Chapter 15 Evolution: Evidence and Theory Theories of Evolution
advertisement

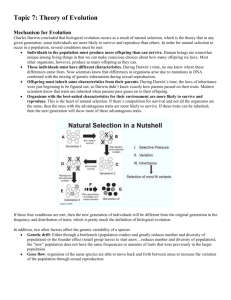
Chapter 15 Evolution: Evidence and Theory Theories of Evolution Ideas of Darwin’s Time o In the 18th century scientists thought that species were permanent and unchanging o They also believed the Earth was only thousands of years old Biological evolution- the change of populations of organisms over generations Lamarck’s Explanation o 1st to propose species modification o Similar species descended from a common ancestor o Acquired traits were passed on to offspring. An acquired trait is initially not genetic. The organism acquires it through necessity. (Not true) Darwin’s Theory o Proposed that species were modified by natural selection o He was a naturalist on a ship called the Beagle. His job was to collect samples of organisms and keep records o He theorized that because environments change over millions of years organisms that lived there changed just as slowly. o Darwin was famous for his studies of finches, turtles, and iguanas on the Galapagos Islands Darwin’s Two Theories o Descent with Modification (evolution) All species descended from one or a few original types of life Modern organisms had evolved from organisms that lived millions even billions of years ago o Modification by Natural selection States how evolution occurs Darwin observed that the environment limits the growth of populations by increasing the rate of death or decreasing the rate of reproduction, or both A population of organisms adapt to their environment as their proportion of genes for favorable traits increases Fitness- a single organisms genetic contribution to the next generation 1 An individual with high fitness is well adapted to its environment and reproduces more successfully than a low fitness members Darwin proposed the following forces could affect natural selection o Overproduction- Organisms produce several offspring in a lifetime because some will be lost to predation, disease, and other factors. This ensures the stability of the species o Genetic Variation- Within a population, individuals have different traits. This ensures adaptability buy the population o Struggle to Survive- Individuals must compete with each other and other species for food, space, and a mate o Differential reproduction- organisms with the best adaptations are most likely to survive and reproduce. Populations will become different as they adapt to different environments Darwin stated that adaptations are those traits that increase the fitness of individuals, and populations tend to be well adapted to survive the conditions in which they live. Evidence of Evolution o Fossil Records o Biogeography The study of the locations of organisms around the world Both Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace saw evidence of evolution in the distribution of organisms They observed animals that seemed closely related yet were adapted to different environments in nearby regions They also observed animals that seemed unrelated but that had similar adaptations to similar environments in regions that were far apart Example: There are native Australian animals that resemble wolves, cats, mice, moles, or anteaters…however most Australian mammals are marsupials, mammals that have pouches for carrying their young 2 o Anatomy and Embryology Homologous structures- anatomical structures in one species that, compared to other anatomical structures in another species, originated from a single ancestor of the two species Example: fore limb of humans, penguins, alligator, bat Analagous structures- anatomical structures in one species that is similar in function and appearance, but not in evolutionary origin to another anatomical structure in another species. Example: Insect wing, bird wing, bat wing 3 Vestigial structures- features that serve no useful function Example: human tailbone, human appendix, snakes with pelvic bones o They allow us to see how an organism evolved over the years and what other organism they could have been related to o Biological Molecules Biologists study DNA, RNA, proteins and other molecules to see how closely related different organisms are. The more closely related they are the closer their DNA and other biological molecules are Evolution in Action o Coevolution- the mutual evolution of two different species interacting with each other. Example: Insects and flowers help each other and evolve together o Convergent evolution- the process by which unrelated species become more similar as they adapt to the same kind of environment Example: Porpoise and shark; mammal and fish that have similar body design and fins o Divergent evolution- the process of two or more related species becoming more and more dissimilar because of differing habitats. Can lead to new species 4 It occurs when descendants of a single ancestor diversify into species that each fit different parts of the environment Adaptive radiation is when a new population in a new environment, such as an island, will undergo divergent evolution until the population fills many parts of the environment 5