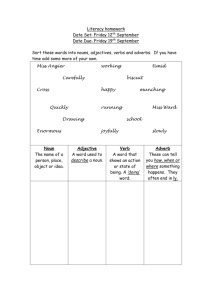
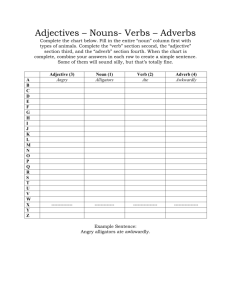
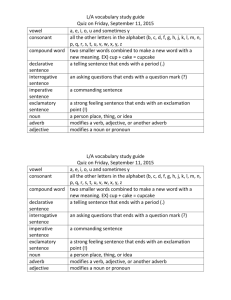
COMPARISON IN ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS
advertisement
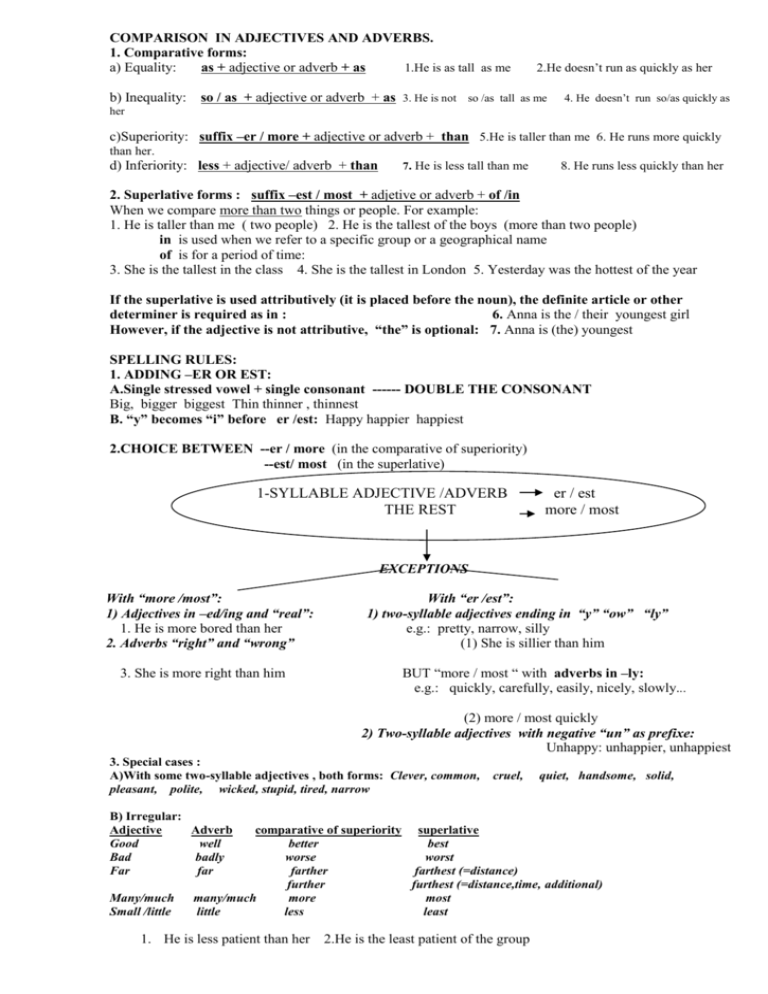
COMPARISON IN ADJECTIVES AND ADVERBS. 1. Comparative forms: a) Equality: as + adjective or adverb + as 1.He is as tall as me b) Inequality: 2.He doesn’t run as quickly as her so / as + adjective or adverb + as 3. He is not so /as tall as me 4. He doesn’t run so/as quickly as her c)Superiority: suffix –er / more + adjective or adverb + than 5.He is taller than me 6. He runs more quickly than her. d) Inferiority: less + adjective/ adverb + than 7. He is less tall than me 8. He runs less quickly than her 2. Superlative forms : suffix –est / most + adjetive or adverb + of /in When we compare more than two things or people. For example: 1. He is taller than me ( two people) 2. He is the tallest of the boys (more than two people) in is used when we refer to a specific group or a geographical name of is for a period of time: 3. She is the tallest in the class 4. She is the tallest in London 5. Yesterday was the hottest of the year If the superlative is used attributively (it is placed before the noun), the definite article or other determiner is required as in : 6. Anna is the / their youngest girl However, if the adjective is not attributive, “the” is optional: 7. Anna is (the) youngest SPELLING RULES: 1. ADDING –ER OR EST: A.Single stressed vowel + single consonant ------ DOUBLE THE CONSONANT Big, bigger biggest Thin thinner , thinnest B. “y” becomes “i” before er /est: Happy happier happiest 2.CHOICE BETWEEN --er / more (in the comparative of superiority) --est/ most (in the superlative) 1-SYLLABLE ADJECTIVE /ADVERB THE REST er / est more / most EXCEPTIONS With “more /most”: 1) Adjectives in –ed/ing and “real”: 1. He is more bored than her 2. Adverbs “right” and “wrong” 3. She is more right than him With “er /est”: 1) two-syllable adjectives ending in “y” “ow” “ly” e.g.: pretty, narrow, silly (1) She is sillier than him BUT “more / most “ with adverbs in –ly: e.g.: quickly, carefully, easily, nicely, slowly... (2) more / most quickly 2) Two-syllable adjectives with negative “un” as prefixe: Unhappy: unhappier, unhappiest 3. Special cases : A)With some two-syllable adjectives , both forms: Clever, common, pleasant, polite, wicked, stupid, tired, narrow cruel, B) Irregular: Adjective Adverb Good well Bad badly Far far Many/much Small /little quiet, handsome, solid, comparative of superiority superlative better best worse worst farther farthest (=distance) further furthest (=distance,time, additional) many/much more most little less least 1. He is less patient than her 2.He is the least patient of the group 3. AFTER THAN /AS : object pronoun; subject+auxiliary verb; noun phrase ; possessive pronoun; adverb phrase. 