Review Sheet - Part II
advertisement
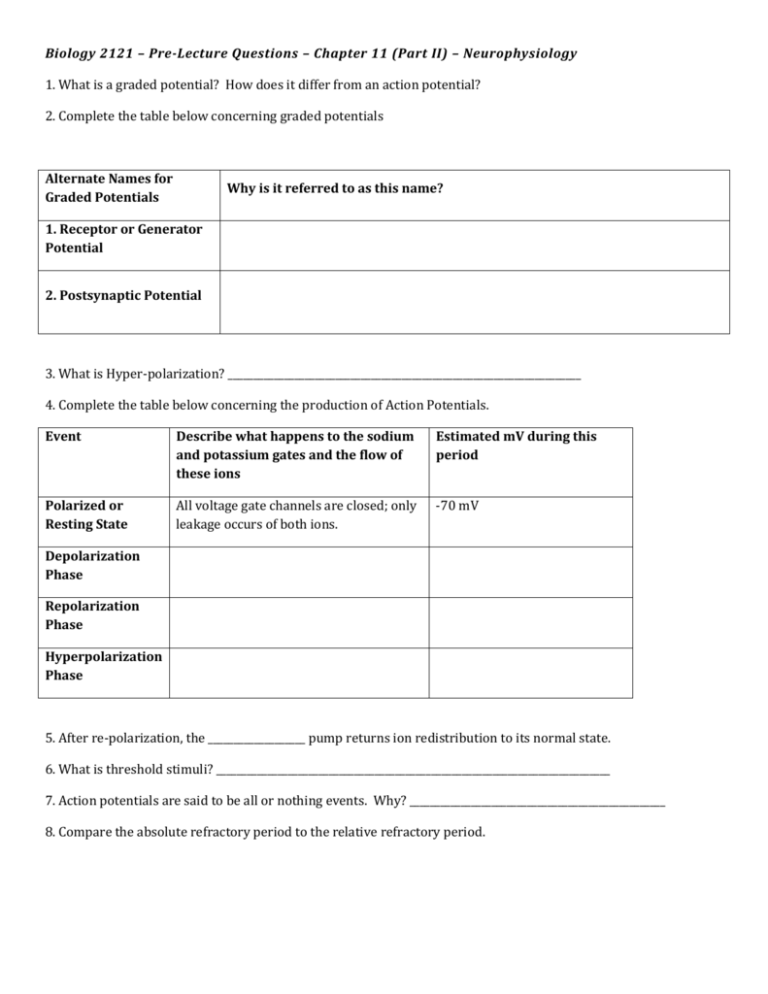
Biology 2121 – Pre-Lecture Questions – Chapter 11 (Part II) – Neurophysiology 1. What is a graded potential? How does it differ from an action potential? 2. Complete the table below concerning graded potentials Alternate Names for Graded Potentials Why is it referred to as this name? 1. Receptor or Generator Potential 2. Postsynaptic Potential 3. What is Hyper-polarization? _____________________________________________________________________ 4. Complete the table below concerning the production of Action Potentials. Event Describe what happens to the sodium and potassium gates and the flow of these ions Estimated mV during this period Polarized or Resting State All voltage gate channels are closed; only leakage occurs of both ions. -70 mV Depolarization Phase Repolarization Phase Hyperpolarization Phase 5. After re-polarization, the ___________________ pump returns ion redistribution to its normal state. 6. What is threshold stimuli? _____________________________________________________________________________ 7. Action potentials are said to be all or nothing events. Why? __________________________________________________ 8. Compare the absolute refractory period to the relative refractory period. 9. Complete the table concerning conduction velocity of neurons below: Characteristics Describe conduction velocity (fast, slow, actual velocity, etc.) 1. Axon has a wide diameter 2. Axon diameter is narrow 3. Axon is heavily myelinated 4. Axon is unmyelinated 10. Complete the table based on the axon diameter, mylenation and type of neuron. Classification Examples Diameter Myelination Velocity Group A Fibers Large diameters Heavy 150 m/s Somatic sensory and motor fibers Group B Fibers Group C Fibers 11. Distinguish between a presynaptic and postsynaptic neuron. ________________________________________________________ 12. Distinguish between a chemical and electrical synapse below: 13. Complete the tables concerning the following neurotransmitters Chemical Neurotransmitter Classification 1. Acetylcholine Acetylcholine Functional Class Excitatory – always with skeletal muscles Inhibitory or Excitatory with Smooth Muscles Site – Secreted From CNS – Brain and Brain Stem Comments Acetylcholinesterase enzyme that breaks down ACh is blocked by nerve gas PNS – Neuromuscular The release of this enzyme is also Junctions inhibited by the bacteria which produces the botulinum toxin CNS only 2. Histamine 3. ATP 14. Complete the table concerning Neural Integration below: Question Description 1. What is a neuronal pool? 2. What is a diverging circuit 3. What is a converging circuit? 4. What is a reverberating circuit? 5. What is a parallel afterdischarge circuit? 15. Compare serial process and parallel processing. Which are associated with spinal reflexes? Example (if applicable)