Goal 3 - To Use Quadratic Functions and Equations
advertisement

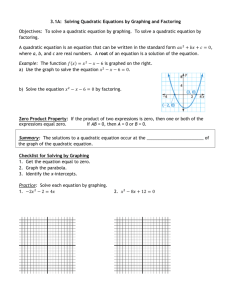
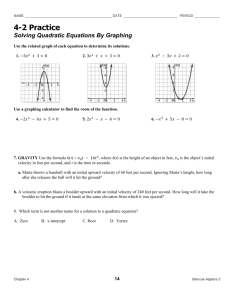
Algebra 2 Goal III: To Use Quadratic Functions, Equations and Inequalities Learning Outcomes Differentiated Instructional Activities 3.1 Graph quadratic functions: Use the Developing Concepts Activity to introduce Lesson 5.3. An alternative way to approach Lesson 5.3 is to use the Graphing Calculator Lesson Opener. Have students copy the characteristics of the graph of a quadratic function, and the vertex and intercept forms and characteristics of the graph the of a quadratic function on 3X5 index cards. Continue vocabulary file or algebra glossary. Make sure that English learners understand parabolas. Students need to understand that only parabolas that open up or down are functions. Writing Activity: Have students explain how to draw the graph of a quadratic equation that is given in intercept form. Use the cooperative learning activity and /or graphing calculator activity. Vertex form Intercept form Standard form Text Book References* Developing Concepts: p. 249 Chapter Resource Book References Warm-Up Exercises: p. 11 Assessments# Examples: 1-6, pp. 250-252 Lesson Opener (Graphing Calculator): p. 12 Guided Practice: p. 253, #’s 1-16 Practice A, B, & C: pp. 15-17 HQ: p. 33^ Practice: pp. 253-255, #’s 17-78 (See Assignment Guide, p. 253) Reteaching with Practice: pp. 18-19 Quiz 1: p. 270, #’s 1-3 RS: Quiz 1: p. 50, #’s 1-2^ WT: p. 31^ Prerequisite Skills Review WT: p. 32^ Checkpoint Exercises: pp. 250-252 Cooperative Learning Activity: p. 21 Real Life Application: p. 22 Challenge: p. 23 Chapter Reference 5.1 * ^ # Graphing Calculator Activity: pp. 13-14 The examples noted are for reference only. Teacher has the decision to assign number of examples to meet the needs of the different abilities of students in the class. These references can be found in the Warm-up Transparencies (WT) and Daily Homework Quiz (HQ) booklet or appropriate Chapter Resource (RS) booklet. End of Chapter Assessments as well as periodic quizzes are to be determined by the teacher. 0 Learning Outcomes Differentiated Instructional Activities Text Book References* Chapter Resource Book References Assessments# 3.2 Solve quadratic equations by factoring: An alternative way to approach Lesson 5.2 is to use the Visual Approach Lesson Opener. Have students copy the special factoring patterns, and the zero product property on 3X5 index cards. Continue vocabulary file or algebra glossary. Help English learners distinguish among monomial, binomial, and trinomial. Provide examples such as monorail, bicycle, and tricycle. Ask students what must be true about a quadratic equation before you can solve it using the zero product property. Give students much practice with factoring trinomials. To avoid errors, have students multiply the factors to make sure the product is the original expression. Writing Activity: Have students name, give an example, and describe how to factor the three special factoring patterns Use the Developing Concepts Activity to introduce Lesson 5.3. An alternative way to approach Lesson 5.3 is to use the Application Lesson Opener. Have students copy the properties of square roots on a 3X5 index card. Continue vocabulary file or algebra glossary. Writing Activity: Have students write a quadratic equation that they would solve by finding square roots and show how to solve it. Then have them explain why they would chose to solve this equation using square roots rather than factoring. Have students do the Using Technology Activity that uses a graphing calculator to solve quadratic equations having real number solutions and/or the graphing calculator activity. Examples: 1-8, pp. 256-259 Warm-Up Exercises: p. 26 WT: p. 33^ Lesson Opener (Visual Approach): p. 27 Checkpoint Exercises: pp. 257-259 Special patterns Find zeros of quadratic functions Chapter Reference 5.2 3.3 Solve quadratic equations by finding square roots Chapter Reference 5.3 * ^ # Guided Practice: p. 260, #’s 1-22 Practice: pp. 260-263, #’s 23-136 (See Assignment Guide, p. 260) Practice A, B, & C: pp. 28-30 Reteaching with Practice: pp. 31-32 HQ: p. 34^ Quiz 1: p. 270, #’s 4-6 RS: Quiz 1: p. 50, #’s 3-4^ Interdisciplinary Application: p. 34 Challenge: p. 35 Developing Concepts: p. 264 Examples: 1-4, pp. 264-266 Warm-Up Exercises: p. 38 WT: p. 34^ Lesson Opener (Application): p. 39 Checkpoint Exercises: pp. 265-266 Practice A, B, & C: pp. 41-43 Guided Practice: p. 267, #’s 1-18 Practice: pp. 267-269, #’s 19-91 (See Assignment Guide, p. 267) Using Technology: p. 271 Reteaching with Practice: pp. 44-45 HQ: p. 35^ Quiz 1: p. 270, #’s 7-11 RS: Quiz 1: p. 50, #’s 5-7^ Real Life & Math and History Applications: pp. 47-48 Challenge: p. 49 Graphing Calculator Activity: p. 40 The examples noted are for reference only. Teacher has the decision to assign number of examples to meet the needs of the different abilities of students in the class. These references can be found in the Warm-up Transparencies (WT) and Daily Homework Quiz (HQ) booklet or appropriate Chapter Resource (RS) booklet. End of Chapter Assessments as well as periodic quizzes are to be determined by the teacher. 