TDG – Unit 4
advertisement

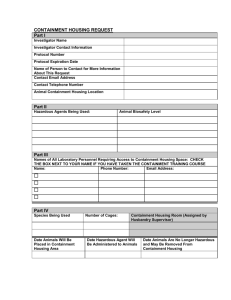
TDG – Unit 4 Dangerous Goods Safety Marks The Act and Regulations establish when it is necessary to display safety marks on dangerous goods in transport. Safety marks include labels, placards, orange panels, signs, marine pollutant marks, numbers, letters, abbreviations and words used to identify dangerous goods and show the nature of the danger they pose. Safety marks provide a quick identification of dangerous goods. This is particularly important in the event of an emergency situation such as an accident or an accidental release of dangerous goods from a means of containment. Dangerous Goods Safety Marks We have already looked at the 9 Classes of dangerous goods in the “Classification” section of this program. As was saw, each of these Classes of dangerous goods was represented by an example of a “safety mark”. We will now quickly review these classes: CLASS 1 - Explosives CLASS 2 – GASES ] CLASS 3 – FLAMMABLE LIQUIDS CLASS 4 – FLAMMABLE SOLIDS/ SPONTANEOUSLY COMBUSTIVE/ WATER REACTIVE SUBSTANCES) CLASS 5 – OXIDIZING SUBSTANCES & ORGANIC PEROXIDES CLASS 6 – INFECTIOUS SUBSTANCES CLASS 7 – RADIOACTIVE MATERIALS CLASS 8 – CORROSIVES CLASS 9 - MISCELLANEOUS PRODUCTS, SUBSTANCES OR ORGANISMS OTHER We will now take a look at some of the “other” safety marks involved in the transportation of dangerous goods. All of these symbols and markings can be found in the TDG Regulations. Other Safety Marks - Elevated Temperature Sign The elevated temperature sign must be displayed for dangerous goods that are in transport in a large means of containment and that are classified as “Elevated Temperature”. The elevated temperature sign must be displayed on each side and each end of the large means of containment next to each primary class placard for the dangerous goods, or, if there is a subsidiary class placard, next to the subsidiary class placard. Fumigation Sign When dangerous goods are used to fumigate a large means of containment, a fumigation sign must be displayed next to or at each entryway into a large means of containment through which a person can enter. The consignor must ensure that the fumigation sign is displayed by the person in charge of the fumigation process. The sign must also display the name of the fumigant and the date and time the fumigant was applied. Other Safety Marks - Marine Pollutant The marine pollutant mark must be displayed for dangerous goods that are marine pollutants in transport by ship. The marine pollutant safety mark is not required to be displayed when marine pollutants are on board a road vehicle or railway vehicle on a roll-on roll-off ship. The mark is also not required when marine pollutants are contained in a small means of containment and are in limited quantity. 5 L for a liquid marine pollutant 5 kg for a solid marine pollutant 500 mL for a liquid severe marine pollutant 500 g for a solid severe marine pollutant, Other Safety Marks - Certification A certification safety mark is required to be displayed by the manufacturer of the means of containment. This is done to illustrate compliance with the safety standard. Other Safety Marks - Foreign Shipments In specific cases, the TDG Regulations allow for the use of safety marks in accordance with other regulations Air shipments - ICAO Technical Instructions International marine shipments - IMDG Code US to Canada shipments (road and rail) - CFR (Code of Federal Regulations) 49 Dangerous Goods Safety Marks Safety marks are a valuable awareness tool for a wide range of people involved in the transportation of dangerous goods – for example: truck drivers, train crews, loading dock workers, aircraft loading personnel, reception personnel at a lab or hospital, and emergency personnel. Responsibility for Dangerous Goods Safety Marking Section 4.1 of the Regulations clearly defines when Safety Marks are required. This section states, “A person must not offer for transport, transport or import a means of containment that contains dangerous goods unless each dangerous goods safety mark required by this Part and illustrated in the appendix to this Part, or illustrated in Chapter 5.2 or 5.3 of the UN Recommendations, is displayed on it in accordance with this Part.” Misleading Dangerous Goods Safety Marks A person must not display a prescribed safety mark on a means of containment, a means of transport, or at a facility, if the mark is misleading as to the presence of danger or the nature of any danger. Effort must be made to ensure that the safety marks adequately reflect the danger at all times during “transport”. Safety Marks - Consignor Responsibilities Before importing dangerous goods, or allowing a carrier in Canada to take possession of dangerous goods for transport, a consignor must: Display or ensure the display of the required safety marks on each small means of containment that contain dangerous goods. Display or ensure the display of the required safety marks on a large means of containment that contain dangerous goods. Provide the carrier with the safety marks for the dangerous goods that the consignor is offering for transport or importing and that are to be transported in a large means of containment. Safety Marks – Consignor Responsibilities The consignor is not required to provide the safety marks if they are already displayed on a large means of containment. This is also the case if the safety marks are not the correct ones to display because of the presence of other dangerous goods in a large means of containment. A “large means of containment” is a means of containment that has a cargo capacity greater than 450 L. (truck, tankcar, etc.). Means of containment, both large and small, will be further reviewed later in this section of the course. When the consignor provides the large means of containment, they are responsible for displaying the safety marks. When