Corals: Landlords of the Reefs
advertisement

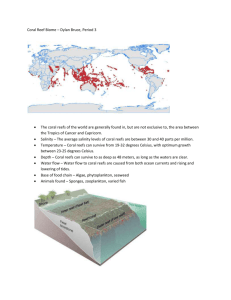
Corals: Landlords of the Reefs What should you know about corals? They are _________________________ _______________live inside of them (________________________________) Two kinds: Soft corals and Hard corals (These build reefs!) They are made of tiny __________ (which look like __________________________) Hard Corals: The Reef Builders. Polyps build hard _____________________________ around their bases. The cups cement together to make a coral colony. Reefs are made of hundreds of hard coral colonies next to and on top of each other. What’s a Polyp? Tentacles release stinging cells when something brushes by them. Polyps make their own limestone cup to hide in during the day. At night, polyps come out to catch plankton floating by. Inside polyps live zooxanthellae, which are _____________. Zooxanthellae give corals their color. Since algae are plants, they use ______________________________ to make food (the process known as photosynthesis). Symbiosis: So Happy Together. ______________________________________________ is called symbiosis. Zooxanthellae: __________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________. Coral polyps protect the zooxanthellae, ______________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________. Reefs: A prominent feature of _____________________________ marine settings is the reef. Reefs are natural structures of rock formed by ______________________________. Today’s reefs are largely made by corals, but in the geological past, have been constructed by ____________________________________________________. Reef-building organisms build skeletons of ___________________________________ in the form of ____________________________________________________. Coral reefs are often called the “________________________________” due to the great diversity of creatures that form them. Note that the brilliant colours apparent in corals are from the microscopic algae in the coral tissues (different colours absorb different wavelengths of light) Conditions necessary for reef development Large reefs are limited to the _________________ seawater areas of the _____________. Calcium carbonate is easier to precipitate in warm water than in cold water. Secretion of calcium carbonate is aided by microscopic cells of algae that live in the tissues of reef builders (the algae remove carbon dioxide from the tissues, decreasing the acidity of the water). Reefs also tend to preferentially form in areas where: 1. Little _________________________________________________________ (such sediment particles smother reef builders). 2. Nutrient levels are _____________________. 3. Water is _______________________. Reef builders are zoned in a reef according to their form (encrusting forms tend to dominate the reef crest where wave action is strongest, while more delicate branching forms are confined to deeper water zones where water action is more gentle) A _________________________ can develop behind a reef, where it is protected from strong waves An atoll is a: ____________________________________________________________. It is likely that Gilligan’s Island was set in a partially formed atoll. An atoll is formed first as a reef that fringes a volcanic island. As the island sinks (after volcanic activity has ceased and the crust has cooled, becoming denser), the reef continues to build upward, eventually ending up as a ring-shaped structure. Great Barrier Reef Overview Located in the Coral Sea on the coast of ______________________________________ Largest Reef System in the world consisting of __________ individual reefs surrounding ______________ islands. ____________________ km long with an area of 344,400 km2 Consists of ______________ species of hard and soft corals and supports 10 of thousands of other species. Reef Building Processes: Reef formation begins with Fringing Reefs Fringing Reefs generally form on: ___________________________________________, but are inhibited by an influx of freshwater and river sediment. Eventually enough reef is formed to become a barrier reef.