Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle
advertisement
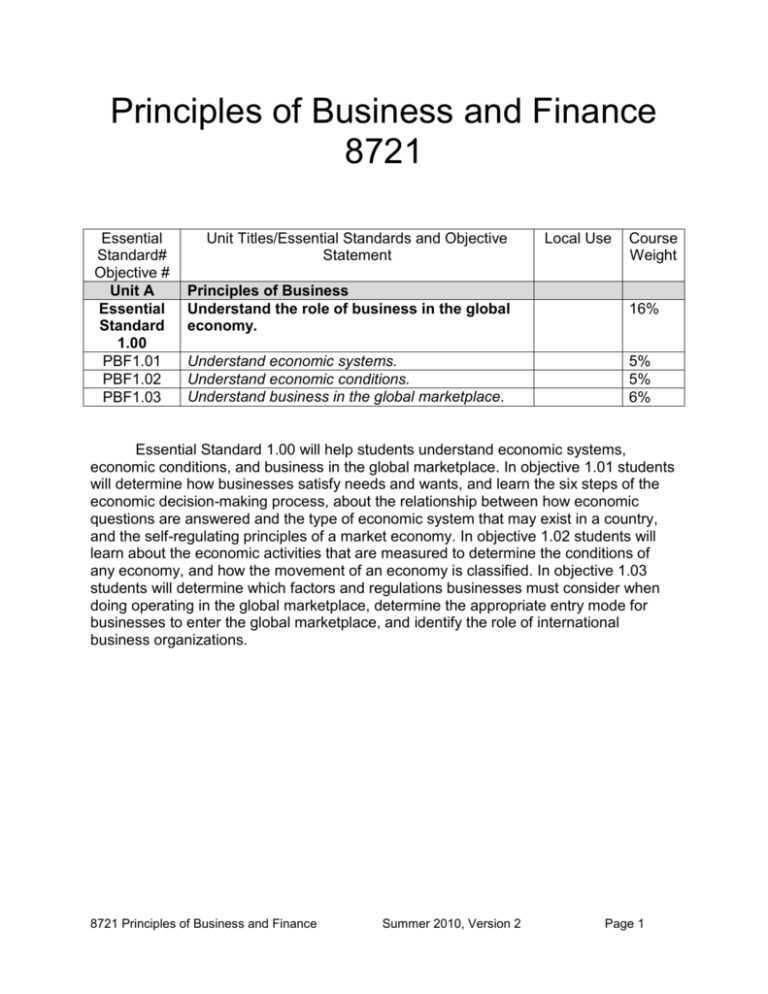
Principles of Business and Finance 8721 Essential Standard# Objective # Unit A Essential Standard 1.00 PBF1.01 PBF1.02 PBF1.03 Unit Titles/Essential Standards and Objective Statement Local Use Course Weight Principles of Business Understand the role of business in the global economy. 16% Understand economic systems. Understand economic conditions. Understand business in the global marketplace. 5% 5% 6% Essential Standard 1.00 will help students understand economic systems, economic conditions, and business in the global marketplace. In objective 1.01 students will determine how businesses satisfy needs and wants, and learn the six steps of the economic decision-making process, about the relationship between how economic questions are answered and the type of economic system that may exist in a country, and the self-regulating principles of a market economy. In objective 1.02 students will learn about the economic activities that are measured to determine the conditions of any economy, and how the movement of an economy is classified. In objective 1.03 students will determine which factors and regulations businesses must consider when doing operating in the global marketplace, determine the appropriate entry mode for businesses to enter the global marketplace, and identify the role of international business organizations. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 1 Course Essential Standard Objective Essential Questions 8721 Principles of Unit A Business and Finance 1.00 B2 16% Principles of Business Understand the role of business in the global economy. 1.01 B2 5% Understand economic systems. How do businesses satisfy needs and wants? What are the six steps necessary for making choices? What is the relationship between who answers economic questions and the type of economic system that exists in a country? What are the self-regulating principles of a market economy? UNPACKED CONTENT I. Economics is the study of the decisions made for production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants. To satisfy needs and wants businesses use economic resources to produce, distribute, and sell goods and services. The types of economic resources are: A. Capital B. Human C. Natural II. The six steps of economic decision-making process are: A. Defining the problem B. Identifying choices C. Evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of each choice D. Choosing one choice E. Acting on the choice F. Reviewing the decision III. The involvement of a nation’s government in answering economic questions determines its economic system. The economic questions address the allocation of scarce resources. A. The three economic questions are: 1. What to produce? 2. How to produce? 3. For whom to produce? B. The main types of economic systems and who decides on the economic questions are: 1. Command (Communist) Economy’s government decides. 2. Market Economy’s people determine. 3. Traditional Economy questions are carried out the same way. 4. Mixed Economy takes on fundamentals of command and market economies. C. The four principles that The United States economic system is based on are: which are: 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 2 1. Competition 2. Freedom of Choice 3. Private Property 4. Profit IV. Individuals, businesses, and government make buying decisions in a market economy. These buying decisions make a market economy self-regulating. The selfregulating principles of a market economy are: A. Consumers set demand. B. Producers establish supply. C. Supply and demand generate competition. D. Demand and supply factors influence market (equilibrium) prices. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 3 INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITIES RELEVANCE TO OBJECTIVE RESOURCES Going Green Please refer to the Going Green document in the introductory materials for suggestions on how to conserve resources while teaching this course. For example, graphic organizers are used to guide students in taking notes. Alternative methods are suggested in the Going Green document to provide this material to students. Course PLC Please refer to the Course PLC document in the introductory materials for directions to join the Moodle Professional Learning Community (PLC) for this course. 1 Business and Finance Introduction Helps students to Website: begin to http://stosselintheclass Assign students to groups of two. UNDERSTAND room.org/index.php?p= Facilitate each group watching a (B2) the search.php business or finance video from the principles of link in the resources column. NOTE: This can also be done as a business and class. Check videos prior to class. finance Facilitate students reflecting on the video viewed by writing at least a paragraph about how what they viewed relates to what they expect to learn in the course. NOTE: Format of reflection may vary. Facilitate several groups sharing reflections with class and how videos relate to the content of the course. 