week 3 (weather)
advertisement

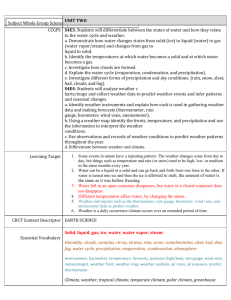
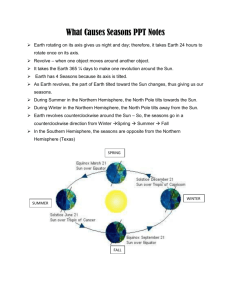
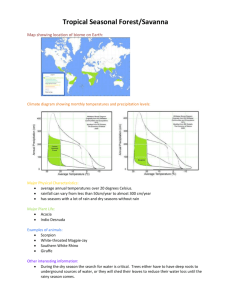
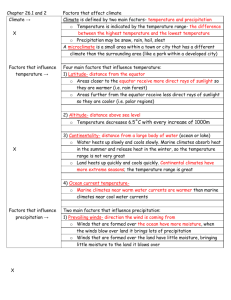
Atmosphere The atmosphere is the air around and above us. It is a mixture of gases (78% Nitrogen, 21% Oxygen, 1% other gases including carbon dioxide, water vapor, helium, methane, hydrogen, and ozone) Earth’s atmosphere has five layers with different properties (students do not need to know the different layers or properties of each) All weather takes place in the lowest layer (the troposphere). Weather is the condition of the atmosphere in a certain place at a certain time. Questions: What is the atmosphere made out of? How much of the atmosphere is composed of nitrogen? Barometer/Air Pressure Air pressure is the weight of air pressing on everything around it. Air presses can change over time due to the amount of water vapor in the air, the temperature of the air and the altitude. When air pressure changes, the weather changes too. A barometer is the tool used to measure air pressure. High or rising air pressure means clear weather is coming. Low or falling air pressure means bad weather is coming. Questions: What is air pressure? Does air pressure always stay the same? What factors affect air pressure? What tool is used to measure air pressure? How does the changing air pressure affect the weather? Humidity Humidity is the amount of water vapor in the air. This water vapor in the air comes from water on Earth’s surface that has evaporated. On humid days your skin might feel damp or your hair might start to look wavy. The amount of water in the air (humidity) is measured by a hygrometer. Questions: What is humidity? Where would it be more humid…in the desert or in the rainforest? Why do you think that is? Rain Gauge/Precipitation A rain gauge is a science tool that is used to measure the amount of precipitation that has fallen to the ground. Usually rain gauges are clear containers that have marks that show either inches or centimeters (like a ruler) Precipitation is any form of water that falls to the ground. This could include rain, snow, sleet, and hail. Questions: What does a rain gauge measure? What is precipitation? If your rain gauge starts off at 2cm and ends up at 8 cm after a storm, how much precipitation fell? Wind/Wind Vane/Anemometer Wind is moving air. Wind is made because Earth’s surface is heated unevenly. The land takes in the sun’s heat much faster than the water. The air above the land becomes warmer than the air above the water. This difference in temperature is what causes the air to move. The direction of the wind is shown by a wind vane. The arrow of a wind vane points to the direction the wind is coming from. Anemometers measure the wind speed. Wind pushes against the cups of an anemometer and causes them to spin around. The faster the wind is blowing, the faster the cups spin. Questions: What causes wind? What tool is used to measure the speed of wind? Which weather instrument shows the direction the wind is blowing? Climate Climate is the general weather of an area over a long period of time. There are three basic climates on Earth: tropical, temperate, and polar. Polar climates are cold and dry. They are located in bands around the North and South Poles. Temperate climates have moderate temperatures that change with the seasons. They are located between polar and tropical climates. Tropical climates are warm. They can be wet, dry, or somewhere in between. Tropical climates are located at and around the equator. Different climates occur because of Earth’s tilt on its axis. Questions: What is climate? What would be different between a polar climate and a tropical climate? (Think of things other than temperature.) Which climate type do we live in? Thermometer/ Temperature Temperature is the measure of how hot or cold something is. Temperature is measured using a thermometer. Can be measured in degrees Fahrenheit or Celsius In science we measure using degrees Celsius. Hints: 30 is hot, 20 is nice, 10 is cool and 0 is ice Questions: What does a thermometer measure? As you travel to the equator, would you expect the temperature to increase or decrease? What is the freezing/melting point of water? What is the boiling point of water? In order for liquid water to freeze, would the temperature have to increase or decrease? Seasons There are four seasons: summer, fall, winter, and spring. Earth is tilted on its axis. Because of this tilt, different parts of Earth have different amounts of daylight and darkness at the same time of the year. The sun’s rays also hit different parts of Earth more directly. These cause the Earth to have seasons. Seasons are opposite in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. When it is summer in the Northern Hemisphere, it is winter in the Southern Hemisphere. Summer occurs when sunlight strikes more directly for more hours each day (when the hemisphere is tilted toward the sun). Winter occurs when the hemisphere is tilted away from the sun. EARTH IS ALWAYS TILTED IN THE SAME DIRECTION, but the part of Earth facing the sun directly or on a slant changes, creating the seasons. Questions: What are the seasons? What causes the seasons? If the Northern Hemisphere is experiencing summer, what season is the Southern Hemisphere experiencing? Why? Why are days longer in the summer?