Teaching Phonetics in Indian Class Room
advertisement

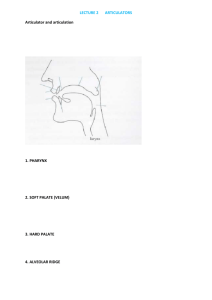
Teaching Phonetics in Indian Class Room: New Strategies THIRUPATHI VENNUM M.A., M.Ed. ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF ENGLISH KAMALA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY AND SCIENCE, SINGAPURAM HUZURABAD, KARIM NAGAR-505468 PHONE: 9848518351 E MAIL:vennumthirupathi@gmail.com ABSTRACT: English is an international language. It is the language that many Asian, African, Pacific, and other countries choose as their official or associate official language. Colonization and Globalization in all the fields make English language a unique world language rather than the language of only the English speaking countries such as the UK and the USA because the number of the people who use English as a means of communication exceeds much more than the number of the people who speak it as their mother tongue. India, more than two centuries, has been had the influence of English language on all the fields. Learning English, the universal language, as a Second Language, becomes inseparable branch as also unavoidable in Indian education System. For those who do not know Hindi or whose mother tongue is not Hindi, it is imperative that they should at least have knowledge of the English language. English is the most commonly spoken after Hindi in India. Phonetics plays an important role in communication in countries where English is a second language to attain proper pronunciation of each word and Phonetics became an inseparable component of English teacher. What is Phonetics? Why should the Indian students learn phonetics? What are the barriers in learning Phonetics? How should they overcome and learn it? Do the English teachers have to face any hurdles while teaching English phonetics? Teaching phonetics to the students in India is too difficult because various dialect problems will arise. The teacher should try to avoid the serious problems in pronunciation of the learners. The article exposes how one can easily learn phonetics. It gives the readers not only the importance of phonetics in the modern days but also tells them how to transcribe the English words in to phonemically. Key Words: CALL, Communication, Phonetics, Pronunciation, Sound and Transcription. Phonetics is one of the important branches of linguistics. As the name indicates it is a science of sounds that deals with the production of different sounds (vowel sounds, consonant sounds and semi vowel sounds), transmission of sounds and reception of the sounds of human speech. Now a day it is observed as a field of modern linguistics. Phonetics was studied as one of the sciences as early as 2000 years ago in ancient India. Since Indians have different demographics and a variety of local languages and dialects, teaching phonetics to students becomes somewhat difficult task. Although phonetics is the part of the syllabus of the students in many schools in India, it is not a separate subject. It is an internal part of English language. Many Indian students think what the constructive things are from learning pronunciation. We know that all languages are learnt with the principle speaking first writing second. Because language learning is not like teaching a subject it is a skill that requires ample practice through sufficient speaking and listening activities. If we speak in English with our local people, however the pronunciation is, it is not observable but whenever we want to communicate with others means especially foreigners, the speakers must articulate in standard pronunciation. Regarding this, P. Tench (1981:1) says that “Pronunciation is not an optional extra for the language learner, any more than grammar, vocabulary or any other aspect of language is. If a learner's general aim is to talk intelligibly to others in another language, a reasonable pronunciation is important.” The students who do not have proper awareness in pronunciation and articulation of different sounds may be weak in other skills also. If the speaker is sure that his accent is understandable, there is no problem. In order to achieve these goals, there’s no doubt, the people will need to think about pronunciation and articulation and they have to spend some time on it. Teaching English pronunciation is still abandoned in the syllabuses in tertiary education in India. Although the course writers spoil the speaking and listening activities for the learners in India especially in southern states where mother tongue dominates, they are not concentrating the importance of phonetics in the curriculum to include it as one of the main components. Till intermediate, the students in the most of the states in India do not have the phonetics in their syllabus. It is necessary to incorporate the phonetics from school studies so that the learners may habituate to articulate words in a correct way. As phonetics is not in the syllabus of high school standard in Southern places, the learners do not realize their mistakes in their pronunciation. Barriers to learn Phonetics: 1) More Theoretical sessions than activities that practical: The activities that for speaking and listening are not at all being practiced during the class and the teachers are also reluctant to get the students practice activities in front of other students where there is the scope for better perception and the time slot allotted for speaking and listening activities is very less so that students are unable to get the knowledge of the place and manner of the articulation of each sound and the knowledge of speech organs and how they are producing the sounds and the syllabus is heavy filled with reading and writing exercises. By the end of the year student is not getting sufficient listening and oral activities.whilch makes student passive in his communication skills and is not competing with the native speakers of English wherever he goes. 2) Faulty methods for teaching English language: Skill based teaching is very much in vogue in professional courses. It is really an uphill task for the language teachers to teach the phonetics for a professional student without proper orientation. They hasten with the syllabus under the pretext of syllabus completion adopting all conservative methods. Language teachers who are teaching phonetics should be well trained with some orientation programs, work shops, symposiams by language exports and not be overburdened by the syllabus. There is a need for syllabus makers to look in to the syllabus before it is set to make sure that it serves all the needs of the student to communicate even after his course. 