2 Satisfying Needs and Wants Helps students to Textbook Introduction begin to UNDERSTAND Have students read Focus on (B2) how needs Real Life on pages 6 and 12 in and wants are Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson satisfied South-Western textbook OR use current events related to needs, wants, and making choices. Facilitate a discussion using the questions: 1. What are needs and wants? 2. What are goods and services? 3. What resources are needed to meet needs and wants? 4. How are decisions made to satisfy needs and wants? Instructional Activities continued on the next page. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 4 INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITIES 3 RELEVANCE TO OBJECTIVE Helps students UNDERSTAND (B2) how needs and wants are satisfied Satisfying Needs and Wants Reading and PowerPoint Presentation Present an overview of the concepts: o needs and wants are different o businesses can provide goods and services to satisfy needs and wants o businesses use economic resources to produce, distribute, and sell goods and services o the basic economic problem of scarcity Facilitate students completing Satisfying Needs and Wants Organizer. Students may obtain information by reading pages 6-15 in Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson South-Western textbook OR by participating during presentation of PowerPoint Presentation 1.01, slides 1-16. Review how goods and services, economic resources, basic economic problem and economic choices contribute to satisfying needs and wants. 4 Economic Resources Helps students to CLASSIFY (B2) Assign students to groups of two. how economic Facilitate students completing resources are Economic Resources Activity. used to satisfy Facilitate a discussion about responses. NOTE: emphasize how needs and wants economic resources are used to satisfy needs and wants. Discuss uses of resources, examples: 1. NC farmers meet the needs of families. 2. NC film industry meets the wants of movie producers. Instructional Activities continued on the next page. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 RESOURCES Satisfying Needs and Wants Organizer Textbook PowerPoint Presentation 1.01, slides 1-16 Economic Resources Activity Page 5 INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITIES 5 RELEVANCE TO OBJECTIVE Helps students to UNDERSTAND (B2) who makes economic decisions in economic systems Economic Systems Introduction Have students read Focus on Real Life on page 17 in Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson South-Western textbook OR use current events related to economic decisions and systems. Facilitate a discussion using the questions: 1. Who makes economic decisions for the United States economy? 2. How are economic decisions made in other countries? 6 Economic Systems Reading and Helps students Power Point Presentation UNDERSTAND (B2) the main Present the concept that how a nation economic systems answers the three questions that determines its economic system: 1. What to produce? 2. How to produce? 3. For whom to produce? Facilitate students completing Economic Systems Organizer. Students may obtain information by reading pages 17-22 in Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson SouthWestern textbook OR by participating during presentation of PowerPoint Presentation 1.01, slides 17-20. 7 Comparing Economic Systems Helps students COMPARE (B2) NOTE: Read pages of Economic the main types of Systems Activity to ensure all materials are available for this activity. economic systems Assign students to groups of four to five. Facilitate students completing Economic Systems Activity. Facilitate students completing Economic Systems Debrief: Comparing the Villes that describes each main type of economic system. NOTE: This can be completed as an exit ticket, as a class. NOTE: This is a formative assessment. Instructional Activities continued on the next page. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 RESOURCES Textbook Economic Systems Organizer Textbook PowerPoint Presentation 1.01, slides 17-20 Economic Systems Activity Materials to complete Economic Systems Activity (see activity) Page 6 INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITIES 8 RELEVANCE TO OBJECTIVE Helps students begin to UNDERSTAND (B2) supply and demand Market Economy Introduction Have students read Focus on Real Life on page 23 in Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson SouthWestern textbook OR use current events related to supply, demand, and determining how much to pay for items. Facilitate a discussion using the questions: 1. How do you determine if a business can satisfy your needs and/or wants? 2. How do you determine how much of a good or service is enough? 3. How do you determine how much you will pay for goods or services? 