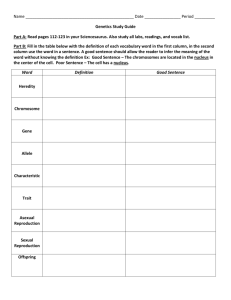
Answers. - OKBU.net
advertisement
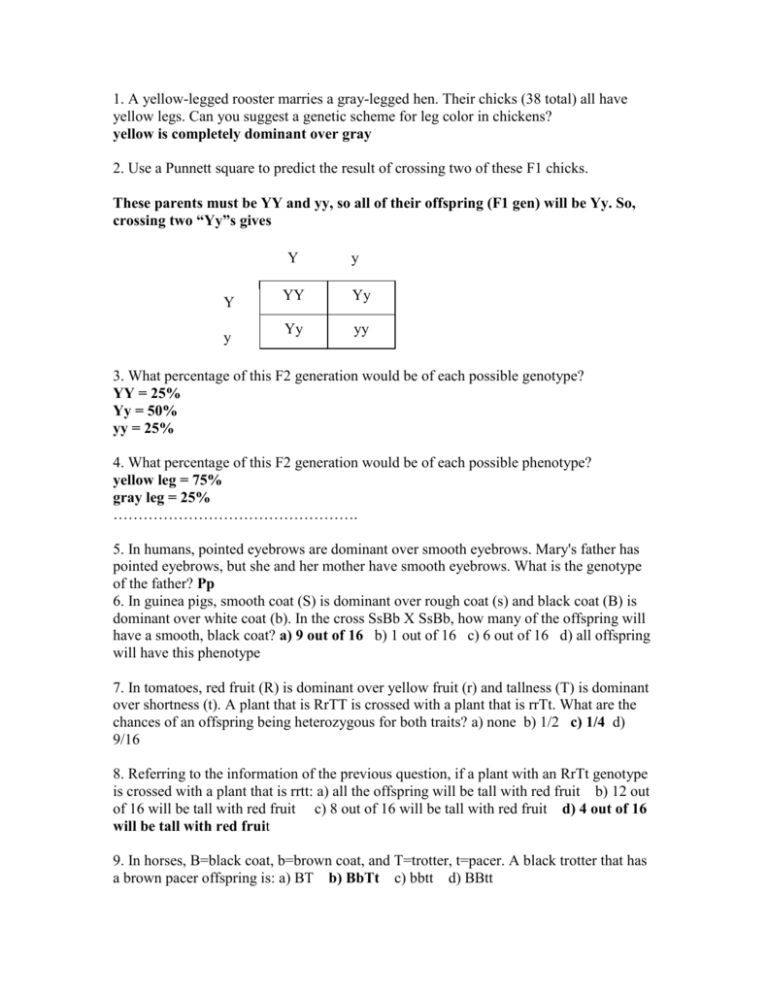
1. A yellow-legged rooster marries a gray-legged hen. Their chicks (38 total) all have yellow legs. Can you suggest a genetic scheme for leg color in chickens? yellow is completely dominant over gray 2. Use a Punnett square to predict the result of crossing two of these F1 chicks. These parents must be YY and yy, so all of their offspring (F1 gen) will be Yy. So, crossing two “Yy”s gives Y Y y y YY Yy Yy yy 3. What percentage of this F2 generation would be of each possible genotype? YY = 25% Yy = 50% yy = 25% 4. What percentage of this F2 generation would be of each possible phenotype? yellow leg = 75% gray leg = 25% …………………………………………. 5. In humans, pointed eyebrows are dominant over smooth eyebrows. Mary's father has pointed eyebrows, but she and her mother have smooth eyebrows. What is the genotype of the father? Pp 6. In guinea pigs, smooth coat (S) is dominant over rough coat (s) and black coat (B) is dominant over white coat (b). In the cross SsBb X SsBb, how many of the offspring will have a smooth, black coat? a) 9 out of 16 b) 1 out of 16 c) 6 out of 16 d) all offspring will have this phenotype 7. In tomatoes, red fruit (R) is dominant over yellow fruit (r) and tallness (T) is dominant over shortness (t). A plant that is RrTT is crossed with a plant that is rrTt. What are the chances of an offspring being heterozygous for both traits? a) none b) 1/2 c) 1/4 d) 9/16 8. Referring to the information of the previous question, if a plant with an RrTt genotype is crossed with a plant that is rrtt: a) all the offspring will be tall with red fruit b) 12 out of 16 will be tall with red fruit c) 8 out of 16 will be tall with red fruit d) 4 out of 16 will be tall with red fruit 9. In horses, B=black coat, b=brown coat, and T=trotter, t=pacer. A black trotter that has a brown pacer offspring is: a) BT b) BbTt c) bbtt d) BBtt 10. In cattle, reddish coat color is not completely dominant to white coat color. Heterozygous individuals have coats that are roan colored (ie. reddish, but with spots of white hairs). Outline a breeding procedure whereby a true breeding strain of red cattle could be established from a roan bull and a white cow. First cross roan bull X white cow ; Next cross the 2 roan progeny = 25% true breed red cattle 11. The X-linked barred gene in chickens controls the pattern of the feathers, with the alleles B for barred pattern (striped feathers) and b for no bars. If a barred male (XBY) is mated to a nonbarred female (XbXb), what will be the appearance of the male and female progeny? All females=barred ; All males=no bars 12. A particular sex-linked recessive disease of humans isn't usually fatal. Suppose that a boy with the disease lives past puberty and marries a woman heterozygous for the trait. If they have a daughter, what is the probability that she will have the disease? a) 0% b) 25% c) 50% d) 75% e) 100% 13. What are the chances that a non-color blind male from a family with color-blindness (an X-linked recessive allele) will pass on the color blind trait to his children? a) 50% b) 100% c) 0% d) 75% e) not enough information is given to determine the answer 14. Princess Eugenie, who was a carrier for hemophilia, married her cousin Prince Albert who was a hemophiliac. a) all their children would be hemophiliacs b) half their children of both sexes would be hemophiliacs c) all their girls would be hemophiliacs d) all their sons would be carriers e) two of the above 15. In humans, attached earlobes are recessive (h). The alternative is free-hanging earlobes (H). a) What is the genotype of someone who has attached earlobes? hh b) What is the phenotype of someone who has one H allele and one h allele? free c) Anne is homozygous dominant. What is her genotype? HH d) What is Anne's phenotype? free e) Henry is heterozygous. What is his genotype? Hh f) What is Henry's phenotype? free g) Henry marries Anne. Draw and label a Punnett square showing the kinds of gametes that Henry and Anne produce, and the possible genotypes of their children. H H H HH HH h Hh Hh