10.1 Units Symbols
advertisement

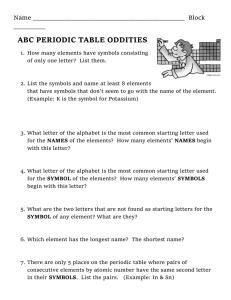
The Centre for Sport and Exercise Science 10.1 Appendices Page 1 10.1 UNITS SYMBOLS AND ABBREVIATIONS The International System of Units (Système International d'Unités) or SI system as it is usually referred to, is the internationally preferred system and uses metric values. The major fundamental and derived units with which we are concerned are: Physical quantity Name of SI unit Symbol metre kilogram second mole m kg s mol joule newton watt J N W Fundamental Length Mass Time Amount of substance Derived Energy Force Power The folowing prefixes can be used in the mantissa and exponent form: Multiple Prefix Symbol Multiple Prefix Symbol 10-1 10-2 10-3 10-6 10-9 10-12 10-15 10-18 deci centi milli micro nano pico femto atto d c m µ n p f a 10 102 103 106 109 1012 1015 1018 deca hecto kilo mega giga tera peta exa da h k M G T P E The Centre for Sport and Exercise Science 10.1 Appendices Page 2 SYMBOLS USED IN THE PHYSIOLOGY OF EXERCISE These are based on the Pappenheimer convention Characteristic Symbol Gas volume V Gas volume per unit time V Gas pressure Factional concentration Respiratory exchange ratio Inspired gas Expired gas Alveolar gas Arterial blood Venous blood Capillary blood Standard conditions Body conditions Ambient conditions P F R I E A a v c STPD BTPS ATPD These tables are not intended to be exhaustive, they simply provide a basis. References McArdle, W.D., Katch, F.I. and Katch, V.L. (1996) Exercise Physiology (Fourth Edition). Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore, Maryland. Pappenheimer, J.L. (1950) Standardisations of definitions and symbols in respiratory physiology. Federation Proceedings, 9: 602-605. Royal Society Symbols Committee (1975) Quantities, Units and Symbols. The Royal Society, London.