9 Market Economy Reading and Helps students PowerPoint Presentation UNDERSTAND (B2) supply and Present how satisfaction and profit demand and the are necessary in a market relationship of economy. both in Present the relationship of supply determining and demand. prices Present how demand for goods or services influence prices. Facilitate students completing Market Economy Organizer. Review supply and demand and the relationship of both in determining prices. Students may obtain information by reading pages 23-26 in Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson South- Western textbook OR by participating during presentation of PowerPoint Presentation 1.01, slides 21-29. Instructional Activities continued on the next page. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 RESOURCES Textbook Supply and Demand Organizer Textbook PowerPoint Presentation 1.01, slides 21-29 Page 7 INSTRUCTIONAL ACTIVITIES 10 11 12 RELEVANCE TO OBJECTIVE Helps students INTERPRET (B2) market prices Interpreting Market Prices Facilitate students completing the What is the Market Price? Activity. Facilitate a discussion about how the relationship between the demand and supply of products determines market price. Key Terms Facilitate students completing Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle. RESOURCES What is the Market Price? Activity What is the Market Price? Activity Key Helps students IDENTIFY (B2) key terms associated with economic choices and systems Supplement Corporate Economics Facilitate a discussion about what kinds of information students provide to other people in order for decisions to be made. Ask students if their career plans include working in an industry that will allow them to provide information that other people will use to make decisions. Introduce the industry of Corporate Economics. Have students read Planning a Career in … Corporate Economics page 5 in Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson SouthWestern textbook. Facilitate a discussion of why people providing services in the corporate economics industry should pay attention to details. Invite guest speakers representing the corporate economics field. Helps students UNDERSTAND (B2) career options related to economics Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle Key Textbook Numeracy Strategy: To make a Math Academic Connection is to see a relationship between a math concept and a real-life situation. Finding math-to-life connections greatly increase the relevance of new information and skills being learned. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 8 Instructional Support Material Textbook Intro to Business, 6e, Thomson SouthWestern Website http://stosselintheclassroom.org/index.php ?p=search.php Handouts (included) Satisfying Needs and Wants Organizer Economic Resources Activity Economic Systems Organizer Economic Systems Activity Materials to complete Economic Systems Activity (see activity) Economic Systems Debrief: Comparing the Villes Supply and Demand Organizer What is the Market Price? Activity What is the Market Price? Activity Key Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle Key 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Other PowerPoint Presentation 1.01 (separate file) Assessment Prototypes (included) Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 9 Name: ______________________ Class: _______ Date: _______ Satisfying Needs and Wants Organizer Directions: Describe in your own words the listed items. Needs Wants Goods Services Economic resources Natural Examples Human Examples Capital Examples The Basic Economic Problem What is the relationship between scarcity and the basic economic problem? 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 10 Satisfying Needs and Wants Organizer Continued Economic Decision-Making Process What is the purpose of the decision-making process? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ What happens to choices in a tradeoff? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ What is opportunity cost? ______________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________ In column one, provide the six steps of the economic decision-making process. In column two, apply the steps and complete an economic decision such as purchasing new equipment, shopping for a gift, or paying for a trip. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 11 Name: ______________________ Class: _______ Date: _______ Economic Resources Activity Directions: Use the listed or other resources to classify how economic resources are used to satisfy needs and wants. Some North Carolina Resources: Bank of America Stadium Christmas Trees NC Legislators Sweet potatoes Brier Creek Apartments Therapists Table of Resources and Uses NC resource Type of resource Does this resource satisfy needs or wants How will this resource satisfy needs or wants for a business? Honey Natural Answers will vary. Answers will vary. Wants A business could sale 12 oz jars of honey at a roadside stand. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 12 Name: ______________________ Class: _______ Date: _______ Economic Systems Organizer Directions: Provide responses for the listed items. What are the three economic questions that economic systems must answer? 