Paper Bag Pet Project Worksheets
advertisement

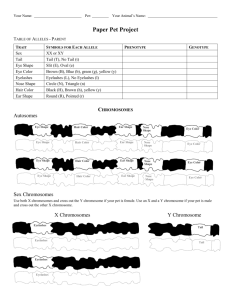
Your Name: Per: Your Animal’s Name: Paper Bag Pet Project TABLE OF ALLELES TRAIT Sex Tail Eye Shape Eye Color Eyelashes Nose Shape Hair Color Ear Shape SYMBOLS FOR EACH ALLELE XX or XY Tail (T), No Tail (t) Slit (E), Oval (e) Brown (B), Blue (b), green (g), yellow (y) Eyelashes (L), No Eyelashes (l) Circle (N), Triangle (n) Black (H), Brown (h), yellow (y) Round (R), Pointed (r) PHENOTYPE GENOTYPE CHROMOSOMES Autosomes Eye Shape Hair Color Ear Shape Nose Shape Eye Color Eye Shape Hair Color Ear Shape Nose Shape Eye Color Eye Shape Hair Color Ear Shape Nose Shape Eye Color Eye Shape Hair Color Ear Shape Nose Shape Eye Color Sex Chromosomes Use both X chromosomes and cross out the Y chromosome if your pet is female. Use an X and a Y chromosome if your pet is male and cross out the other X chromosome. X Chromosomes Eyelashes Eyelashes Eyelashes Eyelashes Y Chromosome Tail Tail Instructions 1. Fill in the phenotype for each trait in the Table of Alleles based on the characteristics of your paper bag pet. 2. Fill in a valid genotype for each phenotype in the Table of Alleles. Select the allele for each genotype based on the method your teacher specifies. 3. Complete the chromosomes for your paper bag pet by filling in the alleles for each trait in the slot for each gene. (Use the chromosomes drawn with a solid line and ignore the dotted lines for now.) 4. Note that the eyelash trait and the tail trait are both sex-linked. The eyelash gene occurs on the X chromosome so male paper bag animals only inherit one copy. The tail gene occurs on the Y chromosome so female paper bag animals can never have tails since they do not have Y chromosomes. 5. Create gametes for your paper bag pet (eggs or oocytes for females and sperm or spermatocytes for males) by performing the primary steps of meiosis: 1) DNA replication – Fill in the dotted-line copy of each chromosome and then cut out each chromosome pair being careful to keep them connected at their centromeres. 2) Crossing Over - Line up each homologous chromosome pair with the other (autosome next to autosome, sex chromosome next to sex chromosome) and randomly exchange segments of the chromosomes between each pair by making cuts and then taping the pieces to the homologous chromatid. 3) Random Assortment – divide the homologous chromosomes from one another by randomly grouping each autosome with one of the sex chromosomes resulting in the formation of two diploid cells. 4) Second Cell Division - divide the sister chromatids from one another in both cells by carefully cutting them apart at the centromere and then randomly grouping each autosome with one of the sex chromosomes resulting in the formation of four genetically unique haploid cells. Names: Period: Date: Predict the phenotypes of your offspring. Sex Tail Male: _______% Tail: _______% Slit: _______% Female: _______% No Tail: _______% Oval: _______% Nose Shape Ear Shape Eye Shape Eyelashes Circle: _______% Round: _______% Eyelashes: _______% Triangle: _______% Pointed: _______% No Eyelashes: _______% Eye Color Hair Color Names: Period: Date: Predict the phenotypes of your offspring. Sex Tail Male: _______% Tail: _______% Slit: _______% Female: _______% No Tail: _______% Oval: _______% Nose Shape Ear Shape Eye Shape Eyelashes Circle: _______% Round: _______% Eyelashes: _______% Triangle: _______% Pointed: _______% No Eyelashes: _______% Eye Color Hair Color Brown: _______% Black: _______% Blue: _______% Brown: _______% Green: _______% Yellow: _______% Yellow: _______% Birth Certificate This document certifies that was born this Child’s Name day of in the year Birth Date in the city of Birth Month Birth Year in the great state of California to Birth City born in Mother’s Birth City/State Mother and to Signature of Mother born in Father Father’s Birth City/State Signature of Father .