the carrier provides the large means of containment, the consignor must provide the carrier with the appropriate safety marks. Safety Marks - Carrier Responsibilities A “carrier” is the person who, whether or not for hire or reward, has possession of dangerous goods while they are in transport. With respect to safety marking a carrier of dangerous goods must: Ensure that the required safety marks remain displayed on a “small means of containment” (cargo capacity less than or equal to 450 L.) while the dangerous goods are in transport; Display the required safety marks on the large means of containment, unless they are already displayed on it, and ensure that they remain displayed while the dangerous goods are in transport; Provide and display, or remove, the safety marks if the requirements for marking change while the dangerous goods are in transport. Visibility, Legibility and Colour Dangerous goods safety marks must be visible, legible and displayed against a background of contrasting colour. They must also be made of durable and weather-resistant material that will withstand the conditions to which they may be exposed without substantial detachment or deterioration of their colour, symbols, letters, text or numbers. Safety marks must also be displayed in the colours specified in the appendix to Part 4. Removal of Dangerous Goods Safety Marks Dangerous goods safety marks must remain displayed on a means of containment until its contents have been neutralized or the means of containment have been unloaded, unpacked, cleaned or purged. This is to ensure that there is no longer any danger in the means of containment. The person who neutralizes the contents of the means of containment, or who unloads, unpacks, cleans or purges it, must cover or remove the dangerous goods safety marks when there is no longer a danger present in the means of containment. Means of Containment To better understand the application and requirements for safety marks, we will now take a look at the “means of containment” required by the TDG Act and Regulations. This part of the course will identify the types of “means of containment” used for transporting dangerous goods, and, describe the procedure in selecting and safety marking a means of containment. The requirements for “means of containment” are in the form of published standards that are adopted by reference in the TDG Regulations. The standards relate to the design, manufacture, marking and use of various types of containers. The TDG Directorate administers registration programs for facilities or persons that manufacture and maintain means of containment in accordance with these standards. Means of Containment The Transportation of Dangerous Goods (TDG) Act and Regulations, along with a number of applicable standards, require that dangerous goods be transported in a safe means of containment. A “safe means of containment” prevents the release of dangerous goods that could constitute a danger to life, health, property or the environment. The TDG Regulations often refer to other regulations or standards for the manufacturing and the selection and use of means of containment for dangerous goods. Regulations and standards may be specific to a class of dangerous goods, means of containment or mode of transport. Most means of containment standards in Canada are based on the UN Recommendations. UN standardized means of containment are internationally recognized and can be used anywhere in the world and by any mode of transport. Some means of containment standards are specific to Canada, as no international standards exist. Cylinders, tubes, highway tanks, some portable tanks and tank car tanks are examples of these “TC” standardized means of containment. These means of containment can be used in Canada and sometimes in the United States if the specification to which they are manufactured corresponds to American standards (DOT specification). Mode of Transport / Destination There may be additional packaging requirements based on the mode of transport and/or destination. Refer to the appropriate regulation for more information. The International Civil Aviation Organization Technical Instructions (ICAO Technical Instructions) must be consulted for air transport requirements. The International Maritime Dangerous Goods Code (IMDG Code) must be consulted for segregation requirements and international marine transport. The Code of Federal Regulations, Title 49, (CFR 49), must be consulted for road and rail shipments to the United States. Certification Safety Marks on a Means of Containment All standardized means of containment bear certification safety marks to indicate that they were manufactured in compliance with a standard. A certification safety mark is any design, symbol, device, letter, word, number or abbreviation that is displayed on a means of containment, or means of transport, to indicate compliance with a safety standard. To remain in standard, some means of containment must be periodically inspected and tested and marked at intervals specified by the standard or regulation. These marks describe what, when and by whom the inspections and tests were performed. All certification safety marks must be durable, visible, legible and easily accessible for inspection. The Types of “Means of Containment” The TDG Act and Regulations define two types of “means of containment”. 