Chemistry
advertisement

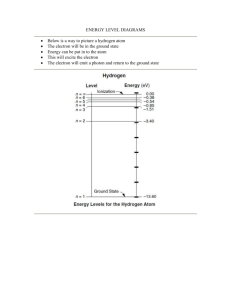
Chemistry NYOS School Name____________________ Date ____________________ Quiz 4 E = h* c = * h = 6.626 x 10-34 Js 1 nm = 1 x 10-9 m 1. A photon of which form of “light” has the greatest energy? a. microwaves b. ultraviolet c. visible light d. all are the same 2. A photon of which form of “light” has the greatest frequency? a. microwaves b. ultraviolet c. visible light d. all are the same 3. A photon of which form of “light” has the greatest speed in a vacuum? a. microwaves b. ultraviolet c. visible light d. all are the same 4. What is the frequency of visible light whose wavelength is 400 nm? Show your work for full credit. 5. What is the energy of a photon of light whose frequency is 6.5 x 1016 Hz? Show your work for full credit. 6. What is the energy of a photon of light whose wavelength is 600 nm? Show your work for full credit. 7. Which scientist modified Rutherford’s nuclear atom model to indicate that electrons could only be found in quantized energy levels? a. Heisenberg b. Schrodinger c. Bohr d. deBroglie 1 8. Which scientist proposed the idea that electrons can be thought of as both waves and particles? a. Heisenberg b. Schrodinger c. Bohr d. deBroglie 9. Match the symbols below to their definitions on the right. __c a. wavelength __n b. frequency __E c. speed of light __ d. energy __J e. energy level __ f. Planck’s constant __h g. unit of energy called a Joule 10. Which scientist said we cannot know with certainty exactly where an electron is once we observe it? a. Heisenberg b. Schrodinger c. Bohr d. deBroglie 11. Which particle absorbs and then releases energy (often in the form of visible light)? a. electron b. photon c. neutron d. proton 12. A ___________________ can be considered a “particle of light” (fill in the blank). 13. What color of light was emitted when we passed electricity through a dill pickle? a. red b. ultraviolet c. blue d. yellow 14. What metal ion was responsible for the light that was emitted when we passed electricity through a dill pickle? a. sodium b. potassium c. lithium d. strontium 15. Energy levels where an electron can be found are also known as what? a. orbitals b. suborbitals c. shells d. seashells 2 16. A pair of parentheses like this: ( ) is shorthand notation for which of the following? a. energy level b. suborbital c. electron d. proton 17. An arrow like this: is shorthand notation for which of the following? a. energy level b. suborbital c. electron d. proton 18. The maximum number of electrons that can be placed into a suborbital is________________ (fill in the blank with a number). 19. Which one of the following orbitals cannot be found on the third energy level? a. s b. p c. d d. f 20. Which one of the following orbitals is represented by drawing below? a. b. c. d. s p d f 21. What element is represented by the following orbital diagram? () () ()()() 1s 2s 2p a. b. c. d. neon oxygen phosporous chlorine 22. Fill in the orbital diagram for aluminum, including the orbital notation below the orbitals (in other words, place arrows in the parentheses and numbers in the diamonds). ( ) 1s ( ) 2s ( )( )( ) 2p ( ) ( )( )( ) 3s 3p 3 23. How many unpaired electrons are there in the diagram you prepared for aluminum in question number 22?__________________ 24. Examine the electron configuration shown below to decide which atom it corresponds to. 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 a. sulfur b. zinc c. silicon d. chlorine 25. Examine the noble gas short-hand electron configuration shown below to decide which atom it corresponds to. [Ne] 3s2 3p5 a. sulfur b. zinc c. silicon d. chlorine 4