Monster Central Dogma - Lincoln Park High School
advertisement

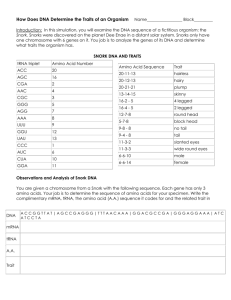
Name:_______________________________________________________________ Date ___________ Period ____ Monster Central Dogma We looked at genetic crosses in our monsters in genetics. In this activity, you will use amino acid sequences for the traits described below, and then see if your classmates can take your DNA through Central Dogma to make a monster with the same traits. PART 1 1. In the MY MONSTER’S GENOME table below, fill in the “Your Monster’s Trait” column for each trait. 2. For each trait, look up the amino acid sequence in the AMINO ACID KEY and fill in the “Polypeptide Amino Acid Sequence” column in the table. 3. Determine which mRNA codons correspond to each amino acid sequence using the GENETIC CODE CHART to fill in the “Your Monster’s mRNA” column. o Ex: Amino Acid Sequence Met-Tyr-Pro-STOP = mRNA sequence AUG-UAU-CCG-UGA. 4. Use the rules of complementary base-pairing to determine the original DNA (gene) sequence based on the mRNA codons to fill in the “Your Monster’s DNA” column. o Ex: mRNA sequence AUG-UAU-CCG-UGA = DNA sequence TAC-ATA-GGC-ACT 5. Draw your monster with the correct traits in the space to the right or on a separate sheet. MY MONSTER’S GENOME Your Monster’s Trait Trait Polypeptide Amino Acid Sequence Your Monster’s mRNA codons Your Monster’s DNA codons # of Eyes (1, 2, or 3) Fur / Scales / Fur & Scales Fangs / No Fangs Wing Size (large or small) Straight Horns / Curly Horns PART 2 1. For each trait you picked above, list the DNA sequence in the correct gene box in the MY MONSTER’S DNA SEQUENCE on the other page. 2. Exchange this with a classmate, and write his/her name below. Then follow the directions on the other page. o I am exchanging monster’s with:_________________________________________ RUBRIC Score Monster’s Genome Partner Central Dogma 6 The Monster’s genome correctly reflects the chosen traits at the Amino Acid, mRNA, and DNA level Based on the DNA sequence you provided, your partner was able to correctly decode the DNA to determine your monster’s traits Your Drawing Your drawing correctly reflects the traits you chose Your Partner’s Drawing of your Monster Your partner’s drawing of your monster has the exact same traits that you chose for your monster 4 The Monster’s genome correctly reflects the chosen traits at most levels, but there are mistakes in 1-2 genes Based on the DNA sequence you provided, your partner was able to take the DNA through Central Dogma with 12 mistakes Your drawing has 1 trait incorrect based upon the traits you chose Your partner’s drawing of your monster has the similar traits that you chose for your monster with 1-2 mistakes 2 The Monster’s genome correctly reflects the chosen traits, but there are mistakes in 3-4 genes Based on the DNA sequence you provided, your partner was able to take the DNA through Central Dogma with 34 mistakes Your drawing has 2 traits incorrect based upon the traits you chose Your partner’s drawing of your monster has the similar traits that you chose for your monster with 3-4 mistakes 0 The Monster’s genome has mistakes at some level in 5 or more of the genes Based on the DNA sequence you provided, your partner was able to take the DNA through Central Dogma with 56 mistakes Your drawing has 3 or more traits incorrect based upon the traits you chose Your partner’s drawing of your monster has the similar traits that you chose for your monster with 5-6 mistakes Total PART 3: POST-ACTIVITY QUESTIONS 1. Explain how this activity was Central Dogma in reverse. (1) 2. To which categories of organic macromolecules does DNA belong? _____________________________ (1) 3. To which categories of organic macromolecules does RNA belong? _____________________________ (1) 4. To which categories of organic macromolecules does a polypeptide belong? __________________________ (1) 5. Suggest a substitution mutation in the DNA that would cause the first amino acid in the “# of Eyes” gene to change from alanine (Ala) to valine (Val). Write the original DNA codon, then the mutated DNA codon. (1) 6. There is a substitution mutation in the gene for Fangs in which the first DNA base changes from guanine to thymine. How does this affect the polypeptide amino acid sequence? (1) 7. Explain why you and another student could have chosen the same traits with the same amino acid sequences but arrived at different DNA sequences during Part 1. (1) TOTAL SCORE: _______ / 31 PART 3: EXCHANGING MONSTERS 1. Based upon the DNA sequence you have been provided, make a complimentary mRNA strand in the appropriate boxes. 2. Using the Amino Acid chart below, make the amino acid sequence that goes with your RNA codon sequence 3. Using the AMINO ACID KEY provided below, list the traits your partner’s monster has. 4. Draw a monster that shows these traits in the space at the bottom of the page. AMINO ACID KEY Trait 3 eyes 2 eyes 1 eye Fur Scales Fur and Scales Fangs No Fangs Big Wings Small Wings Straight Horns Straight/Curly (1 loop) Curly Horns (3 loops) GENETIC CODE CHART (bases are in mRNA) Amino Acid Sequence Ala-Asp-Phe-Leu-Tyr-STOP Ala-Asp-Arg-Leu-Tyr-STOP Ala-Asp-Lys-Leu-Tyr-STOP Pro-Thr-His-Ser-STOP Pro-Thr-His-Val-STOP Pro-Thr-His-Phe-STOP Pro-Ser-Met-Leu-Arg-Gly-STOP Pro-Ser-Val-Leu-Arg-Gly-STOP Thr-His-Ser-Ala-Asp -STOP Thr-Cys-Ser- Ala-Asp -STOP Arg-Tyr-Leu-Ser-Gly-STOP His-Tyr-Leu-Ser-Gly -STOP His-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Ser-Gly -STOP MY MONSTER’S DNA SEQUENCE Gene Eye # Fur/Scales DNA mRNA Amino Acids Traits Teeth Wings Horns