passed and reflected waves, as well as the field in the cavity, are recorded in the experiment. The created near-surface electric field is estimated using measurements of the Stark broadening of ion lines. In addition, the estimated "technological effect" of the laser-plasma system from the influence of the imposed additional microwave field and enhancing the technological capabilities of laser-plasma method [2] modification of the metal surface. References [1] [2] G. Grachev, А. Myakushina, А. Smirnov, P. Statsenko. Multikiloherz CO2 laser generatoramplifier system with high beam quality and average power of up to 2,5 kW. ICONO/LAT 2010. Kazan, Russia, August 23-27, 2010, Lth09. S.N. Bagayev, G.N. Grachev, А.G. Ponomarenko, А.L. Smirnov, V.N. Demin, A.V. Okotrub, А.M. Baklanov, А.А. Onischuk. A new method of laser-plasma synthesis of nanomaterials. First results and prospects. Proc. SPIE, 2007, 6732-673206. 1