1. ________________________________________________________________ 2. ________________________________________________________________ 3. ________________________________________________________________ Main Economic Systems Features Command Economy Who owns the resources? Market Economy Traditional Economy Who answers the three economic questions? 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 13 Name ____________________ Class __________ Date __________ Economic Systems Activity TEACHER’S GUIDE Summary: Students will have an opportunity to participate in the main economic systems (command, market, and traditional). Each economic system is referred to as Told, Want, or Always Done Ville. Students will be able to compare the advantages and disadvantages of each system. Materials: Six balls of light packing string Different colored wooden or plastic hobby beads (Varies with class size. See Instructor Cheat Sheet and situation section of each We Make As Much As We …. Ville System Profile) A ruler, scissors, and bowl/cup for beads for each group Copies of each system profiles-see Step 2 Overhead of the scoreboard sheet or poster to present results Student copies of Economic Systems Debrief: Comparing the Villes Job labels sheet (one set per group) Steps: 1. Have the room set up in six small groups, 4 or 5 students per group. 2. Each group should have a ball of string, bowl/cup for beads, scissors, a ruler, and six copies of one of the system profiles. 3. Each student in the group is given a job label. This may be changed during the activity if needed. 4. Walk students through the reading of the first “Ville” so that they understand the directions. 5. Play three ten-minute rounds. The profiles are rotated during the rounds. (The teacher should be aware of each set of directions so the scoring will be quick at the end of each round.) 6. Groups are to follow whatever directions are on their profiles. The teacher distributes beads at each round and acts as the quality control person. 7. After each round, post group scores on the scoreboard. The winning group is the one that has the most dollars per person after the third round. 8. After all rounds have been completed, review the Economic System Debrief Activity: Comparing the Villes** sheet is completed for each student and discussed as a group. Discuss with students which system they prefer and explain why. Examples of each type of system can be given at this time. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 14 Scoreboard Team Told Ville Want Ville Always Done Ville 1 2 3 4 5 6 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 15 Job Labels (Make one set per group) String Cutter Bead Sorter Bead Stringer Knot Tier Knot Trimmer 8721 Principles of Business and Finance String Cutter Bead Sorter Bead Stringer Knot Tier Knot Trimmer Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 16 Instructor Cheat Sheet Price List Told Ville Ring $2 Bracelet $5 Necklace $10 Want Ville 1 black 1 red 1 blue 1 pink 2 black 2 red 2 blue 2 yellow 2 black 2 red 2 blue 2 green 3 black 3 blue 2 red 2 green 3 black 3 blue 2 red 2 yellow Reminders 5 bracelets Any number necklaces $10/person; rest to government Specialization Make whatever they choose Whatever method Always Done Ville 3 red 2 black 3 blue 1 bracelet Say it is beautiful by all Wait 5 minutes to start again No specialization Note: Keep in mind that economies have limited resources. It is not important to just have the colors mentioned on the list. Teaching the ideas of scarcity is also part of this activity. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 17 Values: We Make As Much As We Are Told Ville System Profile The government runs a very strict and strong central leadership group. You are highly organized and the people of your group are assigned specific tasks by the leader. Your country strives for efficient use of time and resources, which will increase economic growth and hopefully raise the standard of living. It is up to the central leaders to determine what is needed and how the resources are used. Goals: To produce what the central leadership finds necessary for your society. Also, there must be an efficient use of time and resources so increased production and growth will occur. Situation: With your limited resources of string, bead, ruler, and scissors you can create rings, necklaces, or bracelets. Your group will receive amounts per item: $2 Rings $5 Bracelets $10 Necklaces You must immediately make 5 bracelets as your country is in desperate need of them, and then the central planners want necklaces to be produced by your group. Production Process: The central planners emphasize specialization. The person sitting closest to the front of the room will be the string cutter, then going clockwise around the group, the next person is the bead sorter, the bead stringer, knot tier, and knot trimmer. Bracelet – 12” piece of string with 8 beads in this sequence 2 black 2 red 2 blue 2 yellow Necklace – 20” piece of string with 10 beads in this sequence 3 black 3 blue 2 red 2 green After the beads are on the string it should be tied in a knot and the knot should be neatly trimmed. The finished product is then handed to the quality control person (teacher) who marks down the dollar amount. Your group will receive $10 per person if the required quota is filled. After that, the dollars earned by your production will go to the central planner and will not be added to your total dollar amount. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 18 We Make As Much As We Are Want Ville System Profile Values: Your country and economic system reflect values which centers on individualism and freedoms. It allows each person to make herself/himself more prosperous than other people. Your country produces whatever brings the highest price and produces it with the method that costs the least. Individual rewards and material incentives are used to encourage and stimulate continuous economic growth and production. Goals: To produce whatever your group decides will be most beneficial for it. You will also want to organize yourselves so you can make the most efficient use of time and resources. Maximized profit is the key. Situation: With your limited resources of string, bead, ruler, and scissors you can create rings, necklaces, or bracelets. Your group will receive the amounts per item: $2 Rings $5 Bracelets $10 Necklaces Your group produces whatever it wants. Production Process: It is up to you to organize your group and choose jobs in whatever fashion you want. You should have a string cutter, bead sorter, bead stringer, and knot tier. Ring – 6” piece of string with 4 beads in this sequence: 1 black 1 red 1 blue 1 pink Bracelet – 12” piece of string with 8 beads in this sequence: 2 black 2 red 2 blue 2 green Necklace – 20” piece of string with 10 beads in this sequence: 3 black 3 blue 2 red 2 yellow After the beads are on the string it should be tied in a knot. You may trim the knot neatly if you want. After the tying is done the finished product must be handed to the quality control person (teacher). Your group will be paid in full for as many of the items as you can produce within the time limit. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 19 We Make As Much As We Always Done Ville System Profile Values: Your group is really concerned with the way things were done in the past. Positions of authority, jobs, etc. are handed down according to tradition. You value the past and see no need for concern about increase economic growth in the future. Basically everything in your society is determined by beliefs and customs. Goals: To produce what your ancestors did and in the same way that they did. Following tradition is your basic underlying goal. Situation: With your limited resources of string, bead, ruler, and scissors you can create rings, necklaces, or bracelets. Your group will receive the amounts per item: $2 Rings $5 Bracelets $10 Necklaces Production Process: Each person must make the entire bracelet with no specialization of tasks. The person that is the oldest in your group will use the string, ruler, and scissors first and then pass it clockwise around the table. Bracelet – 12” piece of string with 8 beads in this sequence: 3 red 2 black 3 blue After the beads are on the string it should be tied in a knot to finish the bracelet. The knot should be neatly trimmed off, as done by past generations. After each bracelet is finished it must be passed around the group clockwise and each member must tell the maker how beautiful it is. (This is an old tradition of your country.) The maker then hands it to the quality control person (teacher) who records the $5 if all procedures are followed correctly. According to tradition, each person can only make 1 bracelet every 5 minutes before starting a second one. So, after you complete your first one, relax for 5 minutes before starting the second one. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 20 Name ____________________ Class __________ Date __________ Economic Systems Debrief: Comparing the Villes Is progress important to this economy? Who chooses your job? What motivates you to produce? How is the product produced? How is it decided to produce? For whom is the product produced? Told Ville Highly stressed Want Ville Highly stressed Always Done Ville Highly stressed To some degree To some degree To some degree Not at all Individual preference Not at all Individual preference Not at all Individual preference Government directed Government directed Government directed Custom directed Traditional incentives Custom directed Traditional incentives Custom directed Traditional incentives High self-gain High self-gain High self-gain Limited social gain Least cost method Limited social gain Least cost method Limited social gain Least cost method High cost method High cost method High cost method Traditional ways Government decides Traditional ways Government decides Traditional ways Government decides Most