3) Heterogeneneous class rooms: In many Indian classrooms teacher has to face the problem of multi-lingualism. And he gets the students with different demographics, with different educational backgrounds, different socio-linguistic backgrounds, different boards of educational system and different socio- economic backgrounds so the teacher finds it difficult to handle students of such varied backgrounds. Some students learn the things very quickly and some are little bit slow so the teacher takes much time to get all the students understand and he has to spend much time which requires more patience so this heterogeneity hampers the attainment of learning the standard pronunciation. The languages in India such as Hindi, Telugu, Tamil, and Kannada and Malayalam dialects interfere in their pronunciation so that the errors will generally occur in Indian pronunciation. Phonetic Transcription: In order to know what the phonetic transcription is, we have to first know what a phoneme is. A phoneme is a set of similar sounds illustrating meaning differences or differentiating between words. A syllable consists of a vowel as an essential element and one or more consonants at the onset which is pronounced with a single contraction of the lungs. The English language has twenty vowel phonemes, i.e., twelve pure vowels and eight diphthongs. We have twenty four consonant phonemes. While the vowels are articulated without any obstacle in the vocal tract, the consonants are produced with some friction of the air passage. The treatment of the segmental basically includes sound contrast in words, pronunciation of vowel and consonant phonemes. The phonemes which are not available in the learner's mother tongue and problematic to him or her and they should receive special treatment in the teaching material and methodology and sufficient room in the learner's practice. Phonetic transcription means a written or printed representation of using a phonetic alphabet. It is necessary, because the spelling of an English word does not tell us how we should pronounce it. The interesting thing is that we can not say that each alphabet gives the sound(s); sometimes two or more alphabets provide only one sound. For example employee has four vowel letters but it has three syllables and the last two letters “ee” give one sound only that is /i:/. A letter can represent many sounds such as “c” as in car /ka /, cell /sel/ and church /t?t?/ and one of the alphabets stands for a sequence of two Sounds. E.g. Quality, queen and exact. So we can say that there is no relationship between sound and spelling. Some more complexities are: 1. some words can have the same spelling but different pronunciation: I saw him at chaurasta yesterday. I saw a saw near the sea. Some words have different spelling but the same pronunciation, for example: He gave me a one rupee note. She won the cup. In the first example, both the verbs (a) and (b) “saw” give same meaning but in (b) “saw” is used as a verb and a noun. Though the pronunciation is same, it gives the different meaning whereas in the second example, “one” and “won” are pronounced same although they have different meanings. If one knows the phonetic transcriptions, one can be able to understand the correct pronunciation by looking at the transcription in the dictionary. There are two well-known dictionaries that are available in the market. One is Danial Jones English pronouncing dictionary and the other one is Oxford. Though many people think that it is very hard to learn English phonetic transcription, the learned masters utter that it is not that much difficult that we expect. As most of us do not keep our concentration on phonetics, the Indians are not good at articulation. D. Dalton (2002) rightly says: “We are comfortable teaching reading, writing, listening and to a degree, general oral skills, but when it comes to pronunciation we often lack the basic knowledge of articulator phonetics (not difficult to acquire) to offer our students anything more than rudimentary (and often unhelpful) advice.” The learners should notice improved pronunciation of individual words. Besides the students, the English teachers should also practice phonetic transcription. They should teach in RP English so that they make the learners to learn and articulate the correct Pronunciation. If they teach their classes with Indian pronunciation which is happening in India, the students may not know the RP so we would like to say that it is the onus of the English teachers to make the learners to speak in RP. They should unfold the easy methods in phonetic transcription and exemplify the differences between Indian English and R.P.How should the English teachers create the atmosphere of good pronunciation? What should the learners do to improve their pronunciation? What are the techniques that make them to learn and articulate good English? Although there are many procedures to learn phonetics, the final choice is to transcribe the words in to phonemically and give the ears to the speeches. I would like to propose a few techniques and activities that appear to be useful for learners and teachers alike: 1) Learners should be asked to read aloud the lessons in class room it self: The learner should read the paragraphs or text aloud to improve good pronunciation in the class room it self so that he will be able to overcome all his inhibitions and the domination of his mother tongue also. Teacher should try to identify the errors and mistakes in pronunciation made by the learner and immediately give feedback in such a way that how the learner pronounced that particular word or sound and what is the exact pronunciation by pronouncing himself or through some audio records which will help the learner to improve his pronunciation and for the next time he will not commit the same mistake. The classroom techniques and activities for teaching EFL pronunciation make the learners to add their talent in improving good pronunciation. J. Morley says that (1991: 507), “the teacher can perform the role of a 'speech coach' or 'pronunciation coach' who, rather than just correcting the learner's errors and mistakes, he should supply information about all the sounds, give models, offer cues, suggestions and constructive feedback about the performance, sets high standards, provides a wide variety of practice opportunities, and overall supports and encourages the learner.” 