Japan
advertisement

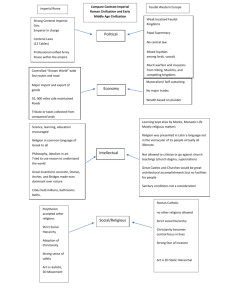
Japan Japan: Timeline Imperial Age & Chinese influence 604-784 Taika Reforms (645) Nara (710-784) Heian (794-1185) Adaptation of Chinese forms & “ultra-civilized” Age of Feudal Warlords 1185-1600 Fun Factoid Japan has “always” had an emperor Japan has only had one dynasty (all members of Yamato clan) Why? Japan’s Origins in the Classical Period Decentralized Japan (-604) Shinto, but growing Buddhist influence Large provincial estates with aristocratic governors ruling with power derived from emperor Japan’s Imperial Age (604-784) The Imperial Age Efforts at Centralization (604-784) → Taika Reforms (646) Focused on creating absolute-powered emperor with Chinese style bureaucracy Referred to emperor at “Son of Heaven” Professional bureaucracy Peasant conscript army The Imperial Age Nara (710-784) “Nara” derived from Japan’s 1st capital city Intense direct borrowing from China, but increasing power of Buddhism The Imperial Age Why might some historians refer to the late Imperial Age as the “crisis at Nara”? What was the response to the crisis? Heian Period (794-1185) Early Heian (794-857) Move capital to Kyoto Borrowing from China declines as adaptation begins Aristocratic families re-exert influence Court life Remote from common life Ultra-civilized – superficial focus on beauty & social interactions Early Heian (794-857) What is “court life”? Why is the court life during Heian period called “ultracivilized”? Late Heian (857-1185) Sign of failed centralization Reign of emperor continues, but Real power rests with most powerful aristocratic family Fujiwara Taira Minamoto Feudal Age (1185-1600) • Most power rests with regional lords Era characterized by civil war Bakufu / Shogunate (1185-1600) Attempt at formalizing rule of aristocratic house Create military dictatorship with blessing of emperor Shogun Gov’t sometimes called a Bakufu (military government) or Shogunate Feudal Age (1185-1600) Attempt at centralization fails, but heritage of political model established Emperor still in place (figure head) Shogun in place (increasingly ignored and treated as figurehead) Aristocratic families still reign supreme Daimyo / Bushi Impact of Feudal Warfare Regional lords (daimyo) invest in villages on manor Irrigation, tax collection, encourage handicraft production Economic boom during feudal age & civil war