CONSERVATION OF MASS LAB
advertisement

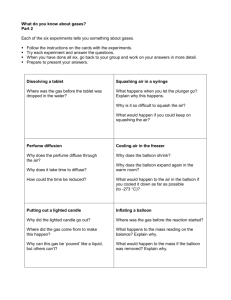
CONSERVATION OF MASS LAB Pre-lab Questions 1. Define the law of conservation of mass. 2. If 30g of sodium reacts with 20g of chlorine to create sodium chloride, how much sodium chloride should be produced? Purpose: To observe mass being conserved during a chemical reaction. Hypothesis: Materials: Erlenmeyer flask, graduated cylinder, alka seltzer tablet, balloon, electronic balance, scoopula Procedure: 1. Obtain a clean Erlenmeyer flask and a new balloon. 2. Measure 50 mL of water into the flask. 3. Take the tablet and put it in the balloon. 4. Place the balloon over the opening of the flask without the tablet falling into the flask. 5. Mass the apparatus and record the mass. 6. After recording the mass, lift the balloon and dump the tablet into the water. 7. Swirl the flask to complete the reaction. 8. Do not remove the balloon!!!!!!!!!! 9. Take the mass of the apparatus again. Record the mass. 10. Finally remove the balloon. 11. Take one final mass of the flask with its contents and the balloon lying off to the side. Data: Mass of the Balloon and Flask Apparatus After the balloon is Before the reaction After the reaction removed Conclusion Questions: 1. Compare the masses of the apparatus before and after the reaction. How do they compare? 2. Why did the balloon expand? 3. Did the substance in the balloon have mass? Explain. 4. How does the mass of the apparatus after the balloon has been removed compare to the mass of the apparatus after the reaction? Explain any discrepancies in your data.