profitable Most profitable Most profitable Traditionally produced Those Declared in Need Traditionally produced Those Declared in Need Traditionally produced Distributed by Custom Distributed by Custom Distributed by Custom Highest Bidder Cooperation Highest Bidder Cooperation Cooperation Competition Competition Competition Custom Custom Custom Those Declared in Need Highest Bidder What base values does this economy have? Type of Economy 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 21 Name: ______________________ Class: _______ Date: _______ Market Economy Organizer Directions: Provide responses for the listed items. Summarize The U.S. Economic System Describe each of the principles of The U.S. Economic System. Market Economy What are the roles of in a market economy? Consumers Producers Self-Regulating Principles of a Market Economy How does demand impact businesses? How does supply impact businesses? Examples: 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Examples: Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 22 Name ____________________ Class __________ Date __________ What is the Market Price? Activity Directions: Use the figures provided to graph the demand, supply, and market price. Determine the market price and explain the relationship between the demand and supply of the products. 1. Johnson’s Jacket Depot Demand table Quantity Price 1000 1550 2000 2500 $24 $22 $20 $18 Demand graph Supply graph Supply table Quantity Price 1000 1550 2000 2500 $18 $22 $24 $26 Use the demand and supply lines above to determine how much the jackets will cost. Graph the market price for the jackets by using the graph below. Market price graph 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 23 What is the Market Price? Activity continued Directions: Use the figures provided to graph the demand, supply, and market price. Determine the market price and explain the relationship between the demand and supply of the products. 2. 3. Software House Price per game $15 $13 $11 $9 Games demanded 15 30 45 60 Software House Price per game $13 $15 $17 $19 Games supplied 15 35 45 60 Burn’s Baby Dolls Price per doll $40 $30 $20 $10 Dolls demanded 10 20 30 40 Burn’s Baby Dolls Price per doll $20 $25 $30 $45 Dolls supplied 10 20 35 40 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 24 What is the Market Price? Activity KEY Directions: Use the figures provided to graph the demand, supply and market price. Determine the market price and explain the relationship between the demand and supply of the products. 1. Market price graph 2500 * 2000 * * * 1500 * 1000 * * $18 $20 $22 $24 $26 Market price: $22 Customers are willing to buy 1500 jackets and the business is willing to supply the jackets at $22 each. 2. Market price graph 60 * 45 * * * * 30 * 15 * * $9 $11 $13 $15 $17 $19 Market price: $14.00 Customers are willing to buy 25 games and the business is willing to supply the games at $14.00 each. 3. Market price graph 40 * * * 30 * 20 10 * * * * $10 $20 $30 $40 $45 Market price: $29.00-$29.50 Customers are willing to buy 25 games and the business is willing to supply the games at $29.00-$29.50 each. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 25 Name ____________________ Class __________ Date __________ Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle Directions: Complete the crossword puzzle. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 26 Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle Across 1. Combines elements of the command and market economies 3. The initiative to combine natural, human, and capital resources 5. Value of the next-best alternative that is forgone to produce or obtain another product 8. Businesses that offer the same goods to the same customers 11. Individuals and organizations that determine which goods and services will be available for consumption 16. Process of choosing which needs or wants will be satisfied 20. Means from which goods and services are produced 22. Right to purchase, use, and discard of things of value 23. Activities that can be consumed at the time of purchase to satisfy needs and wants 24. Condition that exists when wants or needs exceed resources available 25. Study of the decisions made for production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants 26. Necessities required for living 27. Buys and uses the goods and services Down 2. Goods and money used in the production of goods and services 4. Raw materials supplied by nature 6. People using efforts, knowledge, and skills at work to produce goods and services 7. Economic system which freedom to consume and produce goods and services exists 9. Economic system in which decisions are based on customs and centered on family 10. Items that can be purchased to satisfy needs and wants 12. Money left after selling goods and services and costs of operating a business have been paid 13. Goods that are purchased to add comfort or pleasure to life 14. Anywhere goods and services exchange hands 15. Process of giving up something for gaining something else 