Curved Mirrors: Concave & Convex Ray Diagrams Worksheet
advertisement

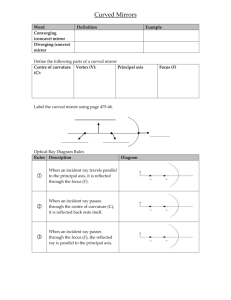
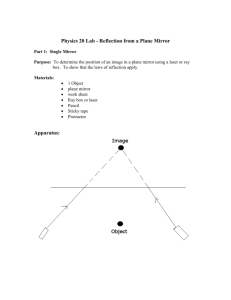
Curved Mirrors Go to go to http://www.physicsclassroom.com/class/refln/Lesson-3/The-Anatomy-of-aCurved-Mirror to see a diagram. Use V instead of A for the vertex for the diagram. Word Converging (concave) mirror Diverging (convex) mirror Definition Example Define the following parts of a curved mirror Centre of curvature Vertex (V): Principal axis (C): Focus (F) Label the curved mirror. VC- F- Optical Ray Diagram Rules- go to http://www.montgomeryschoolsmd.org/schools/whitmanhs/academics/science/physics/ talaat/webpages/notes/apB/RayDiagrams.pdf to see each of these rules and draw it on the sheet below, please use a ruler. Rules Description Diagram When an incident ray travels parallel to the principal axis, it is reflected through the focus (F). When an incident ray passes through the centre of curvature (C), it is reflected back onto itself. When an incident ray passes through the focus (F), the reflected ray is parallel to the principal axis. Mirror Ray Diagram Directions: Use the rules from the Optical Ray Diagram Rules information sheet, use the following applet to determine where the images form. http://www.physicsclassroom.com/Physics-Interactives/Reflection-and-Mirrors/OpticsBench/Optics-Bench-Interactive. Be sure to click on mirror on the top and NOT lens. Play around with the height and focal point once you have drawn your images. Hint: a couple are tricky, you will need to do some research if you are unsure of your answer. Also, you will have to use the rules to draw the diverging mirror on your own, feel free to google or youtube how to do this. Curved Mirrors Concave (converging)Mirror Case 1: Object is far beyond C Object Location Size Attitude Location Type Case 2: Object is at C Object Location Size Attitude Location Type Case 3: Object is between C and F Object Location Size Attitude Location Type Case 4: Object at F Object Location Size Attitude Location Type Case 5: Object between F and Mirror Object Location Size Attitude Location Type Convex (Diverging) Mirror Optical Ray Diagram Rules for Convex Mirror Any ray traveling parallel to the principal axis is reflected such that it appears to pass through the virtual focus (F). Any ray appearing to travel through the virtual focus (F) is reflected parallel to the principal axis. Any ray appearing to travel through the centre of curvature © is reflected back along itself Case 1: Anywhere Object Location Size Attitude Location Type