Final Exam Review Sheet
advertisement
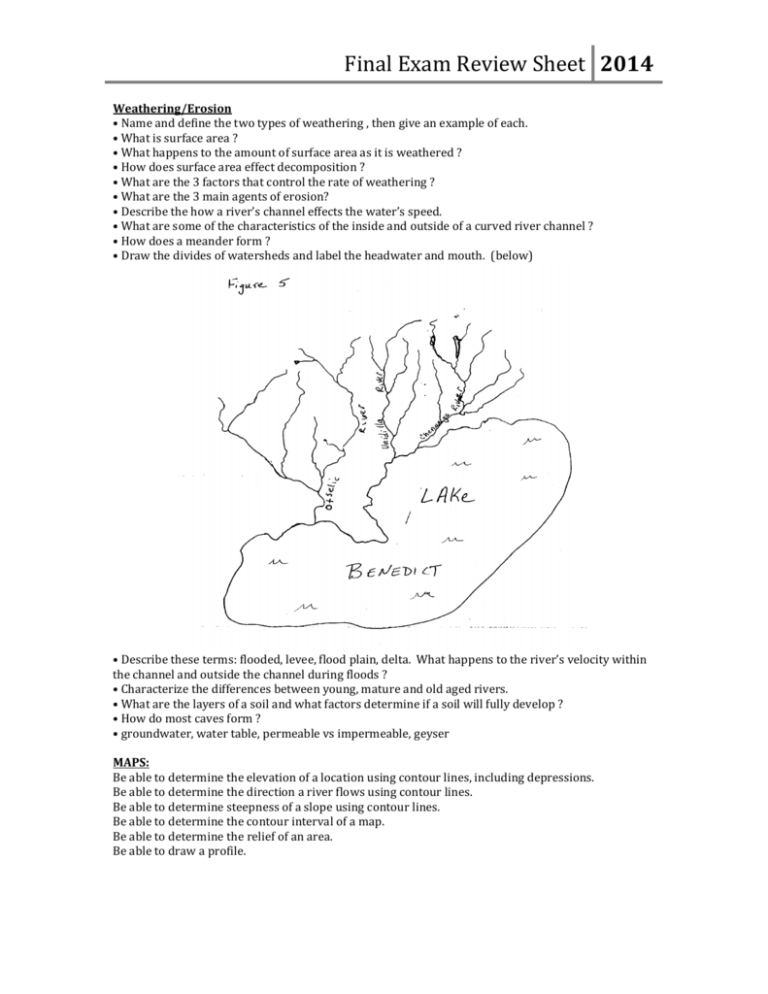
Final Exam Review Sheet 2014 Weathering/Erosion • Name and define the two types of weathering , then give an example of each. • What is surface area ? • What happens to the amount of surface area as it is weathered ? • How does surface area effect decomposition ? • What are the 3 factors that control the rate of weathering ? • What are the 3 main agents of erosion? • Describe the how a river’s channel effects the water’s speed. • What are some of the characteristics of the inside and outside of a curved river channel ? • How does a meander form ? • Draw the divides of watersheds and label the headwater and mouth. (below) • Describe these terms: flooded, levee, flood plain, delta. What happens to the river’s velocity within the channel and outside the channel during floods ? • Characterize the differences between young, mature and old aged rivers. • What are the layers of a soil and what factors determine if a soil will fully develop ? • How do most caves form ? • groundwater, water table, permeable vs impermeable, geyser MAPS: Be able to determine the elevation of a location using contour lines, including depressions. Be able to determine the direction a river flows using contour lines. Be able to determine steepness of a slope using contour lines. Be able to determine the contour interval of a map. Be able to determine the relief of an area. Be able to draw a profile. Final Exam Review Sheet 2014 ABSOLUTE DATING Element "L" has a half life of 7 years. Element "L" decays into element "P". Which element is the daughter element ? Which element is the parent element ? What is the half-life of this radioactive isotope ? What percentage of "L" is left after 35 years ? What percentage of "P" is there after 21 years ? How many half lives does it take to get "L" down to 6.25% ? What percentage of "L" is left after 14 years ? If there was an original mass of 52 grams of L, how many grams would remain after 3 half-lives ? How many half lives does it take to get "L" down to 3.125% ? RELATIVE DATING What is an unconformity ? Starting with #1, label the rock layers, intrusion, and unconformities from oldest to youngest. VIRGINIA GEOLOGY • Which province contains the youngest rocks ? • Which province contains the oldest rocks ? • Which province contains coal deposits ? • Which province contains karst topography ? • Which province do we live in ? • Which province contains the youngest rocks ? • How is it possible to have billion year old rock exposed at the top of mountains ? • What is the Fall Line ? Why are major cities located near the Fall Line ? • List each of the geologic provinces of Virginia and give 2-3 characteristics of each. Final Exam Review Sheet 2014 ROCKS Define each of the mineral properties and characteristics- luster, streak, hardness Diagram the entire rock cycle. igneous rock Explain the difference between intrusive & extrusive. sedimentary Explain the difference between clastic vs chemical & organic. Explain why fossils are found only in sedimentary rocks. metamorphic Explain the difference between foliated & nonfoliated. Plate Tectonics • Alfred Wegener Continental Drift- Pangaea (250 mybp) ° Similar fossils- "lystrosaurus" ° Rock structures- Appalachians ° Fit of continents- South America and Africa • Glomar Challenger 1960's ° the Atlantic Ocean floor ° Sea-Floor Spreading • Plate Tectonics ° Plates lithosphere, asthenosphere ocean vs continental plates- baslt vs granite ° Convergent Boundariesocean vs. ocean- island arc, Japan continent vs. ocean- volcanic mountain chain, Andes continent vs. continent- folded mountains, Himalayan Mountains subduction zone, trench ° Divergent Boundaries rift- Mid-Ocean Ridge and Rift Valley in Eastern Africa ° Transform Faults- San Andreas Fault • earthquakes where they occur, what causes them fracture vs fault intensity vs magnitude focus vs epicenter P- wave vs S- wave vs surface waves locating the focus using triangulation • earth’s interior layers- crust, mantle, cores • Hot Spot- Hawaii is forming and it is not at a plate boundary • What are the 2 types of eruptions ? What are the 3 types of volcanic mountains ? Final Exam Review Sheet 2014 Answer the next questions using the following charts: What is the apparent magnitude of the sun ? What is the apparent magnitude of Jupiter ? How much brighter is the moon than Jupiter ? Can a 15 cm telescope see an object with an apparent magnitude of 18.5 ? Our sun is what color ? Be able to determine the elements a star consists of when given the its spectral lines. The apparent magnitude of a star tells you how bright the star is as viewed from _________ On the H-R Diagram which group do most stars fall? Blue stars are ________than red stars. What factor determines a star’s color ? Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of _______ Approximately 10% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of______ We can “see” about ____% of the stuff that the universe is composed of. “Dark Matter” may account for _____% of the universe. In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ______ and________ The most widely held astronomical theory about the origin of the universe is the ______ theory. The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are ________ Diagram the correct sequence of a star’s life cycle. Final Exam Review Sheet 2014 Using the H-R Diagram below, answer the following questions: White dwarfs have _______temperature and _______ absolute magnitudes Red giants have ________temperature and _______ absolute magnitudes A star with an absolute magnitude of -6 is ________than a star with an absolute magnitude of +2.