1. She is more intelligent than me / you / him/ her/ us/ you/ them (object pron.) 2. a.She is more intelligent than I am (subject + auxiliary verb) b. She writes more slowly than I do (subject + auxiliary verb) c. She can write more quickly than I can (subject + auxiliary verb) 3. She is more intelligent than Mary ( noun phrase) 4. My trousers are cheaper than your trousers (noun phrase) 5. My trousers are cheaper than yours (possessive pronoun) 6. I arrived earlier than yesterday (adverb phrase) COMPARISON IN NOUNS a) Equality: the same + noun+ as him b) Inequality: 1. different from 1.He wears the same trousers as me 2. I arrived at the same time as 3. Roses are different from violets 2. not such+ noun + as : 4.. He isn´t such a good player as before; 5. They aren´t such good players as before c) superiority: more than 6. I have more money than you d) inferiority: less + uncountable / fewer+ plural 9. I have less bread than you 10. I haver fewer children than you SUPERLATIVE IN NOUNS: the least + uncountable / the fewest + plural 11. I am the one with the least bread (of all) ; 12. I am the one with the fewest friends (of all) NOTES: 1) We can emphasize an adjective IN A SUPERIOR DEGREE ( much, far, a lot, rather ) IN AN INFERIOR DEGREE (alittle, a bit , slightly). 1.It´s much faster by tube 2. A bus is far cheaper than a taxi 6. This bed is a bit more comfortable 3. Business is rather better this year 7. I got up a little later than usual 4. I need a lot more water 8. This month´s figures are slightly less good 5. A computer will do it much more efficiently 2) Faster and faster We use expressions like faster and faster and more and more expensive to say that something is increasing all the time. 1. The caravan was rolling faster and faster down the hill 2. The queue was getting longer and longer 3. Everything gets more and more expensive We can use less and less for something decreasing 4. As times passes, , we felt les and less enthusiastic. 3) The faster, the better We use this pattern to say that a change in one thing goes with a change in another. Look at these examples. 1. There´s no time to lose. The faster you drive, the better. 2. The higher the price, the more reliable the product 3. the more the customer complained, the ruder and more unpleasant the manager became 4. The sooner we leave, the sooner we´ll get there 5. the cheaper, the better.