Nucleic acids are macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen
advertisement

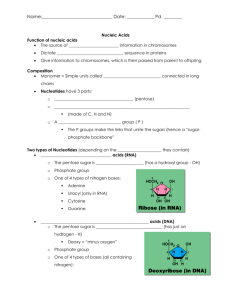
Name____________________________ Pd___________________ Date_____________________ Mr. Orend Honors Biology Nucleic Acids Nucleic acids are macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorous. Some nucleotides, including the compound known as adenosine triphosphate (ATP), play important roles in capturing and transferring chemical energy. Individual nucleotides can be joined by covalent bonds to form a polynucleotide, or nucleic acid. The heritable genetic information of an organism is stored in the molecule called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA is a kind of nucleic acid, a polymer built from monomers called nucleotides. Another group of nucleic acids, called ribonucleic acids (RNAs), also plays a key role in cells. As their names indicate, RNA contains the sugar ribose and DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose. Nucleotides are the building blocks (the monomers) of nucleic acid polymers. Only four types of nucleotides make up DNA. Examine the chemical structure of a single nucleotide in Figure 11-5. Notice that each nucleotide has three parts: 1. A ring-shaped five-carbon sugar. 2. A phosphate group (a phosphorus atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms) 3. A nitrogenous base (ny TRAW juhn us): a single or double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms with functional groups (nitrogenous means "nitrogencontaining") Just as amino acid monomers combine and form a polypeptide, the nucleotides of a nucleic acid polymer can combine in many different sequences. Nitrogenous Bases - The four nucleotides found in DNA differ only in their nitrogenous bases, called bases for short (Figure 11-6). The bases thymine (T) and cytosine (C) are singlering structures called pyrimidines (py RIM uh deenz). Adenine (A) and guanine (G) are larger, double-ring structures called purines (PYOOR eenz). The one-letter abbreviations stand for both the bases alone and for the nucleotides containing them. Complementary Base Pairs The nucleotide adenine pairs with the nucleotide thymine, and the nucleotide guanine pairs with the nucleotide cytosine. In the biologist's shorthand, A pairs with T, and G pairs with C. A is also said to be "complementary" to T, and G is complementary to C. So, while the sequence of nucleotides along the length of one of the two DNA strands can vary in countless ways, the bases on the second strand of the double helix are determined by the sequence of the bases on the first strand. Each base must pair up with its complementary base. In RNA, there is no thymine, so adenine pairs with uracil (U). Questions: Write the answers in complete sentences in your notebook. 1. What are the three parts of a nucleotide? 2. List the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA. Now complete your summary blue table on nucleic acids