1.1LightAsRays 1.2 ReflectonOfLight
advertisement

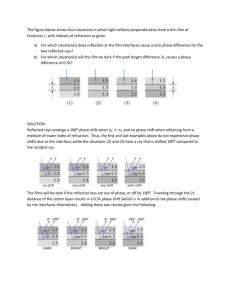
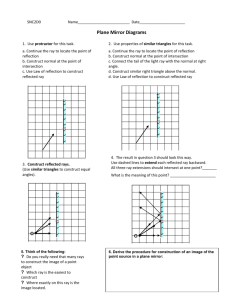
ECF Saint Too Canaan College S.3 Physics Light rays and Reflection 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 Light as rays Reflection of light Refraction of light Lenses In this unit, we will learn the ray model of light how a plane mirror forms images how light is refracted at the boundary between two media how lenses form images 1.1 Light as rays Light rays from a point source travel along straight lines in all directions. Light beams and light rays The following figures show three kinds of light beams from a ray box: a parallel beam, a divergent beam and a convergent beam. We draw sets of rays to represent these beams. (i) A parallel beam (ii) A divergent beam (iii) A convergent beam Cone of rays When we see an luminous (發光) object, many light rays from the object enter our eyes. To keep thing simple, we only draw two rays at the edges. For a near object, light rays reach the eye as divergent rays 1 Light rays become more parallel if the object is moved away For a distant object, light rays reach the eye as parallel rays Example 1 Locate the light sources in the following figures. (a) (b) 1.2 Reflection of light When you look into a plane mirror (平面鏡), you see an image of yourself and the things around you. How does the mirror form an image? Laws of reflection 1. The angle of reflection r is always equal to the angle of incidence i. 2. The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane. 2 Example 2 A device consists of two mirrors at right angles to each other. If a ray of light is incident at one of the mirrors at 45 o, complete the path of the ray Regular reflection and diffuse reflection A plane mirror has a flat, smooth surface. When a parallel beam of light falls on it, the reflected beam is also parallel. However, most surfaces are not perfectly smooth. The reflected beam is irregular in direction. A man wearing a rough aluminium cap A smooth aluminium pan Example 3 The following figures show the light beams falling on a smooth surface and a rough surface. Complete the light rays in Fig a. smooth surface Fig a rough surface Fig b Example 4 A light ray is incident at 20o on a plane mirror as shown in the following diagram. (a) Draw the normal and the reflected ray on the diagram. (b) What is the angle of reflection? (c) Redraw the diagram if the mirror is turned 90o anti-clockwise. 3 How a plane mirror forms an image When diverging light rays enter our eyes, our brain perceives (察覺) the light by extending the rays backwards. If the extended rays meet at a point, they are perceived as coming out from this point. Properties of the image formed by a plane mirror The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual (虛) of the same size as the object erect (直立) laterally inverted (橫向倒置) Locating the image formed by a plane mirror The image formed by a plane mirror is behind the mirror. The rays do not exist. The rays and the image are virtual and are represented by dotted lines. When drawing ray diagrams, do as the following steps: 1. Locate the image behind the mirror object distance is equal to image distance the object seems to be flipped to the opposite side the image must be drawn in dotted lines 2. Extend the rays from the observer the rays behind the mirror must be drawn in dotted lines 3. Extends the rays to the light source add arrows on the rays 4 Example 5 A girl 150 cm tall stands facing a mirror mounted on a wall 150 cm away. She can just see her feet at the bottom edge of the mirror and her eyes are 10 cm below the top of hear head. (a) What is the distance between the girl and her image in the mirror? (b) How high above the floor is the bottom edge of the mirror? Exercise 1. Locate the image formed by the plane mirror. (a) (b) plane mirror plane mirror object object observer observer 5 2. Letters P, Q are printed on a card as shown below. Sketch the image of the letters on the plane mirror. 3. An object XY is placed in front of a plane mirror as shown. (a) Locate and sketch the mage of the object. (b) State the nature of the image. 4. The figure below shows an incident ray striking to two plane mirrors which are perpendicular to each other. (a) What is the angle of incidence? (b) Draw all the reflected rays. (c) What is the angle of reflection for the final ray? 5. A boy stands 3 m from a plane mirror. His eyes are 1.5 m above the floor. (a) Draw light rays to show how he sees his head and his feet. (b) How high should the bottom of the mirror from the floor be if he can just see his feet? 6