e-Prescribing Overview
advertisement

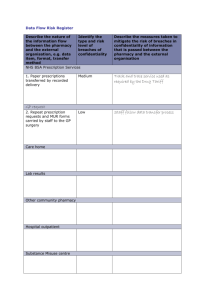
e-Prescribing Overview The current process today begins with a physician generating a handwritten prescription that the patient delivers to a pharmacy. The pharmacy interprets the hand written information and enters the data into a computer system that connects with the pharmacy benefit management (PBM) program that is used by the patient’s insurer. The PBM checks the prescription (electronically) for its compliance to a pharmacy program, possible drug interactions based on the patient’s medication history, and any other utilization criteria. If there is an issue on any element, a message is sent back to the pharmacist, who then may need to intervene. Many times this requires a call back to the physician to change the prescription to another medication. The pharmacist who is not the prescriber is connected to key pieces of information but the physician is not. E-Prescribing attempts to bridge this information gap by providing physicians with information at the point of decision making and there by eliminating administrative and operational costs as well as reducing the potential for medication errors. The case for e-Prescribing : Prescription writing process today is a disconnected and manual process that presents several opportunity for errors. Medication errors cause an estimated 770,000 injuries or deaths each year in hospitals. (Source: 1999 IOM Report, To Err is Human) o Cost approximately $5.6 million each year per hospital, depending on size. (Source: Reducing and Preventing Adverse Drug Events To Decrease Hospital Costs. Research in Action, Issue 1. AHRQ Publication Number 01-0020, March 2001. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.) o Contribute to approximately 7,000 deaths a year, with an estimated cost for drug-related morbidity and mortality exceeding $77 billion a year. (Source: Reducing and Preventing Adverse Drug Events To Decrease Hospital Costs. Research in Action, Issue 1. AHRQ Publication Number 01-0020, March 2001. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, Rockville, MD.) Specifically, what is the value of e-Prescribing to the physician? It has the ability to issue prompts that warn against the possibility of drug interaction, allergy or overdose. It provides accurate, current information that helps physicians keep up with new drugs as they are introduced into the market, provides drug-specific information that eliminates confusion among drug names that sound alike, improves communication between physicians and pharmacists and reduces health care costs due to improved efficiencies. It can also make the physician’s office more efficient by decreasing prescription related calls and provides a legible and clean prescription to the pharmacy. What specifically will the e-Prescribing application do? e-Prescribing enables a physician at the point of writing a prescription to have access to a relevant list of medications and formulary based on that patient’s drug benefit. The application also performs eligibility verification and a drug utilization assessment to check for drug interactions or contra-indications based on the patient’s medication history. The physician may also be able to receive that patient’s full medication history. Application can be integrated with the physician’s office management system. The application can reside on a desktop, laptop, tablet or PDA. e-Prescribing Process Flow & Conceptual Data Flow Pharmacy Claims to PBM for Payment 6 E-RX Vendor Pharmacy (retail or mail) requests submitted by vendor 4 d an ry on o t i t is n H rma atio y Info c i r d Me mula r ist Fo tL en i t Pa Physician Practice Management System Eligibility, Formulary Medication 3 &History based on Electronically Submitted Scripts (EDI or Fax) 5 PBM Printed Prescription 2 1 Eligibility Requests based on patient lists from Physicians Data being transferred: • First Name • Last Name • Date of Birth • Member ID • Member Plan Information e-Prescribing Process Flow & Conceptual Data Flow Diagram Process Description: 1. The physician’s patient list or patient schedule (for next day) is provided to the selected e-Prescribing vendor to be used for verification of eligibility, formulary and drug history. This patient data is stored at the ISV’s secure data center for use during the execution of an electronic prescription. 2. The vendor uses the data provided by the physician to request the eligibility, formulary and drug history for a patient from the patient’s payer or Pharmacy Benefit Manager. 3. The PBM checks for a matching member in their system and provides the appropriate data back to the e-Prescribing vendor for use during the patients visit. 4. The physician now has all of the information needed to confidently write a prescription at the point of care utilizing the e-Prescribing package that connects real time to the vendors secure data centre. 5. The prescription is sent via Fax or EDI to the appropriate pharmacy where it is filled and ready to be picked up by the patient. The physician also has the option to print the prescription in the office for the patient to take to the pharmacy of their choice. 6. Once the prescription is filled, the pharmacy submits a claim to the PBM for payment. This claim will then be part of the drug history provided to the physician the next time the patient is seen.