organic reactions - A
advertisement

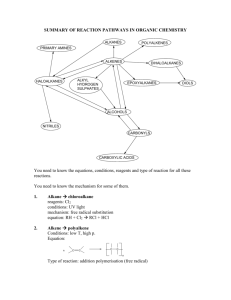
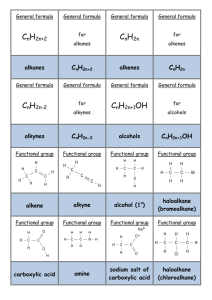
SUMMARY OF REACTION PATHWAYS IN ORGANIC CHEMISTRY ALKANES POLYALKENES PRIMARY AMINES ALKENES DIHALOALKANES ALKYL HYDROGEN SULPHATES HALOALKANES EPOXYALKANES DIOLS ALCOHOLS NITRILES CARBONYLS CARBOXYLIC ACIDS You need to know the equations, conditions, reagents and type of reaction for all these reactions. You need to know the mechanism for some of them. 1. Alkane chloroalkane reagents: Cl2 conditions: UV light mechanism: free radical substitution equation: RH + Cl2 RCl + HCl 2. Alkene polyalkene Conditions: low T, high p. Equation: n C C C C n Type of reaction: addition polymerisation (free radical) 3. Alkene bromoalkane Reagent: HX(g) Conditions: room T Equation: C + C H Br C C Br H Type of reaction: electrophilic addition 4. Alkene dibromoalkane Reagent: Br2 in water or in an organic solvent Conditions: room T Equation: C + C Br Br C C Br Br Mechanism: electrophilic addition 5. Alkene alkylhydrogensulphate Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid Conditions: cold Equation: C + C H OSO3H C C H OSO3H Mechanism: electrophilic addition 6. Alkylhydrogensulphate alcohol Reagent: water Conditions: warm Equation: C C H OSO3H + H2O Type of reaction: hydrolysis 7. Alkene alkane Reagent: hydrogen Conditions: 150 oC, Ni catalyst Equation: C C + H H Type of reaction: hydrogenation C C H H C C H OH + H OSO3H 8. Alkene alcohol Reagent: steam Conditions: 300 oC, 60 atm, H3PO4 catalyst Equation: C + C H H O C C OH H Type of reaction: hydration 9. Alkene epoxyalkane Reagent: oxygen Conditions: 300 oC, silver catalyst Equation: O C C + 1/2 O O C C Type of reaction: oxidation 10. Epoxyalkane diol Reagent: water Conditions: 60 oC, H2SO4 catalyst Equation: O C C + H H O Type of reaction: hydrolysis 11. Haloalkane alcohol Reagent: NaOH(aq) or KOH(aq) Conditions: warm under reflux Equation: R-X + OH- R-OH + XType of reaction: nucleophilic substitution 12. Haloalkane nitrile Reagent: KCN in aqueous ethanol Conditions: boil under reflux Equation: R-X + CN- R-CN + XType of reaction: nucleophilic substitution 13. Haloalkane Amine Reagent: ammonia in ethanol in a sealed tube Conditions: heat Equation: R-X + 2NH3 R-NH2 + NH4X Type of reaction: nucleophilic substitution HO C C OH 14. Haloalkane alkene Reagent: KOH in ethanol Conditions: heat Equation: H R C R R C R R C X C X + R R R + Type of reaction: elimination 15. Primary alcohol aldehyde Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid Conditions: warm, distillation Equation: RCH2OH + [O] RCHO + H2O Type of reaction: mild oxidation 16. Secondary alcohol ketone Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid Conditions: heat, distillation Equation: R1CH(OH)R2 + [O] R1COR2 + H2O Type of reaction: oxidation 17. aldehyde carboxylic acid Reagent: potassium dichromate and dilute sulphuric acid Conditions: heat, reflux Equation: R-CHO + [O] R-COOH Type of reaction: oxidation 18. Alcohols alkenes Reagent: concentrated sulphuric acid Conditions: heat Equation: C C H OH Type of reaction: elimination 19. glucose ethanol reagent: yeast conditions: 35 – 55 oC, no air equation: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 type of reaction: fermentation C C + H2O H2O