Write the answers on your notebook paper. Use the poem from your
advertisement

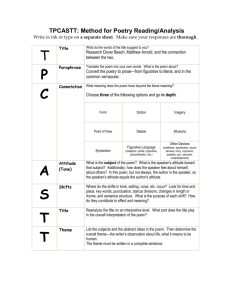
Write the answers on your notebook paper. Use the poem from your text HS English I Unit: 3 Lesson: 2 © 2008, TESCCC 09/20/08 page 11 of 12 “I Wandered Lonely as a Cloud”–Questions 1. What is the rhyme scheme of this poem? 2. How does the rhyme scheme help to set off the final two lines of each stanza? 3. How does setting off the final two lines of each stanza reinforce the meaning? 4. What kind of figure of speech is used in the first line? 5. What does the speaker suggest by comparing himself to a cloud? 6. To what are the daffodils compared in Stanza 2, and what does the comparison suggest about the daffodils? 7. What are possible connotations of the word “host” in line 4? 8. What are possible connotations of the word “wealth” in line 18? 9. What is the tone of the poem? 10. What is the mood of the poem? 11. What is the theme of the poem? 12. Find examples of the figurative language used in this poem. This is a chart that helps you analyze a poem. KNOW these terms and memorize the concepts presented in this chart. HS English I Unit: 3 Lesson: 2 © 2008, TESCCC 09/20/08 page 8 of 12 Using TPCASTT to Analyze Poetry T Title What denotations (dictionary meanings) are presented in the title? What connotations (emotions or reactions) do the words have? P Paraphrase Translate the poem into your own words. What is the poem about? C Connotation What meaning does the poem have beyond the literal meaning? Use the chart below. Form (the way the poem is laid out on the page, its rhyme scheme) Diction (word choice) Imagery (when an author uses words to paint a picture in your mind) Point of View (from whose perspective it’s told) Details Allusions (indirect references to history, current events, other literary works/media) Symbolism (when an author uses symbols: objects literally there in the poem/story, but which also have deeper symbolic meanings) Figurative Language (metaphors: comparing different things without using like, as, or than; similes: comparing different things using like, as, or than; hyperbole/exaggeration) Other Devices (sound devices, irony, oxymoron, paradox, pun, sarcasm, understatement) A Attitude What is the speaker’s attitude? How does the speaker feel about him or herself, about others, and about the subject? What is the author’s attitude? How does the author feel about the speaker, about other characters, about the subject, and the reader? S Shifts Where do the shifts in tone, setting, voice, etc. occur? Look for time and place, keywords, punctuation, stanza divisions, changes in length or rhyme, and sentence structure. What is the purpose of each shift? How do they contribute to effect and meaning? T Title Reanalyze the title on an interpretive level. What part does the title play in the overall interpretation of the poem? T Theme List the subjects and the abstract ideas in the poem. Then determine the overall theme: the author’s main idea or point, the ‘message’ or ‘moral of the story.’ Write the theme as a complete sentence. When you get back to class, ask for the chart that we use for all of the concepts above. It is a chart that helps students analyze poetry.