Seismology & Crust
advertisement

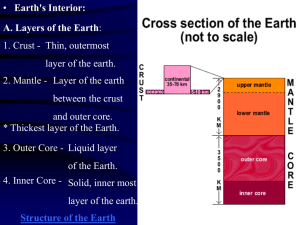
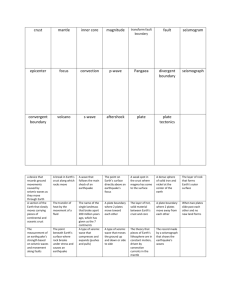
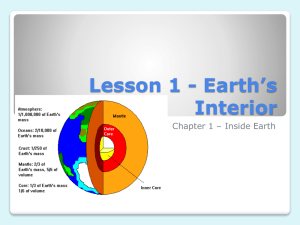
Seismology & Crust G p29 1. 2. GS p121 3. G p31 4. 5. 6. E p469 7. 8. What is a seismic discontinuity? What three things can happen to seismic waves when they reach a seismic discontinuity? Explain the reflection and refraction of seismic waves - use Figure 6.13 and Figure 2.33 in your explanation. What does the Moho seismic discontinuity represent? Explain why two sets of P and S waves are detected Explain what happens to the arrival times of these two sets of seismic waves with increasing distance from the seismic source Copy Figure 2.12a & b Compile a table summarising the characteristics of continental and oceanic crust and lithospheric mantle: Compositi P wave Density Thickness Age on velocity Continent al Crust Oceanic Crust Lithospher ic Mantle GS p122 9. What seismic discontinuity separates upper and lower continental crust? GS p128 10. What are the characteristics of upper and lower continental crust? E p471 11. Explain why the depth of the Moho varies. E p470 12. Copy Figure 18.3 and the formula for calculating crustal thickness. Page numbers refer to the pages in the following text books: G = Geoscience (Edwards & King) GS = Geological Science (McLeish) E = Earth (Press & Siever) GEOTREX | Contributor: Ben Church | Establishment: Monmouth Comprehensive School | Date: 11/04/2005