Cornell Notes Topic: STUDY GUIDE Section 5
advertisement

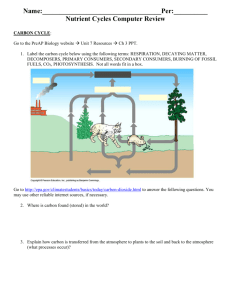
Cornell Notes Topic: STUDY GUIDE Section 5-2 NUTRIENT CYCLES Name: ___________________________ Period: __________________________ Date: ____________________________ Essential Question: Describe how the cycling of materials is accomplished in huge cycles called Biogeochemical Cycles. Questions: Notes: 1. The carbon that is taken in by an organism during photosynthesis is then converted into which type of substance? 1. Page 117 Figure 1.1. 2. Which of these is NOT a way in which nitrogen may enter the soil? 2. Page 126. - Nitrogen enters the soil by: 3. Which of the following may form when carbon from decayed organic matter is buried in the right geological conditions? 3. Page 125. __________ __________ are made up of carbon compounds from the bodies of organisms that died millions of years ago. 4. In the global carbon cycle, carbon appears primarily in coal, oil, and natural gas deposits when found in 4. Page 125. - These molecules can form deposits of coal, oil, and natural gas underground. The deposits are known as _________ ________ . 5. During the carbon cycle, carbon in ocean reservoirs appears primarily as 5. Page 124. - Some carbons enter a long-term cycle. For example, carbon may be converted into ___________, which make up the hard parts of bones and shells. 6. The relative residence time of carbon between coal deposits and the atmosphere is relatively 6. Long because the geological processes that form and oxidize coal are relatively slow. 7. The relative residence time of carbon as it cycles between biomass and atmosphere reservoirs is relatively 7. Short because the processes of photosynthesis and respiration are relatively fast. 8. If the relative residence time of carbon in a reservoir is long, then the processes that drive carbon movement from one reservoir to another in the carbon cycle are MOST likely 8. relatively slow. 9. Human activities, like mining and burning fuel, causes the relative residence time of carbon in coal, oil, and fossil fuel to be 9. shorter than its relative residence time would be under natural conditions. 10. An example of Earth's external sources of energy driving the movement of carbon among reservoirs is 10. Page 117 Figure 1.1 - During ___________, plants use light energy from the _____ to make __________ 6CO2 + 6H2O ------> _____________ + 6O2 _________ __________ _________ can fix atmospheric nitrogen into a useful form called ammonia. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in nodules on the ______ of _______ called legumes. Decomposers are essential to the nitrogen cycle because they break down wastes, such as urine, dung leaves, and __________ _________ and _________ and return the nitrogen to the soil. 11. In various physical and chemical forms, carbon cycles through different reservoirs on Earth. In which reservoir does carbon primarily appear as carbon dioxide gas? 11. Page 125 Figure 2.2 Carbon Emissions This truck releases carbon into the _____________ when it burns fuel to operate. 12. In the nitrogen cycle, nitrogen moves through different processes in various reservoirs on Earth. During nitrogen fixation, bacteria 12. Page 126 - Nitrogen-fixing bacteria, can fix atmospheric nitrogen into a useful form called _________ . 13. In plants and animals, carbon cycles through molecular processes that store and release energy in various molecular forms. In these plant and animal molecular processes, carbon is found in 14. Which of the following is the primary external source of energy behind the water cycle? 15. The oceans and marine organisms play a role in the carbon cycle. When marine organisms die, they settle to the floor to become limestone. If the limestone is exposed at the surface where chemical weathering takes place __________ is produced. 16. Human activities have an effect on the concentration of all of the following atmospheric gases EXCEPT __________. 17. Increased global temperatures have been attributed to increased level of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. All of the following lead to an increased amount of carbon dioxide entering the atmosphere except 18. Animals get their daily nitrogen requirements from __________. 19. Conversion of nitrate ions to gaseous nitrogen by bacteria is __________. 20. The uptake of nitrate ions by plants is __________. 13. Page 124 - As shown in Figure 2.1, carbon enters a shortterm cycle in an ecosystem when producers, such as plants, convert ________ _________ in the atmosphere into _______________ during photosynthesis. 14. Page 73. The continuous movement of water into the air, onto land, and then back to water sources is known as the ______ ______. Evaporation is the process by which liquid water is heated by the _____ and then rises into the atmosphere as water vapor. 15. Page 124 - Limestone is one of the largest _______ sinks, or __________ reservoirs on Earth. 16. Page 125 - Greenhouse gases, including _______ ________ and other gases, absorb and re-radiate infrared energy, warming Earth. 17. Page 125 - Each year, about 8.4 billion metric tons of _______ _________ are released into the atmosphere by the burning, or combustion of ________ _______ and the natural burning of _______ in forest fires. Volcanic activity also leads to an increase of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. 18. Page 126 – Animals get nitrogen by eating _______ or other _________, both of which are sources of usable nitrogen. 19. Your Notebook, Nitrogen Cycle Description: Nitrogen returns to atmosphere by: _________________ bacteria. 20. Assimilation. Summary: The cycling of materials is accomplished in huge cycles called Biogeochemical Cycles..