Ytterbium and Erbium co-doped Ln2BaZnO5 (Ln=Y
advertisement

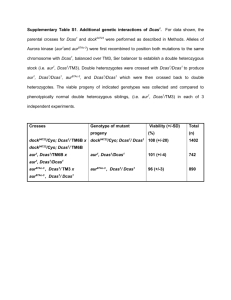
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL FOR: Oxide Phosphors for Light Upconversion; Yb3+ and Tm3+ Co-Doped Y2BaZnO5 12 3 2 2 Isabelle Etchart , Ignacio Hernández , Arnaud Huignard , Mathieu Bérard , Marine Laroche2, William. P. Gillin3, Richard. J. Curry4 and Anthony K. Cheetham1,a) 1 Materials Science and Metallurgy Department, University of Cambridge, Pembroke Street CB2 3QZ, UK 2 Saint-Gobain Recherche, 39 quai Lucien Lefranc, 93303 Aubervilliers, France 3 Department of Physics, Queen Mary University of London, Mile End Road, London, E1 4NS, UK 4 a) Advanced Technology Institute, University of Surrey, Guildford, Surrey GU2 7XH, UK Author to whom correspondence should be addressed. Electronic mail: akc30@cam.ac.uk. 1 (a) 974 nm exc Intensity /a.u. Intensity /a.u. 200 100 1 1200 1250 Wavelength /nm 0 1000 1100 1200 1300 1400 Wavelength /nm (b) Intensity /a.u. 463 nm exc 10 900 1000 1100 1200 1300 Wavelength /nm FIG. S1. Typical down-conversion luminescence spectra of Y2BaZnO5: Yb3+(6%),Tm3+(0.25%) phosphors at room temperature under (a) 974 nm excitation, and (b) 463 nm excitation. 2 Normalized intensity 1.0 463 nm exc 790 nm exc 0.5 0.0 900 1000 1100 Wavelength (nm) FIG. S2. Typical luminescence spectrum of Y2BaZnO5:Yb3+(6%),Tm3+(0.25%) phosphors at room temperature under 463 nm and 790 nm excitations. 2.0 % Tm 3+ 1.5 1.0 0.5 0.0 2 4 6 8 % Yb 10 12 14 3+ FIG. S3. Yb3+ and Tm3+ concentrations of the Y2BaZnO5:Yb3+,Tm3+ samples for which upconversion efficiencies were measured (see FIG. 4). 3 Normalized intensity 1 796 nm 0.1 654 nm 0.01 479 nm 0.000 0.001 0.002 0.003 Time (s) FIG. S4. Typical temporal evolution of the blue (479 nm), red (654 nm) and near-infrared (796 nm) emissions under pulsed 974 nm excitation and data fitting in order to get average lifetimes in Y2BaZnO5:Yb3+(6%),Tm3+(0.25%) at room temperature. Note that the small peak observed at around t ~ - 45 s is due to some pick up of the radiofrequency from the flash lamp firing. 4 excitation 974 nm 974 nm 974 nm 974 nm 463 nm 463 nm 463 nm emission 479 nm 654 nm 796 nm 1022 nm 479 nm 654 nm 796 nm 0% Yb, 0.25% Tm 2% Yb, 0.25% Tm 6% Yb, 0.25% Tm 10% Yb, 0.25% Tm 10% Yb, 0.5% Tm 10% Yb, 1% Tm 10% Yb, 2% Tm N.A. N.A. N.A. N.A. 194 s 193 s 434 s 290 s 279 s 659 s 488 s 191 s 191 s 420 s 176 s 181 s 435 s 303 s 182 s 181 s 352 s 141 s 145 s 319 s 256 s 178 s 175 s 342 s 134 s 135 s 304 s 251 s 157 s 154 s 279 s 71 s 75 s 203 s 199 s 129 s 126 s 222 s 60 s 73 s 180 s 164 s 101 s 102 s 189 s TABLE SI. Concentration dependence of lifetimes corresponding to the 479 nm, 654 nm, 796 nm and 1022 nm emissions under pulsed 974 nm and 463 nm excitations of Y2BaZnO5:Yb3+(x%),Tm3+(y%) (x = 0,2,6,10 and y = 0.25,0.5,1,2). Errors in the reported values are typically of the order 5%. Intensity (a.u.) 0.1 479 nm 454 nm 0.01 1E-3 1E-4 0.000 0.001 0.002 Time (s) FIG. S5. Typical temporal evolution of the 454 nm and 479 nm blue emissions under pulsed 974 nm excitation in Y2BaZnO5:Yb3+(6%),Tm3+(0.25%) at room temperature. 5