Smog in Canada - Map & Article
advertisement

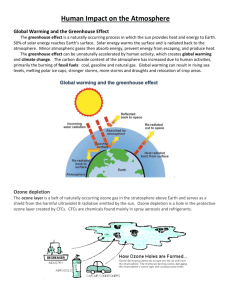
Blowin' in the wind Canada's smoggiest places GET OUT YOUR GAS MASKS: May is the beginning of smog season, which lasts until September. Smog is caused largely by the burning of fossil fuels in power plants, factories, homes and vehicles. It is made up of fine airborne particles, which combine with sulphur dioxide and other chemicals, and ground-level ozone, a colourless gas that forms when nitrogen oxides and volatile organic compounds react in sunlight. As our map shows, much of the pollution that causes smog drifts north from sources in the United States. New research suggests there is no safe level of exposure to airborne particles or ozone at street level (as opposed to the ozone in the stratosphere that protects us from the sun's radiation). Windsor to Quebec City This region has the worst air quality in Canada. While much of the smog is generated locally, about 50 percent of the ozone comes from the Ohio Valley and the Cleveland and Detroit areas. Canada is negotiating with the United States to reduce the cross-border flow of air pollutants. The hot, stagnant summer weather in central Canada is perfect for ground-level ozone formation, with smog blanketing large urban and rural areas for several days at a time. Ontario's five coal-fired power plants are the province's largest industrial source of air pollution. Atlantic Canada Around the Bay of Fundy, southern New Brunswick and parts of Nova Scotia southwest of Halifax, 50 to 80 percent of the smog is caused by cross-border pollution from the northeastern United States or emissions from central Canada. Smog is concentrated around the Saint John, N.B., region, where local sources of sulphur dioxide include a large petroleum refinery, two oil-fired generating stations and several pulp-and-paper mills. Calculating the costs Approximately 5,000 people a year die prematurely as a result of air pollution, according to a study of 11 Canadian cities. Almost one in 12 of all non-accidental deaths in Canada can be attributed to air pollution. Air pollution increases the number of emergency-room visits and cardiac and respiratory hospital admissions. Ground-level ozone causes inflammation of the airways that can persist for up to 18 hours after exposure, while airborne particles penetrate deeply into the lungs, causing irritation Most vulnerable to the effects of air pollution are the elderly, anyone with an underlying illness and children, whose still-developing lung tissue is more sensitive to pollutants. More than half of all Canadians live where ground-level ozone can reach unacceptable levels in summer. Every major Canadian city has levels of airborne particles high enough to constitute a health risk. The Ontario Medical Association states that the components of air pollution "pose a serious health risk to the people of Ontario." The health benefits from improving air quality in Canada are estimated to be worth $8 billion over 20 years. Rank by amount of ground-level ozone Rank by amount of particulate matter 1 Kitchener, Ont. 5 2 Toronto, Ont. 7 3 Windsor, Ont. 3 4 Simcoe. Ont. 11 5 Hamilton, Ont. 10 6 Egbert, Ont. 4 7 Montréal, Que. 1 8 St. Catharines, Ont 6 9 Kejimkujik, N.S. 7 10 Oshawa, Ont. 22 11 Halifax, N.S. 13 12 Québec, Que. 18 13 Saint John, N.B. 7 14 Vancouver, B.C. 16* 15 Calgary, Alta. 11 16 Kamloops, B.C. 1 17 Prince George, B C. 22 18 Winnipeg, Man. 15 19 Chilliwack, B.C. 14 20 Kelowna, B.C. 21 21 Nanaimo, B.C. 18 22 Victoria, B.C. 18 23 St. John's, Nfid. 17 24 Ottawa, Ont. 24 *1997 data, all else: 1998 data Includes all locations for which ground-level ozone and fine-airborne-particulate data (PM2.5) are collected. (Canada Wide Standards) SOURCES: NATURAL RESOURCES DEFENSE COUNCIL (BENCHMARKING AIR EMISSIONS OF ELECTRIC UTILITY GENERATORS IN THE EASTERN U.S.); ENVIRONMENT CANADA; HEALTH CANADA; ONTARIO POWER GENERATION; NOVA SCOTIA POWER; POLLUTION PROBE; ONTARIO CLEAN AIR ALLIANCE; ONTARIO MEDICAL ASSOCIATION; DAVID SUZUKI FOUNDATION