17. Goods and services are owned and controlled by the people 18. Opportunity to make choices of goods and services and accept consequences of decisions 19. Economics system in which the government owns resources and dictates what is produced 21. The point where supply and demand are equal Capital resources Command economy Competitors Consumer Economics Economic decision-making Economic resources Entrepreneurial resources Free enterprise Freedom of choice Goods Human resources Market economy Market price 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Marketplace Mixed economy Natural resources Needs Opportunity cost Private property Producers Profit Scarcity Services Tradeoff Traditional economy Wants Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 27 Economic Choices and Systems Key Terms Crossword Puzzle KEY Across 1. Mixed economy-Combines elements of the command and market economies 3. Entrepreneurial resources-The initiative to combine natural, human, and capital resources 5. Opportunity cost-Value of the next-best alternative that is forgone to produce or obtain another product 8. Competitors-Businesses that offer the same goods to the same customers 11. Producers-Individuals and organizations that determine which goods and services will be available for consumption 16. Economic decision-making-Process of choosing which needs or wants will be satisfied 20. Economic resources-Means from which goods and services are produced 22. Private property-Right to purchase, use, and discard of things of value 23. Services-Activities that can be consumed at the time of purchase to satisfy needs and wants 24. Scarcity-Condition that exists when wants or needs exceed resources available 25. Economics-Study of the decisions made for production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services to satisfy needs and wants 26. Needs-Necessities required for living 27. Consumer-Buys and uses the goods and services Down 2. Capital resources-Goods and money used in the production of goods and services 4. Natural resources-Raw materials supplied by nature 6. Human resources-People using efforts, knowledge, and skills at work to produce goods and services 7. Free enterprise-Economic system which freedom to consume and produce goods and services exists 9. Traditional economy-Economic system in which decisions are based on customs and centered on family 10. Goods-Items purchased to satisfy needs and wants 12. Profit-Money left after selling goods and services and costs of operating a business have been paid 13. Wants-Goods that are purchased to add comfort or pleasure to life 14. Marketplace-Anywhere goods and services exchange hands 15. Tradeoff-Process of giving up something for gaining something else 17. Market economy-Goods and services are owned and controlled by the people 18. Freedom of choice-Opportunity to make choices of goods and services and accept consequences of decisions 19. Command economy-Economics system in which the government owns resources and dictates what is produced 21. Market price-The point where supply and demand are equal. 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 28 ASSESSMENT PROTOTYPES Note: These assessment prototypes are examples of the types of items included in the item bank. All items are comparable to the cognitive process of the understand verb. Questions require students to demonstrate that they understand the content. Assessment prototypes will not be used on the secured test, but questions in similar formats will be used. Revlon, Inc. purchased new machines that will automatically squeeze the appropriate amount of shampoo into different size bottles. What type of economic resources are the machines? A. Capital B. Human C. Natural D. Service ANSWER: A Tanya closed her restaurant, and now needs another way to earn an income. Realizing this need is what part of economic decision-making process? A. Defining the problem B. Identifying choices C. Evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of each choice D. Choosing one choice ANSWER: A Eddie’s Bakery makes cakes as well as other baked goods. Which economic question does this address? A. What to produce? B. How to produce? C. For whom to produce? D. When to produce? ANSWER: A An EXAMPLE of a value for a traditional economy is: A. a central leadership group expecting all the profit from production. B. a local company choosing to produce gaming software. C. a local company upgrading procedures regularly to increase production. D. an individual performing the same jobs as his parents due to his beliefs. ANSWER: D 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 29 ASSESSMENT PROTOTYPES Continued Which is an EXAMPLE of consumers establishing demand? A. Customers waiting in line to purchase new popular boots. B. Customers waiting in line to return recalled equipment. C. Reebok footwear company trying to lease a warehouse. D. Sears Department Store displaying fewer large lawn mowers. ANSWER: A 8721 Principles of Business and Finance Summer 2010, Version 2 Page 30