1. Small means of containment 2. Large means of containment Small Means of Containment Small means of containment are containers with a water capacity of 450L or less. They may be drums, jerricans, boxes, pails, bags, barrels, cylinders or intermediate bulk containers. Large Means of Containment Large means of containment are containers with a water capacity greater than 450L. They may be highway tanks, tank cars, intermediate bulk containers, portable tanks or tubes. “Large means of containment” can be tote tanks, intermodal tanks, portable tanks, intermediate bulk containers (IBC), freight containers, portable tanks, tubes, road and rail vehicles. Once again, a large means of containment means a containment that has a cargo capacity greater than 450 L. Selecting a Means of Containment : When selecting the appropriate means of containment, a person who offers for transport dangerous goods must determine: the class of dangerous good(s); the type and size of the means of containment; the mode of transport; and; the destination of the dangerous good(s). Safety Marks on a Means of Containment Now that we have a basic understanding of the means of containment involved in the transportation of dangerous goods, we can now combine them with our study of safety marks. Labels and Placards Labels and placards are diamond shaped and must be displayed as illustrated below. They are usually identical (except for the size) and they communicate by colour, number and symbol the degree and nature of the hazard of dangerous goods. The specific labels and placard symbols will be examined in detail at the end of this section. Labels and Placards - Dimensions Because of the size or irregular shape of certain means of containment, the TDG Regulations allow for the reduction of labels (30 mm) and placards (100 mm). When this occurs, all means of identification on the safety mark must also be reduced. Under the Clear Language Regulations, Class 7 (Radioactive labels) may not be reduced in size and must be displayed on two opposite sides of a small means of containment. Safety Marks on a Small Means of Containment: Labels Unless otherwise specified in the regulations, labels must be applied to every small container, package and cylinder that contains dangerous goods and is to be offered for transport. One label must be displayed on a small means of containment for the primary class and one for each subsidiary class for each dangerous good in transport. Labeling – Special Considerations A label is not required to be displayed on a small means of containment that is inside another small means of containment if the other small means of containment has a label displayed on it, and, it is not opened during loading or unloading or while in transport. Labeling – Special Considerations If the dangerous goods are included in Class 7, Radioactive Materials, two labels for the primary class must be displayed on the small means of containment. In addition, the oxidizing gas label must be displayed on all small means of containment for the following dangerous goods: UN1072, OXYGEN, COMPRESSED; UN1073, OXYGEN, REFRIGERATED LIQUID; UN3156, COMPRESSED GAS, OXIDIZING, N.O.S.; and UN3157, LIQUEFIED GAS, OXIDIZING, N.O.S. Labeling Requirements When a label is required to be displayed, it must be displayed: on any side of the outer surface of a small means of containment other than the side on which it is intended to rest or to be stacked during transport (top and bottom); on the shoulder of a cylinder containing dangerous goods; or in the case of a label for dangerous goods included in Class 7, Radioactive Materials, on two opposite sides of the outer surface of a small means of containment, other than the side on which it is intended to rest or to be stacked during transport. Reduced Labels A label with sides that are reduced to 30 mm in length may be displayed on a tag that is securely attached to a small means of containment. Labeling Requirements - Small Means of Containment The shipping name, technical name (if any) and UN number must also be displayed on small means of containment. The UN number may appear on or next to the label. Placard Requirements - Large Means of Containment All dangerous goods for transport must be properly marked before loading or packing of a large means of containment. A large means of containment must have the appropriate safety marks displayed on it that will be required when the loading or packing is complete. Placard Requirements Large Means of Containment Placards and UN numbers must be displayed on each side and end of a large means of containment (greater than 450 L), other than a ship or an aircraft, if the dangerous goods: Have a total gross mass greater than 500 kg (UN number is only required when the quantity exceeds 4000 kg); Are in a quantity or concentration that require an emergency response assistance plan (ERAP); or; Are a liquid or a gas in direct contact with the means of containment. Placards - UN Number The UN number must appear on the placard or on a rectangular orange panel next to the placard. Safety Marks on a Large Means of Containment: Placards and UN Numbers A mixed load of dangerous goods of different UN numbers (none requiring an Emergency Response Assistance Plan) may be identified by a DANGER placard instead of the placard required for those dangerous goods. Safety Marks on a Large Means of Containment: Placards and UN Numbers A placard and UN number must be displayed on a large means of containment, other than a ship or an aircraft, if: (a) the dangerous goods: are in a quantity or concentration for which an emergency response assistance plan is required, are included in Class 7, Radioactive Materials, for which a Category III –yellow label is required, are a liquid or gas in direct contact with a large means of containment, or have a total gross mass greater than 500 kg; or (b) the large means of containment contains a consignment on which a placard is required to be displayed but that placard is not visible from outside the large means of containment. Placards and UN Numbers - Display When determining the display of placards and UN numbers the following table should be consulted. Familiarize yourself with this table – it is available in Part 4 of the regulations or in the “Links” section of this website under “Resource Materials”. * Emergency Response Assistance Plans will be detailed later