1 Learning Outcomes Differentiated Instructional Activities Text Book References* Chapter Resource Book References Assessments# 3.4 Solve quadratic equations with complex numbers: An alternative way to approach Lesson 5.4 is to use the Activity Lesson Opener. Have students copy the property of the square root of a negative number, the definition of the absolute value of a complex number, and how to determine whether complex numbers belong to the Mandelbrot set on 3X5 index cards. Continue vocabulary file or algebra glossary. Ask students to describe the procedure for each of the four basic operations on complex numbers. Writing Activity: Have students explain, in one or two paragraphs, complex numbers, imaginary numbers and pure imaginary numbers, and their relationships to each other and to real numbers. Use the Developing Concepts Activity to introduce Lesson 5.5. An alternative way to approach Lesson 5.5 is to use the Application Lesson Opener. Continue vocabulary file or algebra glossary. Have students give an example of a quadratic equation that can be solved using completing the square with the coefficient of x2 being 1 and an example whose coefficient of x2 is not 1; and then show how the method is used in each problem. Have students do the Using Technology Activity that uses a graphing calculator to find maximum and minimum values of quadratic functions. Examples: 1-7, pp. 272-276 Warm-Up Exercises: p. 53 WT: p. 35^ Lesson Opener (Activity): p. 54 Checkpoint Exercises: pp. 273-276 Practice A, B, & C: pp. 55-57 HQ: p. 36^ Reteaching with Practice: pp. 58-59 Quiz 2: p. 298, #’s 1-10 RS: Quiz 2: p. 91, #’s 1-4^ Perform operations with complex numbers Find the absolute value of complex numbers Chapter Reference 5.4 3.5 Solve quadratic equations by completing the square: Write quadratic functions in vertex form. Practice: pp. 277-280, #’s 17-114 (See Assignment Guide, p. 277) Interdisciplinary Application: p. 61 Challenge: p. 62 Developing Concepts: p. 281 (See p. 66 in RS) Examples: 1-7, pp. 282-285 Guided Practice: p. 286, #’s 1-22 Practice: pp. 286-289, #’s 23-118 (See Assignment Guide, p. 286) Using Technology: p. 290 Chapter Reference 5.5 * ^ # Guided Practice: p. 277, #’s 1-16 Warm-Up Exercises: p. 65 WT: p. 36^ Lesson Opener (Application): p. 67 Checkpoint Exercises: pp. 283-285 Practice A, B, & C: pp. 69-71 HQ: p. 37^ Reteaching with Practice: pp. 72-73 Quiz 2: p. 298, #’s 11-17 RS: Quiz 2: p. 91, #’s 5-6^ Real Life Application: p. 75 Challenge: p. 76 Graphing Calculator Activity: p. 68 The examples noted are for reference only. Teacher has the decision to assign number of examples to meet the needs of the different abilities of students in the class. These references can be found in the Warm-up Transparencies (WT) and Daily Homework Quiz (HQ) booklet or appropriate Chapter Resource (RS) booklet. End of Chapter Assessments as well as periodic quizzes are to be determined by the teacher. 2 Learning Outcomes Differentiated Instructional Activities 3.6 Solve quadratic equations using the quadratic formula. An alternative way to approach Lesson 5.6 is to use the Visual Approach Lesson Opener. Have students copy the quadratic formula, and the number and type of solutions of a quadratic equation on 3X5 index cards. Continue vocabulary file or algebra glossary. Remind students that they can solve quadratic equations using factoring or by completing the square, however; factoring cannot be used for every quadratic equation while completing the square can be a complicated procedure. Writing Activity: Have students explain the relationship between the discriminant of a quadratic equation, the number and type of solutions of the quadratic equation, and the x-intercepts of its corresponding graph. Have students do the graphing calculator activity. Chapter Resource Book References Assessments# Warm-Up Exercises: p. 79 WT: p. 37^ Guided Practice: p. 295, #’s 1-16 Lesson Opener (Visual Approach): p. 80 Practice: pp. 295-298, #’s 17-102 (See Assignment Guide, p. 295) Practice A, B, & C: pp. 83-85 Checkpoint Exercises: pp. 292-294 HQ: p. 38^ Quiz 2: p. 298, #’s 18-22 RS: Quiz 2: p. 91, #’s 7-8^ Reteaching with Practice: pp. 86-87 Interdisciplinary Application: p. 89 Challenge: p. 90 Graphing Calculator Activity: p. 81-82 Chapter Reference 5.6 * ^ # Text Book References* Examples: 1-5, pp. 291-294 The examples noted are for reference only. Teacher has the decision to assign number of examples to meet the needs of the different abilities of students in the class. These references can be found in the Warm-up Transparencies (WT) and Daily Homework Quiz (HQ) booklet or appropriate Chapter Resource (RS) booklet. End of Chapter Assessments as well as periodic quizzes are to be determined by the teacher. 3