FEUDAL JAPAN
advertisement

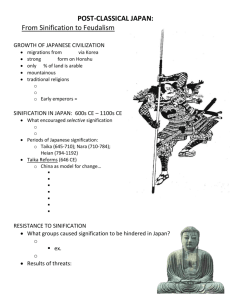
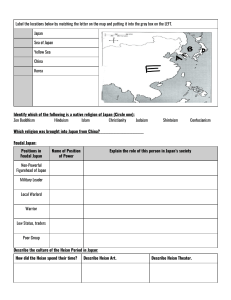
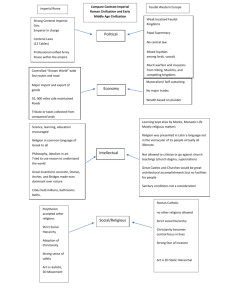
FEUDAL JAPAN EARLY HISTORY Migrants from via Strong clans on Honshu Religion: o – kami o Shintoism – “way of the kami” o Early emperors = ERAS OF POST-CLASSICAL JAPAN Taika (645-710 CE) o Nara (710-784 CE) o Heian (794-1192 CE) o o Sinification rejected o Begin SINIFICATION IN JAPAN ( CE) o China as a model for change… Strong (kanji characters) RESISTANCE TO SINIFICATION What groups caused signification to be hindered in China? o o Results:: o Taika reforms o Capital moved from Nara to ( ) o Aristocrats strong again o Emperor’s power o Aristocrats gained power in o Rural leaders established COURTLY LIFE OF THE HEIAN Elaborate, highly-refined etiquette Personal diaries o by (10th C) Great novel o by Description of superficial life inside Some Chinese artistic styles continued o Writing , Buddhism ( ) BREAKDOWN OF CENTRAL POWER Emperors without true power again until influence over imperial court gains: o : Policy makers, administrators, marriages Banditry & crime grows Local powers dominant in rural provinces: o Deny to imperial court o o = warrior elite personal armies of : loyal to protect & capital duels of champions samurai code of honor: . : ritual suicide o honorable to die in this way. Prove Protect family’s JAPAN’S FEUDAL ERA: 800-1500 CE Families competed for imperial control o (1180-1185 CE) vs. Hardships to peasants & o Minamoto established military gov’t = _____________ led by established = ruling from Heian Emperor & court preserved Feudalism on the rise o Ashikaga Age: 1338-1573 CE Minamoto overthrown by Ashikaga created o Civil war over claims of new shogunate destroyed dismantled kingdoms ruled by warlords ( Samura loyal to rival daimyo & countryside Feudalism becomes order of the day ) FEUDAL STRUCTURE in JAPAN: _________ Land - Shoen Land - Shoen Protection Loyalty Loyalty Food