in the course Safety Marks on a Large Means of Containment: Placards The placard must be displayed on each side and each end of a large means of containment. A subsidiary class placard, without the class number in the bottom corner, must be displayed on each side and each end of a large means of containment for dangerous goods for which an emergency response assistance plan. General Options for Placards and UN Numbers Despite the requirement for the display of primary class placards, when two dangerous goods have different UN numbers but are identified by the same primary class placard, that placard needs to be displayed only once on each side and each end of a large means of containment. Placard Options for Class 1, Explosives A placard is not required to be displayed for explosives that are included in: Class 1.4 and in a quantity less than or equal to 1 000 kg; or Class 1.4S in any quantity. Only the placard for the explosives with the lowest division number is required to be displayed for explosives that are included in more than one division in a large means of containment, except in the following cases: when explosives included in Class 1.2 and Class 1.5 are transported together, the placard for Class 1.1 must be displayed; and when explosives included in Class 1.4 and Class 1.5 are transported together, the placard for Class 1.5 must be displayed. Despite the requirement in section 4.15 for the display of a UN number, a UN number is not required to be displayed for Class 1, Explosives. Placard Options for Class 2, Gases A mixed load of different classes of gases transported by road, solely on land, may be identified by a DANGER placard and a primary class placard for the most dangerous gas according to the following decreasing order of danger: 1. toxic gas, 2. flammable gas, 3. oxidizing gas, 4. any other gas. In addition to the requirements for placards and UN numbers in section 4.15, when one of the gases on a road vehicle or railway vehicle that is to be transported by ship is included in Class 2.1, Flammable Gas, the flammable gas placard must be displayed. Placarding - Oxidizing Gases When dangerous goods are oxidizing gases, the oxidizing gas placard may be displayed for the following dangerous goods instead of the placards: (a) UN1072, OXYGEN, COMPRESSED; (b) UN1073, OXYGEN, REFRIGERATED LIQUID; (c) UN3156, COMPRESSED GAS, OXIDIZING, N.O.S.; and (d) UN3157, LIQUEFIED GAS, OXIDIZING, N.O.S. Safety Marks on a Compartmentalized Large Means of Containment When dangerous goods included in different primary classes are transported in different compartments of a compartmentalized large means of containment: the primary class placard and the UN number for the dangerous goods in each compartment must be displayed on each side of that compartment; the primary class placards and UN numbers for all of the dangerous goods in the compartments must be displayed on each end of the compartmentalized large means of containment. Safety Marks on a Compartmentalized Large Means of Containment(cont.) When all compartments in a compartmentalized large means of containment contain dangerous goods included in the same primary class: the primary class placard must be displayed on each side and on each end of the compartmentalized large means of containment; and the UN number must be displayed on each side of the compartment and on each end of the compartmentalized large means of containment. If all the dangerous goods are included in Class 3, Flammable Liquids, only the UN number of the dangerous goods with the lowest flash point need be displayed on each side and on each end of the compartmentalized large means of containment. Clear Language Regulations Summary of Changes in Safety Marks for Small Means of Containment Labels Labels must be displayed for primary class and all subsidiary classes. Subsidiary class labels must display class numbers and do not need to be placed in a subsidiary location. There is now only one label for Class 9. Class 2.4 and Class 6.1 Packing Group III labels no longer used. Radioactive labels (Class 7) may not be reduced in size, and must be displayed on two opposite sides of a small means of containment. The UN number may be displayed either on or beside the primary class label. Control or emergency temperatures do not need to be displayed. Use of fumigation label has changed. Summary of Changes in Safety Marks for Large Means of Containment A placard with the UN number is required for dangerous goods that: o o o o Are a liquid or gas in "direct contact" with the large means of containment. Require an Emergency Response Assistance Plan (ERAP), Have the same UN number and are in a quantity greater than 4,000 kg and offered for transport by one consignor. The DANGER placard may be used for mixed loads of dangerous goods that do not require an ERAP if the gross mass exceeds 500 kg. General Elevated Temperature Liquid - has been added. Labels no longer used — EMPTY (optional), Attention PCB, Package Orientation ("this side up"). Oxygen Depletion sign is no longer used. There is no longer a requirement for placards to be placed on coupling devices for loading and unloading dangerous goods. There is no longer a requirement to use UN number on orange panel for specific Class 2.3 Toxic Gases. There is no longer a requirement for placards to be retro-reflective. Proceed to test You have completed the reading material for this section of the course. Please proceed to the test when you feel comfortable with the material. To proceed to the test for this section, click on the icon on the lower right of this page. The course material in this section can be reviewed by clicking on the section you would like to review on the main menu found to the left of this page. You will not be able to proceed to the next section of the course until you have successfully completed the test for this section. Good luck!