Focusing teaching and learning information literacy support
advertisement

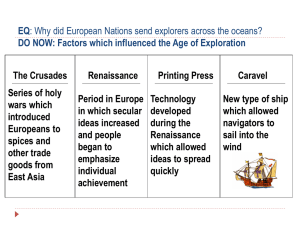
Cross curriculum: Programming ideas for COGs (G): Our fleeting past Sample programming proforma Stage 2: see also matrix for this component. Focusing teaching and learning information literacy support: programming ideas: defining Topic/Unit support: Our fleeting past: Connected Outcomes Group (G): exploring the impact of British colonisation and how it has shaped Australia. Specific focus: How would we find out about early sea explorers to Australia? What was their impact? Quality Teaching elements: Intellectual quality The task requires sustained focus on key concepts & ideas, & requires clear articulation of the relationships between & among concepts. Quality learning environment Students determine many significant aspects of the task either independently or with teacher approval. Significance Students’ background knowledge is substantially incorporated into the task, & meaningful connection to outof-school knowledge is integral to the task. Resources Australian history: European exploration, www.australianhistory.org/exploration.php Captain Cook – Cook claims New South Wales, dl.nfsa.gov.au/module/1319/ [3min 4 sec] Captain Cook – Great southern continent, dl.nfsa.gov.au/module/1320/ [1min 46sec] Captain Cook – Obsession and discovery, www.abc.net.au/tv/captaincook/# Early explorers of Australia, www.abc.net.au/navigators/history/earlyexplore.htm Endeavour journal, www.nationaltreasures.com.au/treasures/endeavorj/ [5min 0sec]) Exploration timeline - Australian land and sea explorers (1606-1770), gutenberg.net.au/explorers.html#exploretimeline The Perth Mint: Great maritime explorers of Australia, www.perthmint.com.au/catalogue/great-maritimeexplorers-of-australia.aspx SMART Notebook: Our fleeting past Who was Captain Cook? www.captcook-ne.co.uk/ccne/who.htm [3min 0sec] See also COGs resource lists. Pre-unit assessment to gauge current level of understanding (in terms of unit/topic/focus) eg pre-test, teacher judgment, brainstorm, discussion questions prior to unit study Through class discussion, gauge what students know about early Australia and its European exploration/ discovery, and how they might find out about them. Brainstorm & concept map: Who are the early explorers who came to Australia by sea? Early explorers of Australia, (model Captain Cook) What stories have you heard? Where did they come from? (model Captain Cook) Why did they come? (model Captain Cook) How would we find out about these early explorers? What do we need to find out about these explorers? (proforma headings) What information sources might be best? (generic) Evidence based practice: To support evidence based practice, gather student work samples at the beginning of a unit. Later, gather work samples which show the progress made by students through explicit teaching and scaffolding. Provide feedback on specific learning. Syllabus outcomes Suggested teaching and learning activities/strategies HSIE: CCS2.1 Describes events and actions related to British colonisation of Australia and assesses changes and consequences researches world explorers and the discoveries they made reviews information and reflects on the importance of these discoveries for Australia. explicit; include some planned assessment) for defining English: RS2.5 Reads independently a wide range of texts on increasingly challenging topics and justifies own (be phase of ISP Assumed knowledge e.g. Introduction from Stage 1 COGs (G) Brainstorm & concept map: Who are the early explorers who came to Australia by sea? What stories …? Where did they come from? How would we find out about these early explorers? What do we need to find out about these explorers? (proforma headings) What information sources might be best? (generic) Teacher provides timeline list of sea explorers (1660-1770) to Australia. © 2010 NSW Department of Education and Training. School Libraries and Information Literacy Unit. Curriculum K–12 Directorate. Thanks to C. Foley, C. Keane, G. Maugle & J. Reynolds Cross curriculum: Programming ideas for COGs (G): Our fleeting past interpretation of ideas, information and events. RS2.6 Uses efficiently an integrated range of skills and strategies when reading and interpreting written texts. Related computer competencies focus: Students discriminate in the choice of applications for a given purpose understand basic terminology of data base-fields, records, files. Related information skills focus area: define By the end of this unit students will be able to suggest possible search words appropriate for a given topic understand concept map/flow chart and plan some headings for information gathering. Literature links Plowman, S. & Pinkney, M. (2001) Bryce Courtenay introduces the Australian history collection SCIS 1040266 Boardman, A. (1997) First Fleet SCIS 896862 Clark, A. (2005) Convicted SCIS 1237052 Teacher may share these resources to provide background information for students Australian history: European exploration Endeavour journal video (5min 0sec). The cartoon shown towards the end of the clip summarises Cook’s voyage. Captain Cook – Great southern continent video (1min 46sec] for 18th century sea exploration. Planned assessment Observation of how well students understand the task as evidenced by Background knowledge o why do people explore? o do we know of the names of some early European explorers? What kind of information they would like to find? o what places did the explorers come from? o how did they travel? o what difficulties did they encounter? o why did they come here? o where can we find some information? o how will we record it? Listing of more than one source that may be appropriate for this task. o books o internet o charts o atlas Teachers could model the creation of a wordle so that students can create their own word cloud to show key ideas and knowledge about the task as a pre unit assessment task, e.g. These instructions may be used to guide students. The wordle task could be repeated at the end of the unit to check student knowledge and understanding. Post unit assessment to determine progress towards stated outcomes e.g. post-test, guided evaluation sheet, skills achieved in context of outcomes (indicators) and planned assessment Assessment for learning: Teacher notes students’ ability to ask questions to clarify the task, suggest possible search words for the topic and plan some headings for information gathering, and explain the task. Can the students create a word cloud to show key ideas and knowledge about the task? Teacher identifies and assists students needing guidance to understand and verbalise the task. © 2010 NSW Department of Education and Training. School Libraries and Information Literacy Unit. Curriculum K–12 Directorate. Thanks to C. Foley, C. Keane, G. Maugle & J. Reynolds