2) Designing communicative Activities: The teacher should design communicative tasks so that he directly or sometimes indirectly improves the learners’ pronunciation as well as speaking skills. The dialogues, mini-conversations and different role plays using the variety of different daily situations for both young and adult EFL learners according to their linguistic level to practice particular sounds, especially those which are not available in their mother tongue. Pronunciation while participating in different role plays, mock debates, group discussions, rehearsal strategies and cover strategies will help the learners to develop their pronunciation and to know how the different sounds are pronounced by other individuals to attain standard frequency and pitch in pronunciation and give the impression that their pronunciation is better than it really is. 3) Making the use of Dictionary: An authentic dictionary provides the meaning as well as phonetic transcription of every word using the standard 44 sounds in phonetics so that learners by looking at different words in the dictionary, will be in the position to distinguish difference among the all sounds. Dictionary enables the learner phonetic transcription including syllable division (dividing words in to different syllables i.e. syllabification) and stress mark (Primary stress and secondary stress). As they see the phonetic transcription, they easily find out the correct pronunciation and easily understand the one to one correspondence of phonemes. When they learn one to one correspondence of phonemes they won’t confuse while using the same sounds in their communication. In this way the dictionary not only serves them to improve the phonetic transcription, command over different sounds but also provides vocabulary and grammar. At present some famous dictionaries available in the market they are “Danial Jones English pronouncing dictionary”, “Oxford English Dictionary (4th Edition)”, “Cambridge English Pronouncing Dictionary (18th Edition)” etc... 4) Repeating the Sounds: Pronunciation is very important in making English and non English native speakers understand the message what we want to convey so learners have to pay close attention to pronunciation and listening activities provided in the classroom as well as in the daily life as early as possible. In order to attain standard pronunciation learners should repeatedly practice the activities relating speaking and listening. By using and repeating the sounds, one can easily remember the correct articulation. Whenever the learners eloquent a word frequently, they can easily remember its pronunciation and phonetic transcription. 5) Self-learning: When the learners practice the phonetic transcriptions and pay the attention to the pronunciation of each sound and the phonetics, the improvement will be come in their articulation. Self-monitoring is also the important action of listening to one's own speech in order to find out mistakes. It is followed by self-correction standing for the process of fixing one's inaccuracy after they have occurred by repeating the word or phrase correctly. If we teach the learners self monitor, we make them to learn sufficiently as they and we expect. The class will be more effective if the learners are able to give feedback regarding their participation and their pronunciation in different role plays, mock debates, group discussions, rehearsal strategies and cover strategies. And giving some model audio records to practice at their homes on their own and asking about their practice in the class room will also make learners more enthusiastic and we can develop their eagerness towards learning standard pronunciation. when the self learning is motivated automatically their practical learning in the class room will also be strengthened. 6. Computer Assisted Language Learning: Computer-assisted language learning plays a significant role in helping the students in learning phonetics. It provides the students to find out their mistakes through using Computer. Today different soft wares are available in the market to learn on computers the standard pronunciation and the other comprehensive skills which are required to compete with the English sounded competitors and to take part effectively in the different phonetics related entrance examinations. If learners want make use of the computer they get many benefits by it. They will be monitored, guided and given full of freedom. It keeps the learners concentration on learning. In addition, the teacher can exploit visual displays of speech patterns to teach intonation, stress and phonemes to individuals and small groups of learners. This tool can be used for all the learners. Conclusion: I conclude that phonetics is one of the important components in English language. With few techniques we can teach effectively in Indian classroom. Learning phonetics is nothing but getting mastery over speaking skill of English and is eloquent in a language. The syllabus designers are not incorporating sufficient listening and speaking activities relating the phonetics in English curriculum so they have to be reminded that phonetics is also compulsory constituent in speaking a second language. More pronunciation materials should be added in the classroom activities so that the learners will come to know the importance of phonetics and will be able to compete in different debates, Group Discussions and Interviews effectively. The techniques and activities that are presented in this article surely bring high-quality articulating abilities and wonderful listening perception. Bibliography: A.S. Hornby, Oxford: OUP, 2007. Danial Jones, Cambridge: CUP, 2006. D. Dalton, “Some Techniques for Teaching Pronunciation,” Retrieved May 1, 2002, J. Morley, “The Pronunciation Component in Teaching English to Speakers of other Languages,” Quarterly, 25:3 (1991): 481-520. P. Tench, London and Basingstoke: Macmillan, 1981. Brownlee-Conyers, J. “Voices from Networked Classrooms.” Educational Leadership. 54.3 (1996): 34-37. Ellis, R. “Planning and Task-based Performance: Theory and Research.” Planning and Task Performance in a Second Language. Ed. R. Ellis. Amsterdam: John Benjamins Publishing Company, 2005. 3-34. Nation, P. Creating, Adapting and Using Language Teaching Techniques. Occasional Publication: Victoria University of Wellington, 2000. Prabhu, N. S. Second Language Pedagogy. Oxford: OUP, 1987.