Env Biology Learning Targets - Semester 1
advertisement
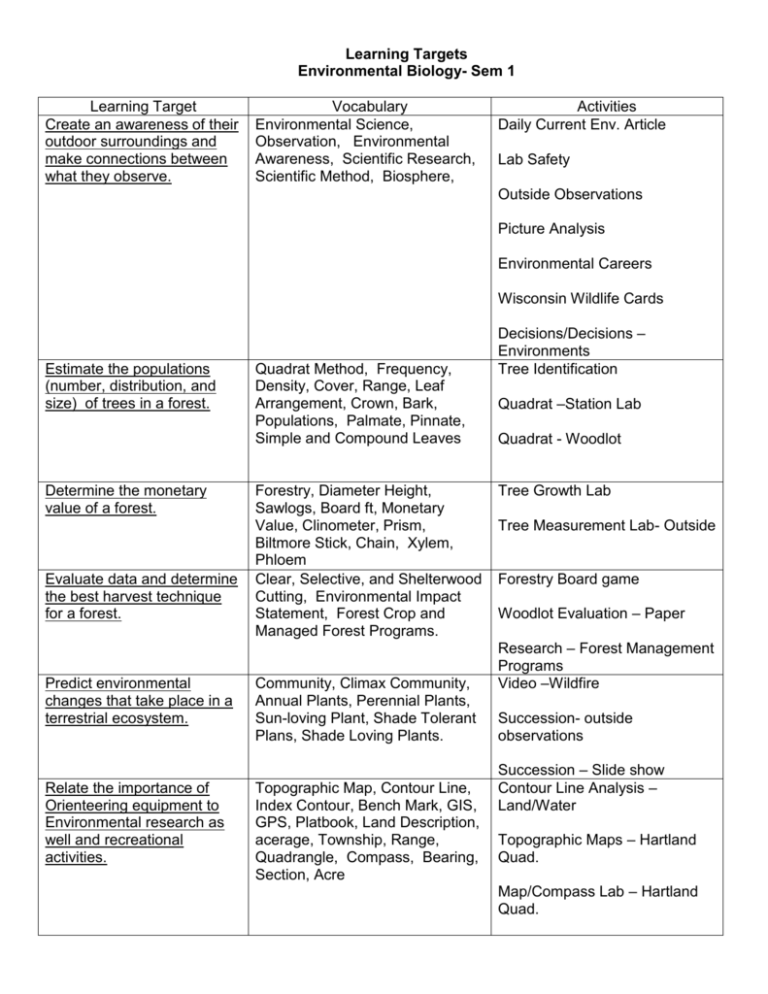
Learning Targets Environmental Biology- Sem 1 Learning Target Create an awareness of their outdoor surroundings and make connections between what they observe. Vocabulary Environmental Science, Observation, Environmental Awareness, Scientific Research, Scientific Method, Biosphere, Activities Daily Current Env. Article Lab Safety Outside Observations Picture Analysis Environmental Careers Wisconsin Wildlife Cards Estimate the populations (number, distribution, and size) of trees in a forest. Determine the monetary value of a forest. Evaluate data and determine the best harvest technique for a forest. Predict environmental changes that take place in a terrestrial ecosystem. Relate the importance of Orienteering equipment to Environmental research as well and recreational activities. Quadrat Method, Frequency, Density, Cover, Range, Leaf Arrangement, Crown, Bark, Populations, Palmate, Pinnate, Simple and Compound Leaves Forestry, Diameter Height, Sawlogs, Board ft, Monetary Value, Clinometer, Prism, Biltmore Stick, Chain, Xylem, Phloem Clear, Selective, and Shelterwood Cutting, Environmental Impact Statement, Forest Crop and Managed Forest Programs. Community, Climax Community, Annual Plants, Perennial Plants, Sun-loving Plant, Shade Tolerant Plans, Shade Loving Plants. Topographic Map, Contour Line, Index Contour, Bench Mark, GIS, GPS, Platbook, Land Description, acerage, Township, Range, Quadrangle, Compass, Bearing, Section, Acre Decisions/Decisions – Environments Tree Identification Quadrat –Station Lab Quadrat - Woodlot Tree Growth Lab Tree Measurement Lab- Outside Forestry Board game Woodlot Evaluation – Paper Research – Forest Management Programs Video –Wildfire Succession- outside observations Succession – Slide show Contour Line Analysis – Land/Water Topographic Maps – Hartland Quad. Map/Compass Lab – Hartland Quad. Compass – Outside Course GIS – Waukesha County Explain the characteristic and importance of the earth’s crust and of minerals. Summarize the positives and negative of the mining process. Explain the characteristic and importance of the rock cycle. Identify the types and characteristic of different soil types. Explain the importance of testing and managing soil for today and in the future. Explain the significance of the WI Glacier on our landscape. Mineral, Color, Luster, Specific Gravity, Hardness, Cleavage, Fracture, Optical Properties, Streak, Open Pit Mine, Surface Mines, Tailing Piles, Reclamation Merton Township – Platbook Activity Mineral Station Lab Mineral Identification/Unknown Lab Research/.Video – Mining Practices Igneous Rock Lab/Activity Rock, Igneous, Extrusive, Intrusive, Glassy, Frothy, Fine Grained, Sedimentary, Sedimentary Rock Lab/Activity Fragmental, Organic, Metamorphic, Foliated, NonMetamorphic Rock Lab/Activity Foliated, Heat, Pressure, Chemical Action, Folding, Rock Station Lab Lithification, Erosion, Weathering, Soil, Organic, Humus, Inorganic, Gravel, Sand, Silt, Clay, Loam, Soil Texture, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Potash, pH, Soil Horizons, Top Soil A, Sub Soil B, Parent Material C, Bedrock, Water Holding Capacity, Water Content, Strip Crop, Contour Plow, Cover Crop, Buffer Zone, Soil Building and Depleting Crops, Fibrous and Tap Root Systems Continental and Alpine Glacier, esker, kame, crevasse fill, terminal, lateral and interlobate moraine, drumlin, till, drift, erratics, Soil Types – Lab Soil Texture Lab Water Holding Capacity Lab Water Content Lab Soil Nutrient Lab Soil Survey Activity Soil Conservation Case Study History of Wisconsin GeologyActivity Glacial Landforms – Slides Stereograph Lab – Glacial Deposits







